* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2#3841 UNIT TWO Participant Handout
Emil Kraepelin wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Szasz wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Community mental health service wikipedia , lookup
Political abuse of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Mentally ill people in United States jails and prisons wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Deinstitutionalisation wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
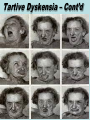
Intermediate CIT Course TCOLE Course # 3841 Texas Commission On Law Enforcement PARTICIPANT HANDOUT 16-hr Two (2) Day Course AND BCCO PCT #4 PowerPoint UNIT TWO Unit Goal: 2.0. • To sensitize the participant to the adversity of mental illness. 2 2.1. • Define the term “mental illness”. 3 Definitions: • General Definition of Mental Illness. • Professional Definition of Mental Illness. • Definition of Insanity. • Abnormal vs. Normal Behavior. 4 General Definition “Illness, disease, or condition that either substantially impacts a person’s thought, perception of reality, emotional process, or judgment, or grossly _______ a person’s behavior, as manifested by recent disturbance behavior.” Professional Definition Mental illness is diagnosed based on ________ and ___________ as evaluated by a psychiatrist, psychologist, licensed professional counselor, licensed social worker, or other qualified professionals using a tool known as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Insanity Legal Term ________________ is considered “a diminished capacity and inability to tell right from wrong.” This is not a psychological term. The definition varies from state to state. It is generally used by the court with regard to an individual’s competency to stand trial. Abnormal Versus Normal Behavior A sharp dividing line between “normal” and “abnormal” behavior does not exist. Adjustment seems to follow what is called a “normal distribution,” with most people clustered around the center and the rest spreading out toward the extremes. Basic Facts • There are two distinct types of mental illnesses _______ to ___________ mental illnesses which are caused by psychological, biological, genetic, or environmental conditions ___________ mental illnesses due to severe stress which may be only temporary 9 Basic Facts – Cont’d • Anyone can have a mental illness, regardless of age, gender, race or socio-economic level. • Mental illnesses are more common than cancer, diabetes, heart disease or AIDS. • Mental illness can occur at any age. 10 Basic Facts – Cont’d • ___ to ___% of individuals may be affected by mental illness. • __.__million children are affected by mental, developmental or behavioral disorders. 11 Basic Facts – Cont’d • Nearly ___ - ______ of all people with a diagnosable mental disorder do not seek treatment. 12 Basic Facts – Cont’d • With proper treatment, many people affected with mental illness can return to __________, productive lives. • Mental illness can - and should - be __________. 13 — Basic Facts About Mental Illness — NAMI Texas OCD Video (View video newscast from “Train the Trainer” materials-updated version )) 14 2.2. Four Categories of Mental Illness Four prominent categories of mental illness. 1. ____________ Disorders 2. ________ Disorders 3. _______________ 4. _________________ Disorders 15 2.3. Personality Disorders Disorders as they relate to law enforcement officer contact. 16 2.3 Personality Disorders Many individuals who are functioning well in their lives may display _____________________of what are known as personality disorders 2.3 Personality Disorders Continued Individuals experiencing these disorders show __________ _______ that are inflexible, maladaptive, or inappropriate for the situation, and this causes significant problems in their lives. 2.3 Personality Disorders Continued Those individuals who have personality disorders usually have very little insight that they have a problem, and tend to believe that the __________ are caused by other people, the “system,” or the world at large. 2.3 Personality Disorders Continued These traits are often accompanied by some form of ____________ and may also be seen in those with chemical dependency problems. 2.3 Personality Disorders Continued Persons with personality disorders are not usually treated like those with other mental illnesses, but are taught a variety of ____________ and ________ skills, or treated for other problems such as chemical dependency or depression. 2.3 Personality Disorders CAUSES Although the causes for these disorders may not seem relevant for the officer dealing with these individuals, their backgrounds are significant Personality Disorders CAUSES – Cont’d It is believed that most personality disorders are caused by a family _______ - usually beginning at a young age - of physical or emotional abuse, lack of ________ and responsibility, poor relationships with one or both parents, and alcohol or drug abuse. 2.4 Personality Disorders Encountered By Law Enforcement Common personality disorders that may be encountered by peace officers include; • _________ personality disorder, • _________ personality disorder, and • _________ personality disorder. 