* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System PPT - Effingham County Schools
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
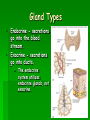
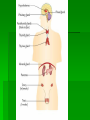
Ch. 13 Endocrine System Endocrine System System consisting of cells, tissues, and organs “glands” that release substances called hormones into the internal environment of the body. Gland Types Endocrine - secretions go into the blood stream. Exocrine - secretions go into ducts. The endocrine system utilizes endocrine glands, not exocrine. Homeostatic Functions Regulate metabolic processes Control rates of certain chemical reactions Transport across cell membrane Regulate water and electrolyte balance Roles in reproduction, development, and growth Hormone Action Biochemical released by one cell to affect second cell(s) Travels into extracellular fluid or by blood stream Works only on specific target cell. Prostaglandin Action Act locally Affect the organ from which they are produced Potent and rapidly activated, not stored Control of Hormonal Secretions Negative feedback system Gland secretes a substance Substance reaches a certain concentration Endocrine gland becomes inhibited (turns off), which is a negative effect. Due to inhibition, concentration of substance decreases. Endocrine gland becomes uninhibited (turns on) Control Sources Hypothalamus controls pituitary Pituitary stimulates other endocrine glands receives constant information from cerebrospinal fluid. info from neural connections in brain Control Sources Continued Brain controls some glands directly (adrenal medulla - sympathetic response) Responds to internal environment (insulin production - blood glucose levels) Diseases of the Endocrine System Dwarfism insufficient secretion of growth hormone during childhood. Gigantism oversecretion of growth hormone during childhood. Diseases of the Endocrine System Cretinism - underactive thyroid gland during infancy and childhood. Graves diseases (hyperthyroidism) overstimulation of the thyroid gland. Goiter - an iodine deficiency causes thyroid to enlarge and function improperly Diseases of the Endocrine System Addison’s disease - adrenal cortex does not secrete hormones sufficiently causing a variety of electrolyte imbalances, low blood pressure, and increased skin pigmentation to name a few. Cushing’s disease - caused by hypersecretion of cortisol (primarily). Causes high blood pressure, fluid retention and thin skin to name a few.