* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetically modified food
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
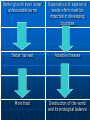
Genetically modified food The genetic modification Change of the genes of a plant in a laboratory Insertion of chemical units which carry the information of special characteristics Aim Due to genetical modification the DNA of a cell changes Controlled change of the DNA aim: gaining a desired gene combination e.g. better harvest General Mutation mainly of corn, soy beans, cotton and oil seed rape Requirement to label genetically modified food in the EU Only small amouts of genetically modified food in the EU exception: genetically modified corn Introduction of genetically modified plants to USA, Argentina, Brasil, Canada, China and India Pros Contras Faster growth Loss of genetical biodiversity Insensitivity against vermin, pesticides and weed killer Unwanted production of weed Improved quality of food Negative effects on the environment Insensitivity to illnesses Possible disadvantages for the health of the users Bigger harvest Blockage of ecological balance Improving of the plant‘s nutrient supply Bringing about new toxins, causing new allergies Diminishing use of fertilizers Damage to useful insects and soil organisms Better growth even under unfavourable terms Dependence of expensive seeds which must be imported in developing countries Better harvest Possible illnesses More food Destruction of the world and its ecological balance