2.4 Personality Disorders Encountered By Law Enforcement 1. Paranoid: A. Tendency to ________the actions of others as deliberately threatening or demeaning B. Foresee being in _________ to be used or harmed by others 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 1. ____________: C. Perceive ___________ from other people 2. _____________: A. Most commonly recognized in males (____________) Lone Wolfe 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 2. Antisocial: B. A pattern of _________________ and antisocial behavior diagnosed at or after age 18 C. May have one or more of the following: 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 2. Antisocial C - Continued: 1.) History of _________ as a child or adolescent, may have run away from home 2.) Starting _______ 3.) Using weapons Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 2. Antisocial C - Continued: 4.) Physically abusing _________ or other ___________ 5.) Deliberately destroying others’ ____________ 6.) ________ 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 2. Antisocial C - Continued: 7.) ____________ 8.) Other illegal behavior D. As adults, these people often have trouble with ______ and are reluctant or unwilling to conform to society’s expectations of family and work 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 2. Antisocial: E. These individuals know that what they are doing is _________, but do it anyway 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 3. ____________: A. Most commonly recognized in females B. May have one or more of the following: 1.) unstable and intense personal relationships 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 3. Borderline B: 2.) ____________ with sex, relationships, spending, food, drugs, 3.) intense ______ or lack of control of anger 4.) recurrent ____________ threats 2.4 Personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers – Cont’d 3. Borderline B: 5.) chronic feelings of ___________ or boredom 6.) feelings of _____________ 2.5. Prevalent behaviors associated with personality disorders. 35 Behaviors associated with personality disorders People with personality disorders usually will not seek _____________ because they don’t think they have a problem Behaviors associated with personality disorders – Cont’d They may end up in the criminal justice system because their disorder may lead them to break laws and come to the ____________ of law enforcement by theft, by hot-check writing, by fraud, etc. Behaviors associated with personality disorders – Cont’d They may use alcohol and illegal substances as a form self-medication, due to the __________and the consequences of their behaviors They often need treatment for chemical dependency or depression. 2.6. Mood Disorders Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact. 39 Discuss Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact A. A mood disorder is another type of mental illness demonstrated by disturbances in one’s _____________ reactions and feelings. B. Severe depression and bipolar disorder, also known as manic ____________, are referred to as mood disorders. Discuss Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact – Cont’d C. Recognizable behaviors that associate with mood disorders could include: 1.) lack of _______ and _________ in activities, 2.) extreme and rapid _____ swings, Discuss Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact – Cont’d C. Continued: 3.) impaired _____________, 4.) explosive ____________, 5.) increased ____________ and 6.) ____________ Discuss Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact – Cont’d D. Causes: Researchers believe that a complex _________ in the brain’s chemical activity plays a prominent role in mental illness selectivity in the individual. E. ________________ factors can also be a trigger or buffer against the onset. 2.7. Two most common mood disorders encountered by law enforcement officers. 1. Depression 2. Bipolar Disorder 44 2.7 Depression Depression is a common, widespread disorder. Most people have experienced some form of _________ in their lifetime or even had repeated bouts with depression. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Depression is a natural reaction to; ____________ ____________, ____________, or ____________. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Major depression is not just a bad mood or feeling “blue” but a disorder that affects thinking and behavior not caused by any other physical or mental disorder. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d A major depressive syndrome is defined as a depressed _____ or loss of _________ of at least two weeks duration accompanied by symptoms such as; weight loss/gain and difficulty concentrating. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Five or more symptoms are generally present during the same two-week period and are represented by a change from previous functioning. Depressed mood or loss of interest must also be included as a symptom. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Other symptoms of depression: Prolonged feelings of __________ or excessive guilt Loss of _______ in usual activities Difficulty ___________ or making decisions 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Other symptoms of depression: Low energy/_________ Changes in __________ level An _____________ to enjoy usual activities 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Other symptoms of depression: Changes in ____________ habits (sleeping more or less); an inability to fall _________, or waking up ______ in the morning and not being able to go _______ to sleep). 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Depression and _______: The single most common factor in suicidal behavior or death by suicide is that the individual is experiencing depression. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Treatment for Depression: A number of non-addictive ______________ are used in treating depression, if needed. It is recommended that persons taking medications for depression not use ______________ 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Alcohol can interact with the medications and increase alcohol’s _________ or _________ problems in reaction time and judgment. 