* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mythology 101 Review Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
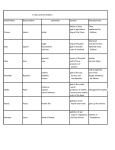
Mythology 101 A Guide to Greek and Roman Myths What is Mythology? o o o o Long ago, people had a hard time explaining what was happening around them. There were no scientists or teachers to explain why things happened - like why we have 4 seasons, for example. They made up their own stories to explain why and how things worked. These stories are called MYTHS. What is a Myth? • Setting is Ancient Greece or another world such as the underworld or heavens. • Has god/goddesses with superpowers, heroic or godly abilities. • Out of the ordinary events or heroic deeds. • Purposes include: to teach a lesson explain how something came to be What is the difference between a myth and a tall tale/folktale? A tall tale is a story that has these features: • A larger-than-life, or superhuman, main character with a specific job. • A problem that is solved in a funny way. • Exaggerated details that describe things as greater than they really are. • Characters who use everyday language. • Animated Tall Tales • Read about these tall tales: Paul Bunyan, Johnny Appleseed, Pecos Bill What is the difference between a myth and a fairy tale? • A fairy tale is a story featuring folkloric characters such as fairies, goblins, elves, trolls, giants, and others. These stories often involve princes and princesses, and usually have a happy ending. Usually fairy tales start with “Once upon a time..” • How many fairy tales have you read? Can you name 3? • Click here for examples: Fairy Tales for children or Fairy Tales by Hans Christian Anderson. What is the difference between a myth and a legend? • Legends are set in the present or recent past. Legends are supposedly true and are used to scare, teach, inform, or entertain. Legends are stories that are handed down through generations- usually by word of mouth. Examples: Legend of King Arthur and the Knight’s of the Round Table, Robin Hood, • Legend Website What is the difference between a myth and a fable? Just what is a fable, you ask? Well, a fable is a kind of story that: • has animal characters that are smart, foolish, sly, or clever • has a character that plays tricks on other characters • has a character that makes a bad decision • has a moral or a lesson learned • is short, sweet and to the point • Click here to read some of Aesop’s fables. • Click here to watch some animated versions of Aesop’s fables. • Fable Webquest Myth, fable, fairy tale, tall tale or legend? The story of The Milky Way • Chinese The seventh Princess of Heaven fell in love with a poor herdsman and ran away to marry him. When her mother sent soldiers to bring her home, the herdsman chased them away. Seeing her daughter’s husband running, the mother dropped a silver pin to make a silver stream to separate the lovers forever. Eventually, her father allowed her to have an annual reunion with her husband — black birds escorted her across the stream. The Milky Way is that silver stream. The young lovers are the stars Vega and Altair on either side of it. • Navajo When the world was created, the people gathered around Black God to place stars in the sky. Coyote was frustrated by how long it was taking. He threw the bag of stars over his head, forming the Milky Way. • Egyptian The goddess Isis spread large quantities of wheat across the sky. We see this bounty as the Milky Way. • African Bushmen The Milky Way is made of the ashes of campfires. • Polynesian The Milky Way is a long, blue, cloud-eating shark. They are ALL MYTHS • Mainly because they all explain how something came to be. Main Greek Myths • • • • • Narcissus Prometheus Pandora Adonis and Aphrodite Apollo *Read in pairs and summarize in comic strip style! See examples: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/english/englis hcart.htm The Principal Gods • Cronos and Rhea were parents of ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Zeus (Jupiter, Jove) Poseidon (Neptune) Hades (Pluto) Hera (Juno) Hestia (Vesta) Demeter (Ceres) • Other Olympians include ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Athena (Minerva) Ares (Mars) Hebe (Juventas) Hephaestus (Vulcan) Apollo (Apollo) Artemis (Diana) Hermes (Mercury) Aphrodite (Venus) Dionysus (Bacchus) Persephone The Olympians Zeus • Roman Name: Jupiter (also Jove) • Supreme god of the Olympians. • Fathered many characters in mythology ZEUS: King of the gods and the sky Roman name: Jupiter Symbol: