* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S8P2 Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
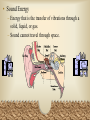
S8P2 Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy Enduring Understandings • Energy appears in different forms such as mechanical energy, gravitational energy, heat energy, and electric and magnetic energy. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only changed from one form into another. • Transformations of energy usually release some energy typically in the form of heat. • Temperature changes as heat is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one. • Heat transfer occurs by conduction, convection, or radiation. • Series and parallel circuits can be used to control the amount of electrical energy produced. • Every object exerts gravitational force on every other object. The force depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy • The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only be changed form one form into another. – Example: Your car changes chemical energy (gas) into mechanical energy (energy of motion), heat energy (thermal), and sound energy) . No energy is created or destroyed. – Some may be converted into unwanted forms (heat). Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy • Potential energy is the stored energy that an object has due to its shape, position (height) or chemical composition. – Examples: • Gravatitional Potential Energy • Elastic Potential Energy • Chemical Potenital Energy • Kinetic energy is energy of motion – Depends on mass and speed. An increase in speed causes a greater increase in kinetic energy than increase in mass. – Potential energy is converted into kinetic energy when an object is acted on by a force and is set in motion. As the object slows the kinetic energy is converted back to potential energy. No energy is created or destroyed. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their characteristics. • Thermal Energy (Heat Energy) – The total amount of energy from the movement of particles in matter. • Light Energy (Electromagnetic) – Energy that comes from electromagnetic energy such as visible light. – Can travel through empty space – Includes visible light, ultraviolet light, x rays, and microwaves. • Electrical Energy – The flow of electrons through a circuit. • Mechanical Motion – Involves the position and motion of objects. – Mechanical energy is the combination of potential energy and kinetic energy. ME=PE + KE • Sound Energy – Energy that is the transfer of vibrations through a solid, liquid, or gas. – Sound cannot travel through space. Describe how heat can be transferred through matter by the collisions of atoms (conduction) or through space (radiation) or through a liquid or gas (convection) • Conduction – transfer through physical contact. • Convection – transfers energy through a liquid or gas. • Radiation – transfers energy through EM waves.