2.7 Depression – Cont’d Many people self medicate their depression with; ___________ or other non-prescribed ________ that may give them temporary relief but tends to only ____________ the depressive symptoms. 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER A mental illness involving _________ (an intense enthusiasm) and depression (see above) 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER Continued Mania Phase may include: Abnormally high, expansive or irritated __________ ________ self-esteem Decreased need for _________ More ____________ than usual 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER Continued Mania Phase may include - Continued: Flight of ideas or feeling of thoughts ____________ ____________ risk-taking 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER Continued Depressive Phase may include: Prolonged feelings of sadness or hopelessness Feelings of guilt and worthlessness Difficulty concentrating or deciding Lack of interest 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER Continued Depressive Phase may include: Low ________ _________ in activity level _________ to enjoy usual activities __________ 2.7 BIPOLAR DISORDER Continued An individual may quickly swing from the ________ phase to the ____________ stage. An individual _________ maintain the level of activity normally associated with mania for a long period of time. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact Definition of Psychosis: “A group of serious and often _______________ mental disorders that may be of ____________ or __________________ origin and are characterized by some or all of the following symptoms: 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact - Continued Definition of Psychosis - Continued: following symptoms: impaired ____________ and _______________ ability, 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Psychosis(Cont’d) perceptual ______________, inappropriate _______________ responses, inappropriate affect, ______________behavior, reduced ____________ control and impaired _____________ of reality.” 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Psychosis is an illness involving a ___________ of reality that may be accompanied by ___________ and/or ______________ 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d The person may be hearing _________, he may look at a person and see a _________, he may think people are _________ him, or he may ____________ himself to be Jesus Christ. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d To the person, these hallucinations and delusions are real. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d These are most commonly seen in persons with ________________, ____________ disorder, severe ________________ or ________ induced disorders. Physical ________________ can also induce a psychotic state. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Potential conditions include: ____________ brain disorders (brain injury or infections to the brain), _______________ disorder, ________ syndromes, and ________ withdrawal. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Delusion: False ________ not based on factual information. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Delusion(Cont’d) The person may ____________ to the situations or may appear to have what is called a “flat affect,” no _________ or does not seem to ________ about what is going on around him. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Delusion(Cont’d) social __________ inappropriate __________, odd ____________, ____________ thinking 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Hallucinations: Distortions in the senses, causing the individual to experience hearing or seeing something that is not there. 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Hallucinations: There is poor processing of information and illogical thinking that can result in disorganized and rambling speech and/or delusions 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Hallucinations(Cont’d) It is not uncommon for a person hearing voices to hear ______or more at a time 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Hallucinations(Cont’d) If you approach the person and start yelling at him, you are only adding to his ____________ 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact – Cont’d Definition of Hallucinations(Cont’d) Imagine having two or three people shouting at you all at once while an officer is trying to give you directions. 2.9 Psychotic episode from consumer perspective The voices are almost always negative, _________ _______ telling the person things like; “Die, die, die,” “Kill yourself,” “You’re no good,” or “They are going to get you.” 2.9 Psychotic episode from consumer perspective – Cont’d These voices are ______ to the person experiencing this episode. Researchers have conducted brain scans on persons hearing voices during a __________ episode. 2.9 Psychotic episode from consumer perspective – Cont’d The part of the brain that is firing when hearing these _________ is the same part of your brain that is firing when you are listening to the instructor’s voice. 