* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-Auditory-function-slides-2004
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Speech perception wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
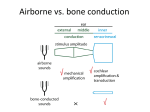
AUDIOLOGY IN ORL and deafness DR. BANDAR MOHAMMED ALQAHTANI, M.D KSMC Tympanic mem & Ossicular Amplification 22:1 in total 1.3:1 maleus to incus (lever action) 17 :1 TM surface to stapes footplate problem in transmission leads to CHL 2 Anatomy of hearing organ THE COCHLEA 3 Traveling wave & Tonotopic organization High frequency at base and low frequency at apex problem inside the cochlea transmission OR nerve transmission lead to SNHL 4 -so hearing loss can be divided into Conductive vs SNHL -both can be congentally/developmental vs aquired -aquired :TINDM OVA -congenital –--- 5 Auditory Assessment 6 Clinical vs audiometric tests Clinical : - finger friction - watch test - speech test - tuning fork test Audiometric tests : subjective vs objective tests - pure tone audiometry - speech audiometry - impedance audiometry a-tympanometry b-acoustic reflex 7 Anatomy 8 Audiometric Assessment 9 Pure Tone Audiometry Speech Audiometry Acoustic Immittance (impedance test ) Auditory Brainstem Responses Electrocochleography Otoacoustic Emissions Pure Tone Audiometry Most common ,subjective test Air conduction testing Frequencies 125,250,500,1000,2000,4000,8000 HZ Bone conduction testing 250,500,1000,2000,4000 HZ 10 Pure tone audiometry 11 USES As baseline test (pre op and post op) To differentiate the conductive vs sensorineural pathway The degree of handicap or heaing loss and which frequencies 12 Crossover Audiometric results are only valid when the results are actually of the tested ear. Interaural attenuation reflects crossover. Air conduction from 40-80dB Bone conduction even at 0dB 13 Masking The audiometric technique used to eliminate responses by the non-test ear. An appropriate noise is presented to the non-test ear while the test ear is being tested. Masking level must exceed the non-test ear threshold, but not create crossover. 14 Speech Audiometry 15 Determines how a well person hears and understands speech,subjective test. Speech reception threshold SRT SRT 50% of spondees SRT should be in close correlation with PTA +- 10 db of PTA. Discrimination score (DS) 30-40 db above PTA 90-100% in normal or conductive DS is 60-70 in sensory hearing loss DS -(normal ,CHL, COCHLEAR &RETROCOCH ROLLOVER ) 16 USES -malingerer patients -for fitting Hearing Aids -for cochlear implant patients -to differentiate cochlear than retro-cochlear lesion 17 Acoustic Immittance Impedance: resistance to acoustic flow,objective test Admittance: ease of acoustic flow Tested by: Tympanometry Acoustic Stapedial Reflex 18 Tympanometry by Jerger 19 20 A normal between 100-(-100) As stiff type otosclerosis or stiff TM. Ad flaccid type ossicular discontinuity B flat –fluid in ME or thick TM C more in negative –retracted TM Acoustic Stapedial Reflex to elicit a stapedial muscle contraction, objective test. 3 primary acoustic reflex characteristics Presence or absence of the reflex Reflex threshold Reflex Decay It tests VIII,brain stem ,VII Good for screening in infants and malingerer 21 Acoustic Reflex Decay 22 Measures the ability of the stapedius muscle to maintain sustained contraction. Lower frequency tone/noise for 10 seconds Facial Paralysis 23 Absent or abnormal stapedial reflex when the recording probe is ipsilateral to the side of the lesion. Can also be helpful in locating lesions proximal or distal to the stapedial muscle. Eighth nerve lesions 24 Absent reflexes when stimuli is presented to the affected ear. Reflexes in eighth nerve lesions are not dependent on the degree of hearing loss. Rapid reflex decay Auditory Brainstem Responses 25 Impulses that are generated by the auditory neural pathway that can be recorded on the scalp. objective test Not affected by sleep, sedation, or attention. Bone Conduction ABR As reliable and repeatable as air conduction ABR. Particularly useful in structural abnormalities 26 Canal Atresia or stenosis ABR Primary goal is a clear and reliable Wave I Wave I : distal 8th nerve Wave II : proximal 8th nerve Wave III : cochlear nuclei Wave IV : SOC Wave V : Lateral Lemniscus 27 ABR 28 Otoacoustic Emissions Low energy sounds produced by the cochlear outer hair cells,objective test. Cochlear amplification. Spontaneous emissions Not present in greater than 25dB hearing loss. Evoked Emissions Transient evoked Distorted Product 29 OAE and middle ear pathology Transmission properties of the middle ear directly influence the OAE characteristics. Otitis media Newborns Tympanic membrane perforations 30 ANY QUESIONS 31