* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Computer Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Introduction to Computer
Science
Fall 2003, 劉震昌
Ref: Computer Science: an overview
J. Glenn Brookshear
Outline
Concept of computers
Computer software: algorithm
Computer hardware: algorithmic machine
Turing Machine
5 major components of computers
Computers ?
Software
Hardware
Software
Package
(Executable)
Source
Program
#include <stdio.h>
main(){
…
}
CSIE class schedule
High level
資網 C
Application
Program 程設 C++
Java
資演(1)
網路
資演(2)
資料庫
作業系統
Operation
System
Hardware
Low level
系統程式
邏設
計組
電路 數電
微算機
Computer software:
Algorithm 演算法
Computers are machines to execute
Algorithm
Fundamental concept of CS
Def. 1: a set of steps that defines how a task
is performed
Def. 2: an ordered set of unambiguous,
executable steps that defines a terminating
activity
Algorithm: example
Sorting: sort the cards from top to down in
alphabetical order 排序
Albert
Baker
Charlie
Algorithm: sort (cont.)
Albert
Charlie
Baker
Albert
Baker
Charlie
After
Step 1
input
Charlie
Albert
Baker
Charlie
Baker
Albert
After
Step 2
After
Step 3
Algorithm: sort (cont.)
Input: 3 cards in arbitrary order
1. Compare the names on the first and second cards.
Exchange them if they are out of order.
2. Compare the names on the second and third cards.
Exchange them if they are out of order.
3. Compare the names on the first and second cards.
Exchange them if they are out of order.
Output: 3 cards in alphabetical order
Properties of algorithms
Goal: find a single set of directions that
describe how any problem could be solved
Algorithm = Programs within computers
The intelligence required to perform the
task is encoded in the algorithm
Computers hardware?
Concept of algorithm appeared first
Computers are designed to implement algorithms
Computers 電腦 are not smart themselves…
+
Development of Algorithmic
Machines
Algorithmic machines:
machines that perform
algorithm tasks
Abacus(算盤): ancient
Greek and Roman
Blaise Pascal(16231662), France
Development of Algorithmic
Machines (cont.)
Charles Babbage(17921871), England
Herman Hollerith
打孔機
解多項式
1st generation computer
1940
真空管
ENIAC
2nd generation computer
1959
電晶體
3rd generation computer
1965
IC (積體電路)
4th generation computer
1971
VLSI (超大積體電路)
Turing machines
The abstract model of general-purpose
algorithmic machines
1936 by Alan M. Turing
You will learn more in the class of automata
and formal language 自動機與形式語言
Turing machines (cont.)
Components of a Turing machine
Control
unit
state of the machines
read/write head
…
…
tape
symbols
Turing machines (cont.)
Prototype of today’s computer
Control unit -> CPU
States -> registers
Tape cells -> memory
Symbols -> 0 and 1
The power of Turing machine
If a problem cannot be solved by a Turing
machine, then it cannot be solved by any
algorithmic system
John von Neumann
machine
In early computing machines, the programs
were built as part of the machine
Store-program concept
Program, just like data, can be coded and
stored in main memory
Control unit extracts the program from memory,
decodes the instructions, and executes them
Some data(bit patterns) were interpreted as
instructions -> machine language
Outline
Concept of computers
Computer software: algorithm
Computer hardware: algorithmic machine
Turing Machine
5 major components of computers
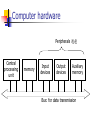
Computer hardware
Peripherals 週邊
Central
processing
unit
memory
Input
devices
Output
devices
Auxiliary
memory
Bus: for data transmission
CPU (central processing unit)
Carry out the instructions in the program
ALU: arithmetic/logic unit
ALU
Control
unit
registers
CPU
CPU – control unit
Instruction fetch
Instruction decoding
Instruction execution
Memory read/write
time
Instruction cycle
Memory
Main memory
RAM(random access memory)
Fast
Volatile 揮發
Auxiliary memory
Secondary storage
Slower
Permanent
Ex. Hard Disk, CD-ROM
I/O devices
Input devices
Keyboard, mouse, …
Output devices
Display, printer, …
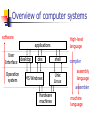
Overview of computer systems
software
High-level
language
applications
User
Interface
Operation
system
desktop
dos
MS Windows
Hardware
machines
shell
Unix
Linux
compiler
assembly
language
assembler
machine
language
Purpose of this class
software
High-level
language
applications
User
Interface
Operation
system
desktop
dos
MS Windows
Hardware
machines
shell
Unix
Linux
compiler
assembly
language
assembler
machine
language