* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs
Rosetta Stone wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Memphis, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum wikipedia , lookup
Great Pyramid of Giza wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Chapelle Rouge wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramids wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
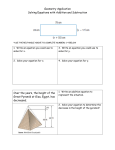
Ancient Egyptian Pharaohs Introduction • Pharaohs - ancient Egyptians rulers; they believed they were gods • Old Kingdom - 2700 B.C.E – 2200 B.C.E – Strong central government during this time; age of pyramids • Middle Kingdom - about 2000 B.C.E. – 1800 B.C.E. – Period of Reunification • New Kingdom – about 1600 B.C.E. – 1100 B.C.E. – Egypt’s Golden Age; increased trade during this time of peace and stability Pyramids • Built as tombs for pharaohs • Pharaohs were believed to be gods • Egyptians also believed in life after death • The pyramids were built to honor the pharaohs forever • Great Pyramid at Giza is one of the greatest Khufu • Ruled from 2551 to 2528 B.C.E • Khufu established the pharaoh as central authority • Had a large network of government officials • Declared himself a god • Built the Great Pyramid of Giza Great Pyramid of Giza • A center of huge complex • More than 2 million stone blocks • Took 20 years to complete • No one is exactly sure how they built it The Sphinx by the Great Pyramid •Head of a man •Body of a lion Senusret I Senusret shown clutching ankh which is an Egyptian symbol for eternal life • Ruled from 1971 to 1926 B.C.E. • Patron of the Arts • Craftspeople thrived under his rule • “The Story of Sinuhe” written during his rule • Greatest accomplishment was religious architecture White Chapel • Chapel is a small temple at Karnak • Made of alabaster – a hard white stone • Beautiful artwork decorated the chapel’s pillar • The white chapel was taken apart by another pharaoh but was later rebuilt by archeologists Stone carvings of Senusret I Menes • Ruled from 3100 to 2850 B.C.E • Founded the city of Crocodilopulus • Credited with uniting Upper and Lower Egypt • Unification is the joining of two parts into one Unification of Egypt Red Crown of Lower Egypt White Crown of Upper Egypt The Red and White Crown were joined together to symbolize the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt What the new crown looked like Hatshepsut • Ruled from 1473 – 1458 B.C.E • Egypt’s first female pharaoh • Greatest accomplishment was gaining power • Sometimes wore male clothing and a fake beard • promoted trade with other countries • Biggest trade expedition was to Punt – Traded jewelry, bronze weapons, papyrus – Over 200 men made the journey Other images of Hatshepsut Hatshepsut’sTemple at Dayr alBahri • Built into a cliff above the Nile River • At the entrance were two tall thin monuments called obelisks • Entrance also had 200 sphinxes Obelisk at temple Ramses II • Ruled from 1290 to 1224 B.C.E • Reigned more than 60 years as Ramses the Great • One of the most famous • Over 100 wives and children • Fearless soldier – he was made a captain at 10 years old The Temple at Abu Simbal Ramses depicted as a warrior Stone figure of Ramses the Great King Tutankhaman • Ruled from 1341 to 1323 B.C.E. • 9 years old when he became pharaoh • 19 years old when he died • Tomb was discovered in 1922 in the Valley of the Kings • It was the greatest discovery of all times The treasures of King Tut’s Tomb