* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5th Period - SMS Intranet
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Animal mummy wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian language wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian hieroglyphs wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta Stone wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Great Pyramid of Giza wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramids wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian religion wikipedia , lookup
Women in ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
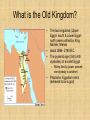
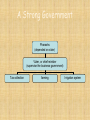
Ancient Egypt: A Glance Back in Time Ancient Egypt Described as the gift of Egypt, the Nile River was the basis for the great Egyptian civilization. The Egyptian civilization was an advanced one with a strong government a complex writing style and unique beliefs about life and death. The topics being covered around the theme of Ancient Egypt are: The Old Kingdom Gods and Serving the Gods Mummification and Preparing for the afterlife Pyramids Great temples The role of women Hieroglyphics and hieratic Rosetta Stone Art The Pyramids of Egypt “Man fears time, Yet time fears the pyramids.” -Arab Proverb The beginning of pyramids • • • • Ancient Egyptians believed that their dead would travel to the Underworld in their death but only if their body was preserved. Mastabas were used to protect and honor the dead. A mastaba is a rectangular tomb made of stone. A Pharaoh named Djoser wanted to have a tomb more spectacular than a normal mastaba. His architect, Imhotep, came up with the 60 meter high Step Pyramid which was six mastabas placed on top of each other in decreasing size. This was an early predecessor of the true pyramid form. A Pharaoh named Sneferu, a descendant of Djoser, also wanted a spectacular tomb. His architect answered this with the Bent Pyramid, named so because the angle of the pyramid was decreased when half way through its construction faults began to form. The 341 ft tall Red Pyramid is the first true pyramid still remaining. The Great Pyramid of Kufu • • • • Pharaoh Kufu of Cheops built his eternal resting place on the Giza Plateau. He began this project in 2589 B.C. and completed it in 2566 B.C. When this granite pyramid was first built it was 481 ft including the limestone casing blocks, but toay it stands 449 ft tall. It was the world’s tallest structure for more than 4,00 years until the building of the Eiffel Tower. Over 2,300,000 blocks of stone each weighing between 2.5 to 9 tons each. These blocks were pulled up mud and brick ramps and then set into place. They were placed together so well that you cannot slip a piece of paper between two stones. The sides of the pyramid measure 227 meters. Ten entire football fields would fit within the base of the Great Pyramid. It is so accurate that the error margin is less then one percent. Each corner was exactly in line with a cardinal direction (East, West, South, and North). The pyramid of Khafre • • • Pharaoh Khafre, the son of Pharaoh Kufu, followed in his father’s footsteps and built a pyramid at Giza that was slightly shorter than Kufu’s pyramid. His pyramid complex includes the Sphinx, a Mortuary Temple, and a Valley Temple. His is the only pyramid at Giza that still has the original limestone casing. This pyramid was built between 2558 and 2532 B.C. and stands at 446 ft although it was originally 471 ft tall. The exact number of stones used is unknown but each block weighs from 2.5 to 7 tons each. The pyramid of Menkaure • • • Pharaoh Menkaure, son of Pharaoh Khafre and grandson of Pharaoh Kufu, went along with family tradition and built the third and last pyramid at the Giza complex. The exact date that this pyramid was built is undetermined but it was more than a thousand years old when Herodotus, a Greek historian, visited the Giza complex. This pyramid was originally 215 ft tall but now it stands at 203 feet. Each block of stone weighs between 2.5 to 7 tons each. Works Cited Unknown. “The Great Pyramids.” The Great Pyramids. Date published unknown. <http://www.geocities.com/SoHo/Atrium/1157/pyramids.html > (9/30/2003). Unknown. “Red Pyramid.” Red Pyramid. Unknown publication date.< http://www.crystalinks.com/redpyr.html > (9/30/2033). Unknown. “Bent Pyramid.” Bent Pyramid. Unknown publication date.http://www.crystalinks.com/bentpyr.html (9/30/2003). PBS. “The Pyramids” The Pyramids. Unknown publication date. < http://pbs.org/wgbh/nova/pyramid.html > (9/30/2003). Unknown. “The Great Pyramids.” The Great Pyramids. Unknown publication date. < http://www.kingtutone.com/pyramids.html > (9/30/2003). Ancient Egyptian Art Millie Hardison 10/2/03 Ancient Egyptian Art •In the Egyptian form of art called Frontalism the people are always drawn in profile •But the eyes are drawn in full •And the body is drawn from the front •This is an example of ancient Egyptian art and it is draw in fontalism •In this picture there is a noble hunting fowl and cat Ancient Egyptian Art • The Ancient Egyptian also made sculptures •The sculpture to the left is made of wood and is an example of frountalism • The sculpture is named Sheik Ancient Egyptian Art •Later the sculptures were made from stone such as this one • This was known as Menkue and his Queen • This sculpture could not stand freely because of the slight unevenness • It was dated to be older than Sheik • This sculpture was a way to show authority Ancient Egyptian Art Works Sited Kremen, Lisa. “Understanding Egyptian Art.” Ancient Egypt A History of Art and Culture. 