* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pituitary Gland
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
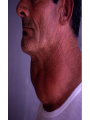
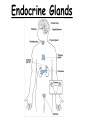
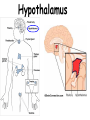
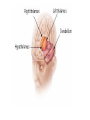
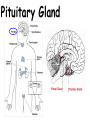
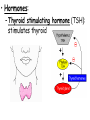
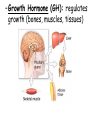
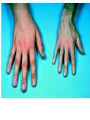
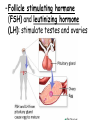
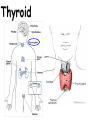
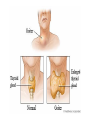
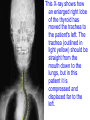
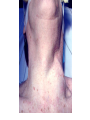
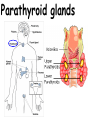
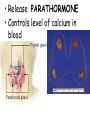
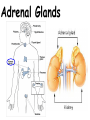
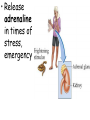
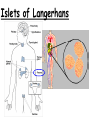
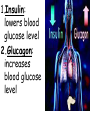
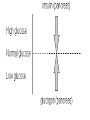
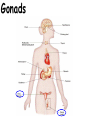
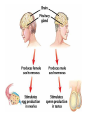
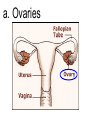
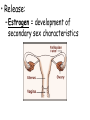
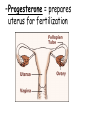
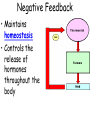
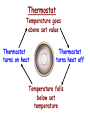
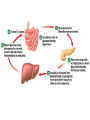
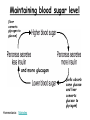
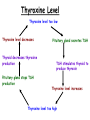
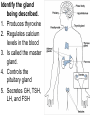
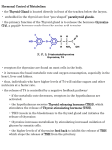
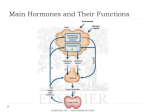
TOPIC: Regulation Aim: Explain the function the different endocrine glands. Do Now: Ditto – Human Nervous System Mapping Review HW: Ditto – Did you Know? X A B X A B C 1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why. 2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why. Endocrine Glands Hypothalamus • Part of the brain • Produces hormones that control pituitary gland Pituitary Gland • Controls activities of other glands (formerly known as the MASTER GLAND) • Hormones: – Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH): stimulates thyroid – Growth Hormone (GH): regulates growth (bones, muscles, tissues) 14-year old Khagendra Thapa Magar shown in the picture with another boy is only 50 centimetres (20 inches) tall and has been submitted to the Guinness world record as the world's smallest person. The previous world record holder was a Jordanian boy at 25.5 inches tall. Weighing only 4.5 kilograms, he is shown in exhibitions to collect fund for his education. – Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and leutinizing hormone (LH): stimulate testes and ovaries Thyroid • Releases THYROXINE • Regulates rate of metabolism This X-ray shows how an enlarged right lobe of the thyroid has moved the trachea to the patient's left. The trachea (outlined in light yellow) should be straight from the mouth down to the lungs, but in this patient it is compressed and displaced far to the left. Parathyroid glands • Release PARATHORMONE • Controls level of calcium in blood Adrenal Glands • Release adrenaline in times of stress, emergency • Increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, sweating Islets of Langerhans • Cells on the PANCREAS • Release: 1.Insulin: lowers blood glucose level 2.Glucagon: increases blood glucose level Gonads a. Ovaries • Release: – Estrogen = development of secondary sex characteristics –Progesterone = prepares uterus for fertilization b. Testes • Release testosterone – sperm production – development of male secondary sex characteristics Negative Feedback • Maintains homeostasis • Controls the release of hormones throughout the body Thermostat Temperature goes above set value Thermostat turns on heat Thermostat turns heat off Temperature falls below set temperature • A hormone can cause the release or stop the release of another hormone • Examples: 1. Maintaining blood sugar levels with insulin and glucagon Maintaining blood sugar level (liver converts glycogen to glucose) and more glucagon (cells absorb some glucose and liver converts glucose to glycogen) Homeostasis: Maindex 2. Amount of thyroxine in the blood Thyroxine Level Thyroxine level too low Thyroxine level decreases Thyroid decreases thyroxine production Pituitary gland stops TSH production Pituitary gland secretes TSH TSH stimulates thyroid to produce thyroxin Thyroxine level increases Thyroxine level too high 3. Maintaining body temperature Identify the gland being described. 1. Produces thyroxine 2. Regulates calcium levels in the blood 3. Is called the master gland. 4. Controls the pituitary gland 5. Secretes GH, TSH, LH, and FSH