Thunder bolts Interesting Facts about Zeus He and his siblings fought to gain control of the universe from the Titans and Cronus (his father) He and his brothers (Poseidon and Hades) divided up creation with Zeus receiving the sky as his domain. He was also accorded supreme authority on earth and on Mount Olympus. Zeus Hera • Roman Name: Juno • Zeus’s sister and wife • Jealous protector of marriage • Punished the women Zeus fell in love with HERA: Queen of the gods • Wife of Zeus • Roman Name: Juno • Symbol: Golden Crown Interesting Fact: Hera hated the great hero Heracles since he was the son of her husband Zeus and a mortal woman. When he was still an infant, she sent snakes to attack him in his crib. • Hera was worshipped throughout Greece, and the oldest and most important temples were dedicated to her. Poseidon • Roman Name: Neptune • God of the Seas and Waters • “The Earthshaker” Poseidon: god of the oceans • Zeus’ brother • Roman Name: Neptune • Symbol: Trident • As the god of horses, he would often adopt the shape of horse. Interesting fact: When the Olympians gained control of the universe, they agreed that the earth would be ruled jointly, with Zeus as king. This led to a number of territorial disputes among the gods. Poseidon vied to be the ruler of Athens. He demonstrated his power by striking the Acropolis with his three-pronged spear, which caused a spring of salt water to emerge. Hades • Roman Name: Pluto • God of the Underworld/ Dead • Kidnapped Persephone HADES: god of the underworld • Brother of Zeus and Poseidon • Roman Name: Pluto • Symbol: Invisible Helmet Hestia • Roman Name: Vesta • Goddess of Home • Powerful Protector HESTA: goddess of home and hearth • Zeus’ virgin sister • Roman Name: Vesta • Symbol: Sacred Fire APHRODITE: goddess of Beauty and Love • Daughter of Zeus • Roman Name: Venus • Symbol: Roses and Doves Demeter • Roman Name: Ceres • Goddess of the Harvest • A Goddess of the Earth DEMETER: goddess of grain and harvest • Responsible for the creation of seasons • Also known for fertility • Roman Name: Ceres • Symbol: Rake Athena • Roman Name: Minerva • Goddess of Wisdom and War • Sprang from Zeus’s head ATHENA: goddess of wisdom and law • Daughter of Zeus • Roman Name: Minerva • Symbol: Armor and an Owl Ares • Roman Name: Mars • God of War • Son of Zeus and Hera • Bloodthirsty and merciless ARES: god of War • Son of Zeus and Hera • Roman Name: Mars • Symbol: Sword and Spear Hephaestus • Roman Name: Vulcan (Mulciber) • God of Fire/Forge • Son of Zeus and Hera • Kind, unlike his brother • Limped HEPHAESTUS: god of fire and forge • • • • Son of Hera Fatherless Roman Name: Vulcan Symbol: Anvil and Hammer Apollo • Roman Name: Apollo • God of Light/Sun and Music • Brother of Artemis APOLLO: god of the sun • Son of Zeus, twin brother of Artemis • Roman Name: Apollo • Symbol: Golden Chariot and Harp Artemis • Roman Name: Diana • Goddess of the Moon/ Hunt • Sister to Apollo ARTEMIS: goddess of the hunt and moon • Daughter of Zeus and twin sister of Apollo • Roman Name: Diana • Symbol: Silver bow and arrow Hermes • Roman Name: Mercury • Messenger of the Gods • Appears in more myths than any other character HERMES: Messenger of the gods • Son of Zeus • Responsible for guiding souls to the underworld • Roman Name: Mercury • Symbol: Winged Sandals Dionysus • Roman Name: Bacchus • God of Wine • Patron god of the Greek stage • A God of the Earth Persephone • Roman Name: Proserpina • Goddess of the Underworld • Daughter of Zeus and Demeter • Abducted by Hades Hebe • Roman Name: Juventas • Goddess of Youth • Cupbearer to the Gods • Restored youth to the aged Eros • Roman Name: Cupid • Young God of Love • Son of Aphrodite and Hephaestus Iris • Goddess of the Rainbow • Messenger for Zeus and Hera • Daughter of the titan Thaumus and the nymph Electra Common Themes in Mythology • Trickery (Trickster=coyote) Sources • Graphics in this presentation were taken from the following web sites: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ http://www.bulfinch.org/fables/search.html http://www.pantheon.org/ http://www.messagenet.com/myths/ http://mythman.com/ http://web.uvic.ca/grs/bowman/myth/index.html http://www.paleothea.com/ http://www.entrenet.com/%7Egroedmed/greekm/myth.html http://classroom.springisd.org/webs/crystalc/upload/greekgodsandgod desses.pdf • This presentation is for educational purposes only; it has not been and should not be sold or used as a vehicle to make money. http://classroom.springisd.org/webs/cryst alc/upload/greekgodsandgoddesses.pdf