* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
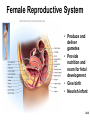
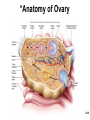
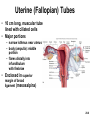
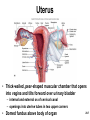
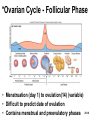
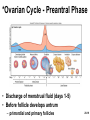
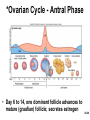
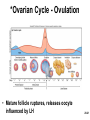
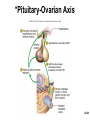
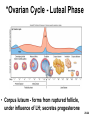
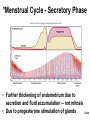
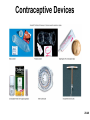
Chapter 28 Lecture Outline See PowerPoint Image Slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. 28-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Female Reproductive System • • • • • • Reproductive Anatomy *Puberty and Menopause *Oogenesis and the Sexual Cycle Female Sexual Response Pregnancy and Childbirth Lactation 28-2 Female Reproductive System • Produce and deliver gametes • Provide nutrition and room for fetal development • Give birth • Nourish infant 28-3 *Ovary • Produces eggs and hormones – almond-shaped, 3 cm x 1.5 cm x 1 cm – tunica albuginea capsule like on testes – cortex produces gametes; medulla holds vessels • Each egg develops in its own fluid-filled follicle and is released by ovulation • Ligaments – attached to uterus by ovarian ligament – attached to pelvic wall by suspensory ligament • contains ovarian artery, vein and nerves – anchored to broad ligament by mesovarium 28-4 *Anatomy of Ovary 28-5 Uterine (Fallopian) Tubes • 10 cm long, muscular tube lined with ciliated cells • Major portions – narrow isthmus near uterus – body (ampulla): middle portion – flares distally into infundibulum with fimbriae • Enclosed in superior margin of broad ligament (mesosalpinx) 28-6 Uterus • Thick-walled, pear-shaped muscular chamber that opens into vagina and tilts forward over urinary bladder – internal and external os of cervical canal – openings into uterine tubes in two upper corners • Domed fundus above body of organ 28-7 Histology of Uterine Wall • Perimetrium - external serosa layer • Myometrium - middle muscular layer – 1.25 cm thick in nonpregnant uterus – smooth muscle • produces labor contractions, expels fetus • Endometrium – simple columnar epithelium with thick layer compound tubular glands • stratum functionalis – superficial, shed each period • stratum basalis - deep layer, regenerates a new 28-8 stratum functionalis with each menstrual cycle Normal/Abnormal PAP Smears 28-9 Breast Cancer • 1 out of 8 American women • Tumors begin with cells from mammary ducts – may metastasize by lymphatics • Symptoms may include palpable lump, skin puckering, skin texture and drainage from nipple • Most breast cancer is nonhereditary – some stimulated by estrogen • Risk factors include – aging, ionizing radiation, carcinogenic chemicals, alcohol, smoking and fat intake – 70% lack risk factors 28-10 *Puberty • Begins at age 9-10 (US) • Triggered by rising levels of GnRH – stimulates anterior lobe of pituitary to produce • follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) • luteinizing hormone (LH) • Follicles develop and begin to secrete estrogen and progesterone 28-11 *Puberty • Thelarche - development of breasts • Pubarche - growth of pubic and axillary hair; apocrine and sebaceous glands • Menarche - first menstrual period – requires at least 17% body fat in teenager, 22% in adult • leptin stimulates gonadotropin secretion • improved nutrition ( body fat) has lowered avg. age of onset to 12 • Female hormones secreted cyclically and in sequence 28-12 Climacteric • Midlife change in hormone secretion – due to age related depletion of follicles – occurs with menopause (cessation of menstruation); average age of 52 • Results – atrophy of uterus, vagina and breasts – skin becomes thinner, bone mass declines, and risks of cardiovascular disease increase – hot flashes (sudden dilation of cutaneous arteries) occur several times a day • HRT = hormone replacement therapy 28-13 *Oogensis and Sexual Cycle • Reproductive cycle - events occurring between fertilization and birth • Sexual cycle - events recurring every month when pregnancy does not occur – ovarian cycle = events in ovaries – menstrual cycle = parallel changes in uterus 28-14 *Oogenesis • Monthly event produces haploid egg by meiosis • Embryonic development of ovary – – – – – female germ cells arise from yolk sac differentiate into oogonia, multiply transform into primary oocytes - early meiosis I most degenerate (atresia) by childhood by puberty 400,000 oocytes remain • FSH stimulates completion of meiosis I, produces secondary oocyte and 1st polar body – proceeds to meiosis II and ceases until fertilization – after fertilization , releases 2nd polar body 28-15 *Oogenesis and Follicle Development 28-16 *Sexual Cycle • Averages 28 days, ranges