* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy, Heat and Temperature What is energy?
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
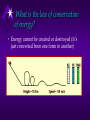
Energy, Heat and Temperature What is energy? • The ability to do work (if the work is done, energy is used) • Energy is transferred from one object to another when work is done. What unit is used to measure energy? • Joule What is potential energy? • (energy of position) • The stored energy resulting from the relative positions of objects in a system What is gravitational potential energy? • Potential energy depends on an objects height above the ground • Depends on mass and height (mass and height are directly proportional to gpe) • GPE = mgh • Gravitational potential energy = (mass)(gravitational acceleration)(height) What is kinetic energy? • The energy of a moving object due to its motion • Depends on mass and velocity (mass and velocity are directly proportional to ke) • KE = ½mv2 • Kinetic energy = ½(mass)(velocity)2 Which of the two factors, mass or velocity, will have a greater effect on kinetic energy? • Velocity, because it is squared KE = ½mv2 What is the law of conservation of energy? • Energy cannot be created or destroyed (it’s just converted from one form to another) What is an example of a kineticpotential energy conversion? • As an object falls, its potential energy decreases and its kinetic energy increases but the total energy (mechanical energy) remains the same What are some other forms of energy? a) Heat energy – caused by the internal motion of atoms Ex. Friction generates heat energy *causes changes in temperature and phase of matter b) Chemical energy – caused by the breaking/forming of bonds between atoms Ex: burning releases chemical energy as heat energy, when you digest your food chemical energy is released c) electromagnetic energy – energy associated with moving charges *there are many kinds of electromagnetic energy: electricity, light, x-rays, radiowaves, etc. • d) nuclear energy – caused by changes in the nucleus of an atom (fission or fusion) Fission Reactor TEMPERATURE AND HEAT What is heat? • A form of energy caused by the internal motion of molecules of matter How can heat be transferred from one object to another? • The heat always moves from the warmer object to the cooler object • • • Conduction Convection Radiation Conduction • Conduction – heat is transferred through a substance, or from one substance to another by the direct contact of molecules • Can take place in solids, liquids, and gases (best in solids) • Remember: insulators and conductors Convection • Convection – heat energy is transferred through liquids and gases by means of up and down movements called convection currents Radiation • Radiation – transfer of heat energy through empty space (does not require a medium in order to travel) – it is transferred by electromagnetic waves • Ex: sun’s heat (infrared radiation), heat given off by an electric heater or fire What is temperature? • A measure of the average kinetic energy of molecules • If heat is added to an object, the average kinetic energy of its molecules increases and therefore its temperature increases How are heat and temperature different? • Heat depends on the mass of the substance present • Ex: 10g of water at 90°C has more heat energy than 5g of water at 90°C • Heat is a measure of the actual amount of energy present where temperature is a measure of the average amount of energy present How is temperature measured? • With a thermometer; it consists of a thin tube filled with mercury or colored alcohol and as the liquid is heated it expands and rises and when it is cooled it contracts and falls What unit is used to measure temperature? • Celsius (metric) • Kelvin (metric) • Fahrenheit (standard) What unit is used to measure heat? • Calorie or Joule The food calorie is used to measure how much energy you get from various foods. One Calorie is equivalent to about 4,180 J. What is specific heat? • Refers to the ability of a substance to absorb heat energy, some absorb heat energy easily (conductors) and have a low specific heat while some do not absorb heat easily (insulators) and have a high specific heat • The specific heat of water 1cal/g·°C (water has a high specific heat – it requires a lot of heat to change its temperature)