* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Powerpoint (GOOD COPY)
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
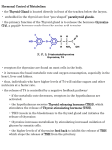
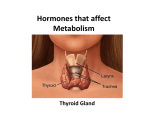
Basic Anatomy The thyroid gland is located in the lower part of the neck and is partially wrapped around the trachea (windpipe). It has two lobes that are joined together in the middle, giving it a shape similar to a butterfly. Posterior (Back) View of Thyroid Gland The four parathyroid glands are located in the back of the thyroid gland. They are roughly the size of a pea and yellow in color. The Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland regulates the body’s metabolism by adjusting the rate at which glucose is oxidized (through cellular respiration). The main function of the thyroid gland is to produce hormones. These hormones regulate how much energy the body expends (called metabolism). The Thyroid Gland and Homeostasis The thyroid gland secretes two hormones that help control metabolism. They are called Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3). Iodine is an essential component of both T3 and T4. Thyroxine (T4) is secreted by the thyroid gland. It is the inactive form of Triiodothyronine (T3). It is easily converted by body cells into T3 by removing one of its four iodine molecules. Triiodothyronine (T3) raises metabolism by stimulating increased sugar utilization by cells. T3 is 8 times more effective than T4 at increasing metabolism. Iodine T4 - Thyroxine T3 -Triiodothyroxinine The Parathyroid Glands and Homeostasis The parathyroid glands help regulate calcium levels in the blood and lower phosphate levels. Calcium is used by the body for development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth. It is also helps the heart, nerves, muscles and other body systems to work properly. When the level of calcium in the blood is too low, the parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH). A rise in PTH causes calcium levels in the blood to increase and phosphate levels to decrease. This hormone increases the level of calcium by influencing the kidneys, intestines, and bones. PTH causes the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium, so less calcium is excreted in the urine. The intestines absorb and retain more calcium from undigested foods. Calcium is released from bones where it is stored. (98% of calcium is stored in the skeletal system.) Kidneys reabsorb Ca2+ Intestines absorb Ca2+ Bones release Ca2+ When bone cells break down, calcium is separated from phosphate ions. The calcium is reabsorbed into the blood and the phosphate ions are excreted in the urine. Calcium levels in the blood return to normal, so PTH secretion stops. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/tutorials/thyroidsurgery/htm/_no_50_no_0.htm Parathyroid Hormone Feedback Loop 1. Low Ca2+ levels in the blood cause the parathyroid glands to release parathyroid hormone (PTH). 2. The kidneys reabsorb more calcium, the intestines absorb and retain calcium from food, and calcium is released from bones. 3. These 3 factors cause Ca2+ levels in the blood to rise. 4. Calcium levels are back to normal so PTH secretion stops. Important Hormones Hormone Secreted by… Target Area(s) Effect Thyroxine (T4) & Triiodothronine (T3) Thyroid All body cells Controls metabolism Thyroid Bone cells Lowers the level of calcium in the blood Parathyroid Kidneys Intestines Bones Raises calcium levels in the blood Calcitonin Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) We already know about feedback loops in Homeostasis… Monitors/ Receptors Effectors/ Regulators Control System Negative Feedback Loop for the Thyroid Gland Hypothalamus (senses decreased metabolism) Thyroid – releasing hormone (TRH) Pituitary Metabolism is back to normal, hormone secretion slows down T3 and T4 Thyroid Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) T3 and T4 Feedback Loop Legend TRH = Thyroid Releasing Hormone TSH = Thyroid Stimulating Hormone T3 = Triiodothyronine T4 = Thyroxine Goiters A goiter is a pronounced swelling of the thyroid gland in the neck caused by insufficient iodine intake in the diet. The main source of iodine in your diet is iodized salt. Thyroid Disorders Hypothyroidism (“Hypo” means less) Hyperthyroidism (“Hyper” means more) Underactive Thyroid Gland Overactive Thyroid Gland Occurs when the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones. Occurs when the thyroid produces excess hormones. Hypothyroidism decreases metabolism. Hyperthyroidism increases metabolism. Hypothyroidism • fatigue • feeling cold • weight gain • depression • reduced concentration • swollen face • dry skin • dry & brittle hair and nails • constipation • goiter Hyperthyroidism • • • • • • • • • • • fatigue feeling hot weight loss increased appetite nervousness and anxiety increased heart rate increased blood pressure shaking hands frequent bowel movements bulging eyes hair loss Treatment Hypothyroidism: most patients take hormone replacement pills (i.e. eltroxin) to bring their thyroid hormone levels back up to normal. Hyperthyroidism: patients are treated with drugs that bind to iodine to partially block the production of hormones, bringing hormone levels back down to normal. However, if medication isn’t working radioactive iodine can be used to destroy the hyperactive thyroid tissue. This can sometimes affect the entire thyroid gland leading to hypothyroidism. Sometimes surgery is required to remove tumors or cysts that could cause either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. http://video.about.com/thyroid/Thyroid-Disease.htm QUIZ 1. True or False? A parathyroid gland is larger than a thyroid gland. FALSE 2. How many parathyroid glands does a typical person have? A) B) C) D) One Two Four Six Answer: C 3. True or False? The thyroid gland plays an important part in controlling metabolism. TRUE 4. What is hypothyroidism? A) The thyroid gland is incapable of making hormones. B) The thyroid gland produces too many hormones. C) The thyroid gland produces not enough hormones. D) The parathyroid glands are cancerous. Answer: C 5. True or False? Hyperthyroidism causes the body cells to burn more energy than normal, decreasing metabolism. FALSE 6. What causes a goiter? A) B) C) D) Hypoparathyroidism Hyperparathyroidism An insufficient amount of iodine in your diet A genetic mutation Answer: C 7. You are a doctor. A patient has inexplicably lost a lot of weight, despite having an increased appetite. They have an increased heart rate and high blood pressure as well. They also feel very tired, and have bulging eyes. What would you diagnose them with? Hyperthyroidism