* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aim: How does the Endocrine System work in our body?
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
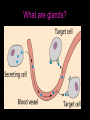
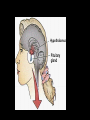
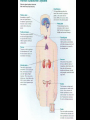
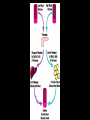
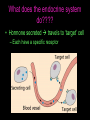
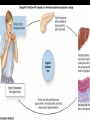
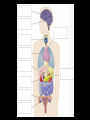
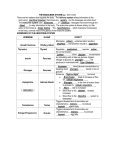
Aim: How does the Endocrine System work in our body? The Endocrine System FUNCTIONS: - Maintains stable body function (homeostasis) - Responds to changes - Collection of glands that produce hormones - Control processes that happen slowly (nervous system controls those that happen quickly) What are glands? - Tissues found throughout your body - Produce chemical messages HORMONES - speed up or slow down cellular activities - Glands release their hormone directly into the blood transports to target tissue FUNCTIONS: - Regulate internal environment - Adapt to stressful situations - Growth & development Types of Glands: • Pituitary – Located in the brain – Growth and reproduction – ‘master’ gland – Hypothalamus • controls the pituitary gland • Specialized cells located in brain that link the endocrine system with the nervous system • Thyroid – Located below the larynx – Regulates metabolism and bone growth Important Hormones Androgens - Testosterone – male reproductive hormone Estrogen – female reproductive hormone Insulin/ Glucagon - Work together to maintain stable levels of blood sugar Insulin- released when levels of blood sugar are high Glucagon- causes the liver to release stored glucose from cells into the body when glucose is low What does the endocrine system do???? • Hormone secreted travels to ‘target’ cell – Each have a specific receptor • Negative Feedback System – Controls the amount of hormones in your body- adjusts hormone levels automatically – Example: STIMULUS- eating a sandwich 1. Intestine takes in glucose • Glucose in bloodstream increases • Glucose detected by insulin from pancreas • Pancreas responds by producing more insulin • Insulin released liver takes up glucose • Glucose level decreases (body consumes glucose) • Homeostasis restored