* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 58 Assessment and Management of Patients With Eye and
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Near-sightedness wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
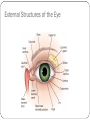
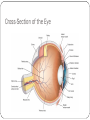
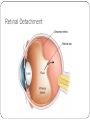
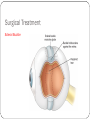
Chapter 58 Assessment and Management of Patients With Eye and Vision Disorders External Structures of the Eye Cross-Section of the Eye Assessment and Evaluation of Vision Ocular history Visual acuity Snellen chart Record each eye 20/20 means the patient can read the “20” line at a distance of 20 feet Finger count or hand motion Diagnostic Evaluation Ophthalmoscopy Direct and indirect Examines the cornea, lens and retina Tonometry Measures intraocular pressure Impaired Vision Refractive errors Can be corrected by lenses which focus light rays on the retina Myopia: nearsighted Hyperopia: farsighted Astigmatism: distortion due to irregularity of the cornea. Due to refractive error in which light rays are spread over a diffuse area rather than sharply focused on the retina, a condition caused by differences in the curvature of the cornea and lens Glaucoma A group of ocular conditions in which damage to the optic nerve is related to increased intraocular pressure (IOP) caused by congestion of the aqueous humor The leading cause of blindness in adults in the U.S. Incidence increases with age Risk factors Family history of glaucoma Older age Diabetes mellitus Cardiovascular disease Nearsightedness (myopia) Eye trauma Prolonged use of topical or systemic corticosteroids Pathophysiology of Glaucoma In glaucoma, aqueous production and drainage are not in balance. When aqueous outflow is blocked, pressure builds up in the eye. Increased IOP causes irreversible mechanical and/or ischemic damage to the optic nerve. Types of glaucoma: 1. Open-angle 2. Angle-closure (pupillary block) glaucoma 3. Congenital glaucomas 4. glaucoma secondary to other conditions Clinical Manifestations “Silent thief ” of vision; unaware of the condition until there is significant vision loss; peripheral vision loss, blurring, halos, difficulty focusing, difficulty adjusting eyes to low lighting May also have aching or discomfort around eyes or headache Diagnosis: Tonometry to assess IOP Treatment Goal is to prevent further optic nerve damage Maintain IOP within a range unlikely to cause damage Pharmacologic therapy Surgery (nursing care) Cataracts An opacity or cloudiness of the lens Increased incidence with aging; by age 80 more than half of all Americans have cataracts Risk factors Aging (Clumping or aggregation of lens protein) Associated Ocular Conditions (Myopia, retenal surgery) Toxic Factors (Corticosteroids, smoking) Nutritional Factors (low antioxidants, poor nutrition) Physical Factors (dehydration, trauma, ultraviolet ray) Systemic Diseases and Syndromes (DM, MS Renal) Cataract Clinical Manifestations Painless, blurry vision Sensitivity to glare Reduced visual acuity Other effects include astigmatism, diplopia (double vision), and color (color value shift to yellow-brown) Diagnostic findings include decreased visual acuity and opacity of the lens by ophthalmoscope, or inspection Surgical Management If reduced vision does not interfere with normal activities, surgery is not needed. Removal of the lens and replacing it with an artificial lens Retinal Detachment Separation of the sensory retina and the RPE (retinal pigment epithelium) Manifestations: sensation of a shade or curtain coming across the vision of one eye, bright flashing lights, sudden onset of floaters Diagnostic findings: assess visual acuity, assessment of retina by indirect ophthalmoscope and fluorescein angiography. Tomography and ultrasound may also be used Retinal Detachment Surgical Treatment Scleral Buckle Trauma Prevention of injury Patient and public education Emergency treatment Flush chemical injuries Do not remove foreign objects Protect using metal shield or paper cup Protective Eye Patches