* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Regulation Endocrine System communication
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
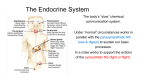
Chemical Regulation Endocrine System Communication Structure and Function Lesson 1 Do Now Brain Pop video: Endocrine System Endocrine System Regulation of the human body through chemical messengers called hormones to maintain homeostasis Homeostasis = stable internal environment Endocrine Regulation Stimulus is detected Impulse sent to brain (hypothalamus) Hypothalamus to pituitary Pituitary sends message to gland Gland releases a hormone Hormone does work New stimulus is detected In class assignment Draw a diagram on poster board of the human endocrine system Include: pituitary gland, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, kidneys, adrenal glands, pancreas, testes, ovaries Describe: the hormone releases from each gland and its function Homework Vocabulary/Multiple choice worksheet Lesson 2 Hormones Do Now Brain Pop video: Hormones Hormones Chemicals released into the blood stream from a gland Needed in very small amounts Contain receptor molecules Act on specific parts of the body – Ex: Insulin will “lock in” to blood cell receptors to lower blood sugar. Insulin cannot “lock in” to other body cells because the receptor sites don’t match. ENDOCRINE GLANDS Pituitary = master gland (controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain) Pituitary Gland Releases hormone messengers (do not “do work”) TSH – thyroid stimulating hormone ACTH – stimulates adrenal glands FSH – stimulates the ovaries Oxytocin – labor contractions Calcitonin – Calcium metabolism ENDOCRINE GLANDS Thyroid Gland – in neck Releases Thyroxine which regulates metabolism Parathyroids – 4 tiny glands behind thyroid Releases Parahormone regulates Calcium in blood Adrenal Gland– on top of kidneys Releases Adrenaline which allows the body to respond appropriately in times of emergency or stress “Fight or Flight” Pancreas – glands located within the pancreas – Releases Insulin which regulates blood sugar levels Diabetes – caused by decreased amounts of insulin which leads to increase blood sugar coma death if not medicated GONADS – sex glands Ovaries Releases Estrogen – 2nd degree sex characteristics/ cycle Releases Progesterone – cycle and maintain pregnancy Testes Releases Testosterone – 2nd degree male characteristics and production of sperm In class assignment Vocabulary and multiple choice worksheet Homework Endocrine Worksheet “case studies” Lesson 3 Feedback Mechanisms Do Now Endocrine Match Up worksheet Feedback Mechanisms A cycle in which the output “feeds back” to modify or reinforce the action of the system 2 types: (a)Positive feedback Change in the environment – increases the response Ex: uterine contractions during labor (a)Negative feedback most common Change in the environment creates a response message makes a change stops the response message Ex: regulate blood sugar Sensor detects high blood sugar Pancreas Negative secretes feedback shuts off insulin production insulin Blood sugar drops - Ex: increase exercise increased muscle activity increases HR and BP and resp. rate O2 to muscles In class assignment Using your human body diagrams from lesson 1, describe a specific feedback process Color in the affected organs List all hormones involved in the process and how they work Homework Human Endocrine Worksheet Lesson 4 Disruption of Homeostasis Do Now Video:Cancer Disease Disease = failure of homeostasis – the body fails to work as it should Causes of disease: 1) Pathogens – organisms (germs) that invade the body ex: virus, bacteria, fungi. And parasites (spread) – Lyme, cold 2) Uncontrolled cell division Cancer mass of abnormal cells called tumor 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Inherited ex: CF, Down’s Poor nutrition Toxins Organ malfunction High risk – skin/lung cancer In class assignment Brain Pop video: Puberty Multiple choice worksheet/vocab Homework Case Studies Research an assigned disease, disorder or cancer which occurs as a result of a disruption of homeostasis and answer questions Labs