* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion Iodine and Starch Reaction - OG
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
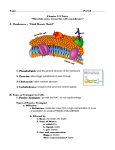
Diffusion Iodine and Starch Reaction http://www.youtub e.com/watch?v=2Th 0PuORsWY&feature =related 1. What caused the color change you observed? • Starch solution inside the dialysis tubing • Water outside the dialysis tubing • Iodine added to the water • --- REACTION! Color change! How? 2. What was able to diffuse across the membrane? • Starch solution changed color • Water in the beaker didn’t have a reaction • What can you conclude: – About the movement of starch molecules? – About the movement of iodine molecules? – About the movement of water molecules? What molecules were able to diffuse in/out the membrane? • Water • Iodine • Why couldn’t starch move across the membrane? 3. Was the beaker of water hypertonic or hypotonic compared to the starch solution in the tubing? • Hypertonic = more solute (high concentration) • Hypotonic = less solute (low concentration) • What’s a solute? – The substance you’re dissolving (starch) • What’s a solvent? – The substance you’re dissolving the solute IN (water) 3. Where is the highest concentration of solute? The lowest concentration? 4. Why was the weight of your tubing different after adding iodine to the water? • Water moves from high low concentration • Water moved into the dialysis tubing due to … OSMOSIS! • Would water still move across the membrane without using iodine? How does the tubing represent a cell membrane? • Selectively (semi) permeable – only certain molecules can cross the membrane – Water, iodine, NOT starch • Normally, cells exist in isotonic solution – What’s isotonic? What’s the solution? • Osmosis can cause cells to shrivel up, swell, or even burst! How can water cause a cell to burst? • When cells are in a “freshwater” solution • Water rushes in, bursting the cell What about plant cells? • What do plant cells have that animal cells do not? • Notice the cell wall does not collapse (or burst), but the cell membrane can collapse What allows water molecules in/out of the cell? • Aquaporins – water channel proteins – Type of facilitated diffusion, because it requires “help” from a specific channel protein • Special protein channels are embedded in the lipid bilayer – a double-layered sheet that forms a strong, flexible barrier called the … • YOU GUESS IT! CELL MEMBRANE! The Lipid Bilayer 2 sheets of lipids make the lipid bilayer -- PHILIC = loving -- PHOBIC = hating Why is the hydrophilic portion on the outside and the hydrophobic portion on the inside of the two sheets? Recap • Diffusion is… movement of molecules from high to low concentration • Osmosis is… movement of WATER molecules from high to low concentration – This creates osmotic pressure - a force produced by the net movement of water Types of Transport • ACTIVE TRANSPORT • Moves materials against concentration gradient • Requires energy! • Endocytosis - import – Phagocytosis • Exocytosis - export PASSIVE TRANSPORT • Occurs due to concentration gradient • Requires no energy • Diffusion • Osmosis