* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File ap notes chapter 45
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
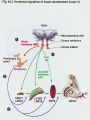
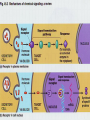
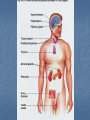
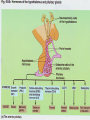
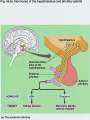
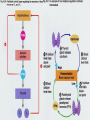
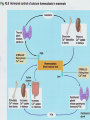
Chapter 45: Hormones & the Endocrine System Regulatory systems Nervous system High speed messages Endocrine Slower; system longer lasting Result of hormone secretion Connections between Nervous & endocrine systems Neurosecretory cells Nerve cells that release hormones Concentrated in hypothalamus Some Ex: hormones act as neurotransmitters epinephrine Hormones Chemical signal secreted into circulatory system through ductless glands Action of hormones Operate at all levels of organization Produce developmental change Intracellular, cell to cell, organ to organ, organism to organism (pheromones) Ex. puberty Metamorphosis (insects & amphibians) Incomplete Eggnymphadult (grasshoppers) Complete Egglarvapupaadult (butterfly) Regulation of hormones Negative feedback Positive feedback Increase in substance inhibits its own production Ex. Metabolic control Increase in substance increases its own production Ex. Release of milk in nursing mother Local regulators Histamines Interleukins Chemical from local cell for antigen-antibody response (allergies) Cytokine acting as communicator between immune cells Prostaglandins Modified fatty acid which stimulates contraction of smooth muscles, induces fever & blood flow to infection sites Classes of molecules acting as hormones Proteins & peptides; H2O soluble Amines (derived from amino acids); H2O soluble Steroids; non- H2O soluble Events of hormone action Reception (signal binds to receptor protein in or on target cell) Water soluble hormones bind to surface receptor triggering activation of internal proteins in transduction pathway Steroid hormones enter cell & bind to internal receptor which enters nucleus to activate genes Signal transduction response Endocrine Gland Hormone Effect on target tissue Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) FSH Stimulate growth of ovarian follicle & sperm production LH Stimulate ovulation; secretion of sex hormones by ovaries/testes Prolactin Induces milk secretion in mammary glands TSH Stimulate throxin production by thyroid ACTH Stimulate adrenal cortex to produce cortisone GH Stimulate growth MSH Regulation of pigment in skin cells; inhibits hunger Beta endorphin Dull pain perception Endocrine Gland Hormone Effect on Target tissue Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) ADH Stimulate increased H2O absorption by kidneys; constrict blood vessels Oxytocin Stimulate uterine contractions & release of milk Thyroxin (T4) & Triiodothyronine (T3) Stimulate oxidative metabolism Calcitonin Regulation of calcium & phosphate blood levels Parathyroid gland Parathormone (PTH) Controls abosorption of Ca & P from blood; stimulates release of Ca from bone Thymus Thymosin Stimulates production of T lymphocytes Adrenal cortex Cortisone* Regulate H2O reabsorption, electrolyte balance, protein & carbohydrate metabolism Thyroid gland Endocrine gland Hormone Effect on target tissue Adrenal medulla Epinephrine & norepinephrine Raises blood glucose levels; increases metabolic activity; constricts blood vessels Pancreas (islet of Langerhans) Insulin (beta cells) Stimulates uptake of glucose by cells Glucagon (alpha cells) Converts glycogen into glucose Estrogen* Stimulate female secondary sex characteristics; build uterine lining Progesterone* Maintain pregnancy Testes Testosterone* Stimulate male secondary sex characteristics Pineal Melatonin Biological rhythms Ovaries *denotes steroid hormone Endocrine Disorders Thyroid Cretinism Goiter Most common form of hyperthyroidism Autoimmune Hashimoto’s disease Enlarged gland usually related to hypothyroidism Graves disease Under secretion of thyroxin in utero Most common form of hypothyroidism autoimmune Pituitary Dwarfism Giantism Under secretion of GH in child Over secretion of GH in child Acromegaly Over secretion of GH in adult Pancreas Diabetes mellitus Type I (insulin dependant) Type II Autoimmune Beta cells destroyed; little to no insulin production Reduced responsiveness of target cells to insulin Controlled through diet & exercise Accounts for >90% of diabetes cases Adrenal gland Addison’s disease Under-secretion of ACTH