2.9 Psychotic episode from consumer perspective – Cont’d Common delusions experienced by persons during a psychotic episode: ____________ voices Feelings of ____________ Visual _______________ Heightening of the _________ 2.10 Behavior Emotional Cues from Psychotic Episode Behavioral cues of persons with a psychosis: Inappropriate or bizarre _________ Body ____________ are lethargic or sluggish Impulsive or ______________ body movements 2.10 Behavior Emotional Cues from Psychotic Episode – Cont’d Behavioral cues of persons with a psychosis: Responding to ______________ Causing ______ to self 2.10 Behavior Emotional Cues from Psychotic Episode – Cont’d Home environment: strange ______________ (e.g., aluminum on windows) ____________ turned over ________ matter/_________ on floors and walls 2.10 Behavior Emotional Cues from Psychotic Episode – Cont’d Home environment – Cont’d: Unusual attachment to ___________ objects or toys 2.10 Behavior Emotional Cues from Psychotic Episode – Cont’d Emotional cues of persons with a psychosis: Lack of ______________ response Extreme or inappropriate ________ Inappropriate emotional _________ 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis Substance and cognitive disorders (drug related disorders included) symptoms include: A major loss of contact with ______ A gross interference with the __________ to meet life’s demands 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance and cognitive disorders (drug related disorders included) - symptoms include – Cont’d: May have possible _________ and ________________ Alteration of ________ Defects in ______________, 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance and cognitive disorders (drug related disorders included) - symptoms include – Cont’d: Defects in language, Defects in memory, and Defects in cognition 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder: Prolonged abuse of any drug (alcohol, prescription medications, or “street” drugs) will cause chemical _________ or ______________ 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: This has an effect on consciousness, and if used long enough or in large dosages, may cause _____________ damage to the central nervous system 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: This may cause a wide range of psychological reactions that can be classified as ______________ 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: Smoking a _________________ like crack cocaine can cause paranoid symptoms, 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: as prolonged alcohol use can produce __________________symptoms 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: A person who is physically _____________ on heroin will show anxious behavior if usage is discontinued. _________ drug and alcohol usage is also a primary concern for individuals with a mental illness 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: These substances can have an adverse effect when used in combination with prescribed medications as well as having a _________ _____________ on more severe symptoms 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: Use of illegal drugs and alcohol in a self-medicating way can also create a ______________ as well as a roller coaster effect due to lack of consistency and medical monitoring. 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: Substance abuse treatment is a critical _____________ in a comprehensive system of care 2.11 Substance Abuse – Cognitive Disorders & Psychosis – Cont’d Substance Abuse Disorder – Cont’d: Research conducted over the last decade has shown that the most successful models of treatment for people with co-occurring disorders provide _________ mental health and substance abuse services. 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis _____________: consists of a group of psychotic disorders characterized by changes in ______________. These disorders cause oversensitivity to ________ and __________ characterized by hallucination and/or impaired distorted thinking 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Schizophrenia: is considered the most ________ and ___________ of severe mental illnesses, typically emerging in teenagers and young people. 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Schizophrenia Statistical Facts: In the U.S., approximately 2.2 million adults, age ___ and older in a given year have schizophrenia. Worldwide statistics remain fairly consistent with U.S. figures. 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Schizophrenia Statistical Facts – Cont’d: Ranks among the top ___ causes of disability in developed countries worldwide. Higher risk of suicide approximately ____% of people with schizophrenia commit suicide. 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Distorted thinking results in: ________________ Poor processing of information / ____________ deficit _________ thinking that can result in ____________ and __________ speech, and/or ______________. 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Changes in Emotion: May ______________ to situations “Flat affect” decreased _____________ expressiveness, diminished _____ expression and ____________ appearance 2.12 Schizophrenia & Psychosis – Cont’d Changes in Emotion – Cont’d: Anhedonia lacking pleasure or interest in activities that were once enjoyable) Person is withdrawn – the media tends to portray this as _______, but it is rarely the case 2.13 Alzheimer’s Disease & Psychosis Alzheimer’s disease: The most common __________ mental disorder of older people is Alzheimer’s disease 2.13 Alzheimer’s Disease & Psychosis – Cont’d Alzheimer’s disease – Cont’d: An individual experiencing this disease may get __________ easily, have poor _________, & become easily __________ 2.13 Alzheimer’s Disease & Psychosis – Cont’d Alzheimer’s disease – Cont’d: It is estimated that 2-3 million Americans are afflicted with Alzheimer’s, and that over 11,000 die from it each year. 2.13 Alzheimer’s Disease & Psychosis – Cont’d Additional Facts: Alzheimer’s is a form of _________ It is not considered a mental illness, and most mental health facilities will not admit Alzheimer’s patients 2.13 Alzheimer’s Disease & Psychosis – Cont’d Additional Facts – Cont’d: Drugs can help the progression of the disease, but there is no cure. It is now being diagnosed in persons considerably younger than ____. 