12/17/96. http://www.bergen.org/AAST/Projects/Egypt/egyptia n_art.html (2 Sept. 2003). The Old Kingdom Sunmi Lee What is the Old Kingdom? • The two kingdoms (Upper Egypt- south & Lower Egyptnorth) were unified by King Narmer, Menes • about 2664- 2180 B.C. • The pyramid age (3rd to 6th dynasties) of ancient Egypt – Ruling family (power passed one dynasty to another) • Pharaohs- Egyptian rulers (believed to be a god) A Strong Government Pharaohs (depended on vizier) Vizier, or chief minister (supervise the business government) Tax collection farming Irrigation system Beliefs on after life • Pyramids – Tombs for eternity – Provided dead kings with everything they would need in their new lives (clothes, jewelries, or even slaves) – All made by human – Take a long time to built that pharaoh even begins to make his tomb right after he gets power Hope Scott Hope Scott Preparation for the Afterlife • Burials customs for Egyptians called that the body be preserved. This process was given ample time once it was known that a ruler might die • The afterlife was to be the same as the life you lived on earth. Supplies for the Afterlife • Since the afterlife was considered to be a continuation of your life on earth, everyday materials were supplied in the tomb • Materials such as writing supplies, clothing, wigs, hairdressing supplies and other tools • Food was also provided for the deceased daily, by it magically transforming to the model that was drawn on the walls of the tomb • There were also blessings written on the wall, so that they would be said once the owner got the food. Shabtis • After the annual floods of the Nile, the population of Egypt was subject to compulsory labor on the irrigation system • Shabtis was a statuette that took the place of ones labor in the afterlife so the deceased person would not have labor • The Shabtis was placed in tombs around the Middle Kingdom(2040-1640BC). • During the third intermediate period, Shabtis was placed in a special box, in the tomb. Parts of Personality • XAt: Mummy in the tomb, after the house of ba • kA: The double individual of the person, printed as a duplicate in the tomb • Ax: The transfigured spirit, which was transferred after the funeral rituals were completed • Rn: Name of the person, which was in scripted on the funerary texts, on papyrus or the tomb walls • Swt: Protected the individual from harm • Ba: Human Headed bird Works Cited • O’Brian, Alexandra A. “Death in Ancient Egypt” Oriental Institute Research Archives. 1996-1999. http://wwwoi.uchicago.edu (30 Sept 2003) . Egyptian Mummification By Chandler Knight What is Mummification? • The preservation of a body, either human or animal. • There are 3 ways a mummy can be preserved and they are wet, frozen, or dried. Http://members.aol.com/egyptart/mummy.html Why Egyptians were Mummified • • • • The physical body, shadow, name, ka (spirit), ba (personality), and the akh (immortality). These are the 6 aspects that Egyptians believed to be important. Each aspect played an important role in the well being of an individual. Each was crucial to achieve rebirth into afterlife. The Egyptians believed that by mummifying their dead they were assuring the person a successful journey into the afterlife. http://members.aol.com/egyptart/mummy.html How the Bodies were Mummified • • • • By eliminating the bodies moisture you eliminate decay. By using Natron (a salt mixture) they dried the bodies. Natron- natural substance found in the Nile River Natrons four salts – Sodium carbonate- dried the body by drawing out the water – Sodium bicarbonate- increase the pH in the body which kills bacteria when subjected to any kind of moisture. – Sodium chloride – Sodium sulfate http://members.aol.com/egyptart/mummy.html Egyptian Gods By: Ligon Brooks Ra • Sun God, King of the • Gods Ra is sees as a falcon with a sun disk on its head or a man with a falcon’s head Osiris God of the dead Osiris is shone dressed in white with crook and flail and green skin Husband to Isis and father of Horus Isis Queen of Goddess Shown with a crown on her head Wife of Osiris and mother of Horus Other Gods • • • • • • • • Seth- god of the desert, storm and violence Hathor- goddess of love, music, and dance Nut- sky goddess and Geb- earth god Thoth- god of wisdom Ma’at- goddess of justice Bastet- cat god Anubis- god of embalming Amun- god of ceation Source “Egyptian gods”.Edkins Family.http://www.gwydir.demon.co.uk/jo /egypt.htm.