* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AKA Psychological Disorders
Functionalism (philosophy of mind) wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dimensional models of personality disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
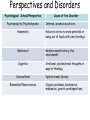
Abnormal Psychology A.K.A. Psychological Disorders A behavior which is judged to be deviant (atypical), distressful (disturbing), and dysfunctional. Could also be maladaptive and unjustifiable. Defining Psychological Well-Being • • • • • • Self-acceptance Positive relations Autonomy Environmental Mastery Purpose in life Personal Growth Early Theories • Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out. • Trephining was often used. Trephening Early Theories • Another way to deal with the demons was to make the body extremely uncomfortable. History of Mental Disorders • In the 1800’s, disturbed people were no longer thought of as madmen, but as mentally ill. They were first put in hospitals. Did this mean better treatment? Early Mental Hospitals • They were nothing more than barbaric prisons. •The patients were chained and locked away. •Some hospitals even charged admission for the public to see the “crazies”, just like a zoo. Philippe Pinel • French doctor who was the first to take the chains off (and declare that these people are sick and “a cure must be found”). Somatogenic or Medical Model • Late 1800’s - it was believed that mental illness had a physical / organic cause - Somatogenic. General Paresis from Syphilis is an example. But Somatogenic could not explain disorders such as hysteria (now called conversion disorder). Many disorders are psychogenic: the origin is psychological, not physical. Current Perspectives • Biopsychosocial Approach: assumes biological, psychological and sociocultural factors interact to produce specific psychological disorders. Most common view today. Some disorders occur worldwide while others are culture-bound. Perspectives and Disorders Psychological School/Perspective Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic Cause of the Disorder Internal, unconscious drives Humanistic Failure to strive to one’s potential or being out of touch with one’s feelings. Behavioral Reinforcement history, the environment. Cognitive Irrational, dysfunctional thoughts or ways of thinking. Sociocultural Biomedical/Neuroscience Dysfunctional Society Organic problems, biochemical imbalances, genetic predispositions. DSM-V • Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: the big book of disorders. • DSM will classify disorders and describe the symptoms. • DSM will NOT explain the causes or possible cures. Two Major Classifications in the DSM Neurotic Disorders • Distressing but one can still function in society and act rationally. Psychotic Disorders • Person loses contact with reality, experiences distorted perceptions. John Wayne Gacy The Rosenhan Study • Rosenhan’s associates were faking symptoms of hearing voices. • They were ALL admitted for schizophrenia. • None were exposed as imposters. • They all left diagnosed with schizophrenia in remission. • What are some of the questions raised by this study? • 1.) It showed the biasing power of diagnostic labels. • 2.) And those labels can serve as selffulfilling prophecies (when the belief you have about a person makes you act in a way that induces the person to appear to confirm your belief). Labeling Psychological Disorders Do you think the mentally ill suffer discrimination today? Why is Mental Illness though of differently in society? Myths and Facts of Mental illness