2.14 Communicative approach when confronting person in psychotic episode 1. The officer should always be cautious. 2. He should never startle the person. 3. He should be patient and try to learn the person’s name and use it 2.14 Communicative approach when confronting person in psychotic episode….Cont’d: 4. The officer should talk in a calm, soft tone of voice. 5. He should allow the person to verbally ventilate. 6. He should not crowd the person’s space 2.14 Communicative approach when confronting person in psychotic episode….Cont’d: 7. The officer should introduce himself and assure the person the officers are there to help, not hurt him. 8. The officer may have to repeat himself several times. 2.15 Mental Illness Sensitize Practical – Guest Speaker GUEST SPEAKER 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face 1. ____________: A developmental disorder, affecting 1 to 2 in 1,000 Americans, usually appearing before age ______, 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism: characterized by; • impaired non-verbal ____________ • including ________ speech patterns • or loss of ________, 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Continued: • lack of ____ _________, a restricted range of interest, • ____________ to change of any kind, • __________________ repetitive body movements, 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Continued: • a lack of awareness of the existence or _________ of ________, and • social ____________. • ____________ vary from child to child 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism Symptoms can range from mild to severe. “The child may; • act as if ___________ of the coming and going of others, or • physically attack and injure others without ______________ 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d Unraveling Autism, 2001). Although autism is diagnosed 3-4 times more in males, females with autism tend to have more severe symptoms and ____________ impairment 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Treatment is experimental, and few autistic children show significant ____________ of symptoms. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Continued: Persons with Autism suffer from ________ ___________that keep them from effectively filtering and blocking painful sensations. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Continued: Their sensory disorders can cause extreme pain from loud noises and bright light that can move them toward frustration and acts of aggression. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Officers in contact with these individuals will notice certain behaviors such as fear of ____________, ______________ behavior, insistence on ____________, ______________ in new situations, & tendency to become ____________ 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism – Officers when interviewing, be ____________, _______, and ____________, which tends to help prevent agitation in questioning process. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism – Officers should use ____________ materials, __________ of previous statements, ____________, encouragement, and attentive ________ will assist in the exchange process. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Social Behaviors: • Lack of ___________ of social rules • Reluctance to make eye _________ • Inappropriate _________ or ______ • Unusual ____________responses 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Social Behaviors: • ______________ habitual behaviors • Extreme _________ for no apparent reason • _____________ to particular objects • Deliberate ____________ of clothes 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Social Behaviors: • Uneven ____________ skills • Self ________________ behaviors 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Communication Behaviors: • May be ____________ limited • May ____________ what is said • When speaking ___________ pitch, rate, or volume 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Communication Behaviors: • ______________ expressing ideas or needs • ________ of pronouns or other parts of speech • Difficulty with abstract __________ and terms 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Other Behaviors: • ___________, pairing, and ordering objects • ______________ compulsively • ________________ lights on and off 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Other Behaviors: • ________________ things repeatedly • _______________, rocking and clapping 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – AUTISM – Cont’d 1. Autism - Other Behaviors: • Chin-tapping, _________-________, spinning • ____________ with colorful and shiny objects . 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation: Mental Retardation (MR) refers to a range of substantial limitations in mental functioning manifested in persons before the age of ____. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: A. Characteristics of MR are; 1.) a below-level intellectual capacity 2.) plus limitations in two or more adaptive skill areas such as a. ______________, b. ________-__________, 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: A. Characteristics of MR are; 2.) c. __________ living, d. __________ skills, e. ____________, f. ____________, 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: A. Characteristics of MR are; 2.) g. academic _____________, and h. ___________. 