(9/30/03) Serving the Gods in ServingEgypt the Gods in Ancient Ancient Egypt Taylor McEwen Taylor McEwen Egyptian Temples • • • • • Egyptian temples were said to be the homes of the gods and goddesses Each temple was dedicated to a god or goddess and he/she was worshipped there The large temples were made of stone so that they would last forever. Walls of the temple were covered with scenes that were carved into stone and then painted. The scenes showed pharaohs fighting in battles and performing rituals with the gods and goddesses Offering Rituals • Food and drink were put before the god. • They believed in keeping the gods happy because they thought the god would provide them with protection and bring them wealth • They offered joints of meat, roasted fowl, bread, fruits, vegetables. • Offering always included flowers bound in garland. Sanctuaries • Sanctuary was located inside the temple • Shrines were built where the statue of a god/goddess would have lived Women In Ancient Egypt Drenika Mosby The Status of Women in Egyptian Society Women and men are equal Legal rights were based on social classes not gender When the Greeks conquered Egypt in 332 B.C.E, Egyptian women had more rights than Greek women Egyptian women could manage, own, and sell land Women can also have slaves Marriage A girl/women got married when she was 14, or when she begin to menstruate Her husband was anywhere from 17-20 or a divorced man A important part of marriage was birth, death and rebirth The placed false penises on the male mummies and false breasts on the women mummies Divorce was a private matter the government did not interfere Fertility Pregnancy was important to an Egyptian women A fertile woman was an successful woman For a man to father a child that would prove his “manliness” Midwives used spells to protect the expectant women A purification ritual for females followed fourteen days after giving birth A Egyptian mother named her child immediately following birth incase the child dies and it would have a name in after life YJulie SaderY ClickNext ~This temple (belonging to Hatshepsut, who ruled Egypt during the Greek/Roman period) was found under decades of sand, engraved into the side of a mountain near the banks of the Nile ~The architect was Senmut, Hatshepsut’s lover for more than 20 titles ~Two ramps connect the three levels and there are sphinxes with Hatshepsut’s head at the entrance ~The temple is said to be dedicated to her so called parents Amon and Hathor ~For Senmut’s work, he was awarded with enough money for him to build himself his own temple, not too far away from his Hatshepsut’s ClickPrevious ClickNext http://www.bediz.com/hatshep/temple.html Click The End http://www.ehabweb.net/hatshebsut_temple.html Egyptian Hieroglyphics • • • • • • • • • • History of Hieroglyphics Language started in 3000 B.C. Last know text is from 394 A.D Used for religious purposes as well as economical purposes in Egypt One of the first languages in the world Hieroglyphics were known as the “words of God” The first hieroglyphics were pictograms that depicted objects Then they moved to more complex writing called ideograms which symbolized an idea or action The language was found in 1799 by one of Napoleon's solders in a stone, know as the Rosetta Stone, but the language was hard to translate In 1822 a French scholar named Champollion discovered the hieroglyphic language The language was lost for 1500 years The Hieroglyphic alphabet • Hieroglyphic's can be written: left to right, right to left, and up to down • There are over 2,000 hieroglyphic symbols • There are three different kinds of signs in the Hieroglyphic language: Alphabetic signs, Syllabic signs and Determinative signs. Work Cited and your name in Hieroglyphics • Your Name in Hieroglyphics http://www.7cs.com/nomhiero.htm • Ellis, Elisabeth and Anthony Esler. World History. New Jersey: Upper Saddle River, 2003. Strachen, Richard and Kathleen Roetzel. “Ancient Egyptian Culture.” The Story of the Rosetta Stone,” Finding a Lost Language.” 1997. http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/prehistory/egypt/hieroglyphics/rosetta.com (1 Oct. 2003) Unknown. “Hieroglyphics.” Hieroglyphics. Unknown Publication date. http://www.eyelid.co.uk/hiero1.html (1 Oct. 2003) Unknown. “Hieroglyphics Overview.” Hieroglyphics Writing. Unknown Publication date. Http://www.greatscott.com/hier/hiero_over.html (1 Oct. 2003) Unknown. “Explore Ancient Egypt.” Explore Ancient Egypt. http://www.mfa.org/egypt/explore%5Fancient%5Fegypt/hiero%5Fwr (1 Oct. 2003) Unknown. “Egyptian Hieroglyphic Alphabet.” Egyptian Hieroglyphic Alphabet. Http://www,jimloy.com/hiero/alpha.htm (1 Oct. 2003) Class, Ashley. “Hieroglyphics.” Egyptian Writing. https://wedsever.sms.org/intranet/classes/history/worldhist/egyptproject/Aclass. html ( 1 Oct. 2003) • • • • • • The Rosetta Stone By Chelsea Jacobs Physical features 1 meter high 70 centimeters wide 30 centimeters deep Very heavy What is the Rosetta Stone? A stone with writing in 2 languagesEgyptian and Greek 3 scripts of Egypt used- hieroglyphic, demotic, Greek Written in 3 scripts so that priests, government officials, and rulers could understand what it said Discovery Carved in 196 B.C Found in 1799 by French soldiers who were rebuilding Egypt Found in small village near the DeltaRosetta Translation Written by priests to honor Pharaoh Lists all things pharaoh has done that are good for Egypt Before the Rosetta Stone no one could uncover the mystries hieroglyphics held Helped to decipher hieroglyphics Francois Champollion translated hieroglyphics in 1822 Champollion figured out what the 7 demitic signs were and by looking at hoe these signs were used he could uncover what they stood for Works Cited Andrew Oakley. “The Rosetta Stone.” Kids Konnnect. 2000 <http://.kidskonnect.com/AntientEgypt/Ros ettaStone.html> (September 30, 2003) “The Rosetta Stone” <file://c:\windows\TEMP\9AOKY8H3.htm>