from 20 to 45 • Hormone cycle: hierarchy of control – hypothalamus pituitary ovaries uterus • Follicular phase (2 weeks) – menstruation occurs during first 3 to 5 days of cycle – uterus replaces lost endometrium and follicles grow • Luteal phase (2 weeks) – corpus luteum stimulates endometrial thickening – endometrium lost without pregnancy 28-17 *Ovarian Cycle - Follicular Phase • Menstruation (day 1) to ovulation(14) (variable) • Difficult to predict date of ovulation • Contains menstrual and preovulatory phases 28-18 *Ovarian Cycle - Preantral Phase • Discharge of menstrual fluid (days 1-5) • Before follicle develops antrum – primordial and primary follicles 28-19 *Ovarian Cycle - Antral Phase • Day 6 to 14, one dominant follicle advances to mature (graafian) follicle; secretes estrogen 28-20 *Ovarian Cycle - Ovulation • Mature follicle ruptures, releases oocyte influenced by LH 28-21 Histology of Ovarian Follicles 28-22 *Pituitary-Ovarian Axis 28-23 *Ovarian Cycle - Luteal Phase • Corpus luteum - forms from ruptured follicle, under influence of LH; secretes progesterone 28-24 *Menstrual Cycle - Proliferative Phase • Day 6-14 rebuild endometrial tissue – mitosis occurs in stratum basalis – result of estrogen from developing follicles 28-25 *Menstrual Cycle - Secretory Phase • Further thickening of endometrium due to secretion and fluid accumulation -- not mitosis • Due to progesterone stimulation of glands 28-26 *Menstrual Cycle Premenstrual Phase • Involution of corpus luteum, progesterone falls – spiral arteries constrict causes endometrial ischemia – stratum functionalis sloughs 28-27 *Menstrual Cycle - Menstrual Phase • Blood, serous fluid and endometrial tissue are discharged 28-28 Pregnancy and Childbirth • Gestation (pregnancy) – lasts an average of 266 days from conception to childbirth – gestational calendar measured from first day of the woman’s last menstrual period (LMP) • Birth predicted 280 days from LMP – 3 three month intervals called trimesters 28-29 Prenatal Development • Age based terminology – blastocyst is less than 2 weeks old – embryo is from 2 to 8 weeks old – fetus is 9 weeks to birth – neonate - newborn to 6 weeks 28-30 *Hormones of Pregnancy • HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) – secreted by trophoblast within 9 days of conception – prevents involution of corpus luteum • Estrogens – increases to 30 times normal before birth – corpus luteum is source for first 12 weeks until placenta takes over – causes uterine, mammary duct and breast enlargement 28-31 *Hormones of Pregnancy • Progesterone – secreted by placenta and corpus luteum – suppresses secretion of FSH and LH preventing follicular development – prevents menstruation, thickens endometrium – stimulates development of acini in breast • HCS (human chorionic somatomammotropin) – secreted from placenta in direct proportion to its size – mother’s glucose usage and release of fatty acids 28-32 *Hormones of Pregnancy • Aldosterone secretion rises – fluid retention mother’s blood volume • Endocrine organs – thyroid gland increases 50% in size • BMR of mother – parathyroid glands enlarge • stimulate osteoclasts to release additional calcium from mother’s bones 28-33 *Hormone Levels and Pregnancy 28-34 *Labor Contractions • Self-amplifying cycle of stretch and contraction – positive feedback cycles increase contractions • cervical stretching oxytocin secretion uterine contraction repeat • reflex arc from uterus spinal cord abdominal skeletal muscles 28-35 *Mammary Gland Development • Lactation – synthesis and ejection of milk from mammary glands in breast • Ducts grow and branch – due to high estrogen levels in pregnancy • Followed by budding and development of acini at the ends of the ducts – due to progesterone 28-36 *Colostrum and Milk Synthesis • Colostrum forms in late pregnancy – similar to breast milk; contains 1/3 less fat, thinner – first 1 to 3 days after birth – contains IgA protection from gastroenteritis • Synthesis is promoted by prolactin (from pituitary) – synthesis of hormone begins 5 weeks into pregnancy, by full term it is 20x normal level – steroid hormones from placenta oppose it until birth 28-37 *Colostrum and Milk Synthesis • At birth, prolactin secretion drops, but 20 times after nursing – without nursing, milk production stops in 1 week • 5-10% of women become pregnant while nursing – inhibition of GnRH and reduced ovarian cycling 28-38 *Milk Ejection • Controlled by a neuroendocrine reflex – infant’s suckling stimulates sensory receptors in nipple, signaling hypothalamus and posterior pituitary to release oxytocin – oxytocin stimulates myoepithelial cells • Myoepithelial cells surround secretory cells in acinus – contract to squeeze milk into duct • milk flow within 30-60 seconds after suckling begins 28-39 Contraceptive Devices 28-40