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: B. Degrees of mental retardation: Mild: IQ 69-55 Moderate: IQ 54-40 Severe: IQ 39-25 Profound: Below 25 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: C. Questioning methods: 1. Be ____________ for a reply 2. _________ __________ as needed 3. Ask short, _______ ________using simple language 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: C. Questioning methods: 4. _________ ____________ 5. Ask _______-____________ rather than “yes/no” questions 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. Strategies to use during officer contact in determining possible mental retardation 1. Criminal Activity a. noticeably ________ than others involved in offense 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 1. Criminal Activity b. ____________ c. readiness to ________ d. ___________ at the scene while others ran e. previous criminal activity patterns 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 2. Educational History a. Below usual grade level b. ID states mental impairments c. Check MHMR records 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 3. Physical Appearance a. Inappropriately dressed for season b. Unusual physical structure 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 3. Physical Appearance c. Awkwardness of movement or poor motor coordination in walking d. Difficulty writing or other fine motor skills 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 4. Speech/Language a. Obvious ________ ____________ b. Limited response or __________________ c. ________________ 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 4. Speech/Language d. Vocabulary or grammatical skills ____________ e. Difficulty _____________ facts in detail 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 5. Social Behavior a. Adult ___________ with children or early adolescents b. Eager to ____________ c. _____________ of personal space 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 5. Social Behavior d. Non-age appropriate ___________ e. Easily ______________ by others f. Easily ___________ or aggressive in response to direct questioning 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 6. Performance Tasks to utilize to help determine if problem exists a. Read/write ____________ phrases b. ____________ telephone number in book c. Give ____________ to their home 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 6. Performance Tasks to utilize to help determine if problem exists d. Tell ____________ e. Count to 100 by multiples of ________ 2.16 Two most common disorders officers face – Mental Retardation 2. Mental Retardation - Continued: D. 6. Performance Tasks to utilize to help determine if problem exists f. Define _________ __________(such as emotions or feeling terms) g. __________ how to make change from a dollar WARNING – CAUTION When performance tasks are used, one should be cognizant of the person’s dignity. The officer needs to realize that failing a performance task could cause the person humiliation, especially in public. WARNING – CAUTION Continued This humiliation could then turn quickly to aggression. 2.16 Guidelines for law enforcement contact with mentally retarded persons 1. Speak directly to the person in; a. ____________, b. ____________, c. __________ ______________ and d. __________ 2.16 Guidelines for law enforcement contact with mentally retarded persons - Continued 2. When possible, move to a less disruptive location to assist with focusing 3. Be highly aware of questioning techniques 2.16 Guidelines for law enforcement contact with mentally retarded persons - Continued 4. a. b. c. d. e. Officer should remain ______________, __________, _____-______________, _________ and fair __________ and ________ manner 2.16 What are the significant differences between Mental Illness and Mental Retardation? Mental Illness vs. Mental Retardation: ___% of the American population is considered retarded 2.16 What are the significant differences between Mental Illness and Mental Retardation? (Cont’d) Sub-average score of 69 or less on Wechler Intelligence Scale or Stanford Binet IQ test), while 22.1% is diagnosed with a mental illness. 2.16 Differences between mental illness and mental retardation include: 1. Mental illness is unrelated to intelligence, while mental retardation is below-average intellectual functioning. 2.16 Differences between mental illness and mental retardation include – Cont’d: 2. Mental illness develops at any point in one’s life, while mental retardation occurs before the age of ____. 2.16 Differences between mental illness and mental retardation include – Cont’d: 3. There is no cure for mental illness, but medications can help. Mental retardation involves permanent intellectual impairment. 4. No ____________ can help. 2.16 Differences between mental illness and mental retardation include – Cont’d: 5. Behavior is less predictable with a mentally ill individual, while a mentally retarded individual’s behavior is consistent to a very specific functional level. 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact The Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act of 1990 defines a developmental ______________ as a severe, chronic disability of a person five years of age or older. 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d Such a ______________: 1. Is attributable to a mental or physical impairment, or a ________________ of the two 2. Is manifested before a person attains the age of twenty-two 3. Is likely to continue indefinitely 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d Such a disability: 4. Is manifested in substantial limitation of three or more specified life e. mobility a. activities f. self-direction b. self-care, g. Independent c. language, living, d. learning, h. economic self-sufficiency 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d Such a disability: 5. Reflects the person’s need for lifelong or extended care, treatment, or other services which are planned and coordinated according to that person’s needs 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d Such a disability: 5. Infants and young children (newborn to age 5) with developmental disabilities have substantially delayed development or specific congenital or acquired conditions, and are likely to suffer developmental disabilities if services are not provided to them. 