* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cold War: Truman-JFK
Survey
Document related concepts
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Yalta Conference wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
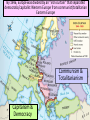
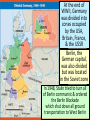
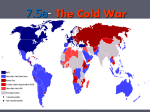
Aim #70: Why did wartime cooperation between the US and the Soviet Union collapse post World War II? Do now! 1. Read Winston Churchill’s “Iron Curtain” speech Stalin’s response and answer the accompanying questions 2. Look at timeline: be ready to discuss what you think changed between the two countries Roots of the Cold War Philosophical Differences World War II Conflicts Postwar Conflicts • Philosophical differences between the Soviet Union and the United States reached back to the 1920s. • Soviet Union: communism, totalitarian dictatorship • United States: free-enterprise capitalism, republic • Allies during the war, but not truly friends • Soviets wanted British and Americans to open a second European front earlier in the war. • U.S. atomic bomb plans worried Soviet Union. • The Soviet Union refused to let Eastern Europe hold elections as promised at Yalta. • The United States resisted Soviet expansion. Cold War Origins: Post-War World Vision ● Soviet Goals ● With tens of millions killed in both world wars the Soviets main goal was… “NEVER AGAIN!” ● ● Soviets wanted buffer states of “friendly” governments to protect them from future invasion Exact revenge/reparations from Germany ● US Goals ● Rebuild Europe/Germany ● “Wilsonian” Peace ● ● ● Self-determination or free elections Decolonization Disarmament (I) What was the Cold War? Military, political and economic competition between US (west) and USSR from 1945-1991 1. Military alliances 2. Arms race 3. Each support opposing sides in civil wars (Korea, Vietnam) b. No direct fighting a. (II) Disagreements over future of Europe after WWII a. Truman: wants democracies in Europe to prevent totalitarianism and provide market for US goods b. Stalin: control of E. Europe (set up satellite nations) and rebuild the Soviet Union’s economy c. Churchill: Europe has been divided by an “iron curtain” (East and West, communism and capitalism) By 1946, Europe was divided by an “iron curtain” that separated democratic/capitalist Western Europe from communist/totalitarian Eastern Europe Communism & Totalitarianism Capitalism & Democracy (III) What was containment? Stopping the spread/expansion of communism b. Policy created by some of Truman’s advisors: 1. Secretary of State: George Marshall 2. George F. Keenan: expert advisor on Soviet affairs (IV) How was Truman Doctrine example of containment? a. Greece and Turkey in danger of communist revolutions b. Congress allocated $400 million in economic and military aid to prevent communism there c. Result…successful! a. V. What was the Marshall Plan? (aka European Recovery Plan) US offered economic aid to European nations to prevent communist revolutions and strengthen democratic governments b. Countries faced harsh economic conditions after war c. $12billion in aid (SU refused aid) a. Questions: Why would Stalin WANT TO block the Marshall Plan? Why do you think the Soviets wouldn’t accept aid under the plan? 1 What is the overall message of the cartoon? 2. Do you think Block favors the Marshall Plan? Use evidence from the cartoon to support your answer. GERMAN CITY OF HAMBURG IN 1945 BEFORE THE MARSHALL PLAN HAMBURG, 1952, AFTER THE MARSHALL PLAN VI. How did US update its military in 1947? a. National Security Act 1. Created Department of Defense (coordinate Army, Navy and Air Force Efforts) 2. Created the National Security Council to advise the president on foreign policy 3. Created the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) to gather information on foreign governments At the end of WWII, Germany was divided into zones occupied by the USA, Britain, France, & the USSR Berlin, the German capital, was also divided but was located in the Soviet zone In 1948, Stalin tried to turn all of Berlin communist & ordered the Berlin Blockade which shut down all ground transportation to West Berlin VII. What was the Berlin Airlift? (June 1948-May, 1949) 1st major crisis of Cold War b. Soviets cut all land access to Wester Berlin: want US to withdraw from city c. Truman’s response 1. US planes flew supplies into West Berlin d. Soviets ended an 11 month standoff by opening roads to Berlin e. Impact of airlift 1. Soviets established e. Germany as a separate nation with a Communist govt. 2. US, Britain and France combined their zones into W. Germany (democratically elected government) a. VIII. Why did the US join NATO? (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) a. b. c. d. Military alliance designed to protect western Europen from Soviet invasion Promise to defend each other from attack US troops are stationed in Europe as deterrent USSR’s response: formed the Warsaw Pact (alliance of communist nations in Eastern Europe) NATO: THE NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION IS FORMED IN 1949 WARSAW PACT FORMED BY THE USSR TO COUNTER NATO IN EUROPE MAY 1, 1955 Exit Ticket Question: Who do you think was primarily responsible for the starting the Cold War: the US or the Soviet Union? Explain your answer. You can use today’s notes and/or last night’s homework.