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d Put more simply, a DD is a condition that an individual may have had since birth or childhood which has prevented them from full social or vocational independence in adulthood, and which continues on into old age. 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d The four kinds of life skills that are normally mastered during this time and could be affected are 1. __________ motor, 2. _________ motor, 3. ______________, and 4. ____________ skills. 2.17 Developmental Disorders Ref: Officer Contact - Cont’d The number of persons with developmental disabilities who commit crimes cannot be reported accurately due to lack of identification prior to conviction, sentencing, or incarceration. 2.18 ID Behaviors Developmental Disorders & Officer Contact An officer should consider the following points when approaching an individual with a developmental disorder. The individual: 1. May be ________________by police presence 2.18 ID Behaviors Developmental Disorders & Officer Contact – Cont’d An officer should consider the following points when approaching an individual with a developmental disorder. The individual: 2. May attempt to run out of ______of uniform 3. May ________ to a crime to please the officer or end the line of questioning 2.18 ID Behaviors Developmental Disorders & Officer Contact – Cont’d An officer should consider the following points when approaching an individual with a developmental disorder. The individual: 4. Is usually a ___________ thinker - speak slowly and clearly utilizing concrete words and concepts 5. Needs ________ cues to assist in understanding 2.18 ID Behaviors Developmental Disorders & Officer Contact – Cont’d An officer should consider the following points when approaching an individual with a developmental disorder. The individual: 7. May need a more in depth explanation of their ___________ and an advocate to verify understanding 2.18 ID Behaviors Developmental Disorders & Officer Contact – Cont’d An officer should consider the following points when approaching an individual with a developmental disorder. The individual: 8. May be sensitive to touch, creating a “________ or __________” reaction - always explain any tactile intentions prior to action Tartive Dyskensia A ____________ ________caused by long-term use of neuroleptic drugs, which are prescribed for psychiatric disorders Not considered a mental illness within itself…drugs utilized to treat can lead to TD 180 Tartive Dyskensia – Cont’d The neurotransmitters are _____________ which over time may cause uncontrolled involuntary movement of the body and face Treatment is highly individualized and should be monitored by the physician for a plan of action Tartive Dyskensia – Cont’d __________, quick movement is common. Note: This movement may distract or trigger defensive actions from the officer when not needed, which could _________ a situation unknowingly. Tartive Dyskensia – Cont’d Autism Video (View ‘Autism’ video from “Train the Trainer” (updated version) course materials)) 184 Questions? DEFINE & PROCESS Define 2.1 Mental Illness Process: 186 DEFINE & PROCESS Define & List 2.2 Four prominent categories of mental illness Process: 187 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.3 Personality Disorders as they relate to officer contact Process: 188 DEFINE & PROCESS List 2.4 The three most common personality disorders encountered by law enforcement officers Process: 189 DEFINE & PROCESS Identify 2.5 prevalent behaviors associated with personality disorders Process: 190 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.6 Mood Disorders as they relate to officer contact Process: 191 DEFINE & PROCESS List & Explain 2.7 the two most common mood disorders encountered by law enforcement officers Process: 192 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.8 Psychosis and how it relates to officer contact Process: 193 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.9 A psychotic episode from a consumer’s perspective. Process: 194 DEFINE & PROCESS Define Explain 2.10 The behavioral/emotional cues a person displays when experiencing a psychotic episode Process: 195 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.11 How substance abuse and cognitive disorders relate to psychosis. Process: 196 DEFINE & PROCESS Define & Explain 2.12 Schizophrenia as it relates to psychosis Process: 197 DEFINE & PROCESS Define & Explain 2.13 Alzheimer’s disease and its involvement with psychosis Process: 198 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.14 The communicative approach an officer should take when confronting a person in a psychotic episode. Process: 199 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain Appraisal 2.15 Personal impressions of mental illness after viewing the consumer presentation Process: 200 DEFINE & PROCESS List & Explain 2.16 The two most common developmental disorders that relate to officer contact Process: 201 DEFINE & PROCESS Explain 2.17 Developmental disorders as they relate to officer contact Process: 202 SOURCES All Course Sources and/or Resources are listed in your Participant Handout Crisis Intervention TRAINING (CIT) Course # 3841 Bexar County Constable Office PCT#4 “Knowledge is “POWER” Stay informed, stay SAFE, stay Vigilant & stay Alive”