* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 幻灯片 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
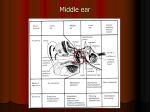
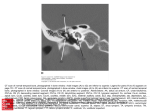
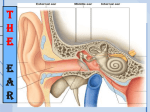
Clinical anatomy & physiology of the ear YANG Jun, MD, Ph.D. 09/18/09 Otology & neurotology Surgical management on hearing loss Conductive hearing loss: tympanoplasty, ossicular chain reconstruction, stapes surgery Sensorineural hearing loss : implantable hearing-aids, cochlear implatation Tumor in the lateral skull base,such as acoustic neuroma Facial nerve: facial paralysis, facial spasm Surgical management on vertigo Trigeminal neuralgia Repaire of CSF leakage Temporal bone Location : lateral skull Neighbour : parietal bone, sphenoid bone, occipital bone Composition: squamous part, tympanic part, pars mastoidea, petrosal part Anatomy of the external ear auricle anterior notch of ear-an incision can be made less subcutaneous tissue difficult absorption of hematoma prone to cold injury Anatomy of the auricle Anatomy of the external ear external auditory canal 2.5-3.5cm outer1/3:cartilage inner2/3:bone Stenosis: juncture of bone and cartilage, bony part (0.5cm from the tympanic anulus) Anatomy of the middle ear Tympanic cavity Eustachian tube Tympanic sinus Mastoid cavity Tympanic cavity Attic, mesotympanum, hypotympanum Six walls: interior, exterior, anterior, posterior, superior, inferior Tympanic cavity 面神经管凸 镫骨底板 外半规管凸 匙突 鼓窦入口 大脑颞叶 锥隆起 鼓索神经孔 鼓岬 面神经 砧骨 锤骨 鼓膜张肌 鼓膜张肌 半管 附着处 咽鼓管鼓口 鼓索神经 鼓膜 颈内动脉 蜗窗小窝 颈静脉球 Exterior wall-tympanic membrane Tympanic membrane Semi-transparent film, 1cm2, 1mm Upper is pars flaccid, lower is pars tensa Three layer construction: epithelial lamina, fibrous lamina, mucous layer tympanic membrane Interior wall Namely exterior wall of the inner ear Center-promontorium tympani Post-superior : vestibular window-vestibule Post-inferior : cochlear window-scala tympani horizontal part of facial nerve canal prominence of lateral semicircular canal cochleariform process Anterior wall Namely carotid wall Inferior part is separated with the carotid artery Two openings at the superior part: semicanal for tensor tympani (upper), semicanal for auditory tube (lower) Posterior wall Minipore at the posterior wall- aditus ad antrum tympanicum incudal fossa- juncture of horizontal part and perpendicular part pyramidal eminence-about at height of vestibular window facial recess-posterior tympanotomy Superior wall Namely tegmen tympani Be separated with the temporal lobe of the cerebrum in the middle fossa The petrosquamous fissure in infant is not closed-one of the route by which infection from the middle ear could get into Inferior wall Namely jugular wall Be separated with the jugular bulb blue drum Content in the tympanic cavity ossicles(smallest bone in the human body): malleus, incus, stapes- ossicular chain ligamenta ossiculorum auditus: ligament of the malleus, incus and stapes muscle in the tympanic cavity: tensor tympani muscle, stapedial muscle chorda tympani nerve Ossicular chain Eustachian tube Passageway between tympanic cavity and nasopharynx, outer 1/3bony part, inner 2/3- cartilaginous part. Isthmic portion-junction of bony part and cartilaginous part. The opening at the nasopharynx is open when muscle contraction in order to adjust air pressure in the tympanic cavity. Infection is prone to enter the tympanic cavity because of Horizontal, short and wide Eustachian tube in child. Tympanic sinus and mastoid cavity Tympanic sinus: pneumatic space and passage between the attic and mastoid cavity Mastoid cavity: cells in the temporal bone-pneumatic type, diploetic type, constrictive type and mixed type CT scan of temporal bone Anatomy of the inner ear Also labyrinth, containing apparatus responsible for hearing and balance The inner ear is divided into bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth Perilymph is full of the space between bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth, endolymph is full of the membranous labyrinth bony labyrinth Compact bone Vestibule, semicircular canal, cochlea Vestibule Between the cochlea and the semicircular canal Five openings from three bony semicircular canals saccular recess, utricular recess Exterior wall- vestibular window: sealed by footplate of the stapes Bony semicircular canals Three curved bony ducts that form right angle mutually- lateral, superior and posterior semicircular canal A common crus is formed by the superior and posterior semicircular canal, therefore, five openings from three semicircular canals enter the vestibule Membranous labyrinth Composed of membranous duct and membranous sac fixation at bony labyrinth by fiber bundle dividing into utricle, saccule, membranous semicircular canal and membranous cochlea (scala media) cross-connection each other Membranous labyrinth Utricle Utricular recess Macula utriculi-sense of balance Five openings in the posterior wall connect with three semicircular canals Connection with the utriculosaccular duct and endolymphatic duct in the anterior wall. Vestibular aqueduct. Endolymphytic sac (within dura behind the petrosal part of the temporal bone) Membranous labyrinth Saccule Saccular recess Macula sacculi-sense of balance Connection with utriculosaccular duct and endolymphatic duct Membranous labyrinth Membranous semicircular canal Connection with the utricle Membranous labyrinth Membranous cochlea (scala media) Between the osseous spiral lamina and the lateral wall of the osseous cochlear canal, also between scala vestibuli and scala tympani, containing endolymph Basilar membrane: from free edge of the osseous spiral lamina Organ of Corti : hearing receptor composed of outer hair cells and inner hair cells Physiology of the ear Hearing Balance Route of sound conducting Air conduction Sound wave auricle external auditory canal vestibular window perilymph/endolymph organ of Corti auditory nerve nucleus auditory cortex Route of sound conducting Bone conduction Sound wave makes the perilymph vibrate through skull route, then stimulates the organ of Corti by which hearing generate. Translatory mode of bone conduction Compressional mode of bone conduction Physiological functions of the external ear Gathering sound Discriminating direction Resonance Protection Sound wave pressurizing Physiological functions of the middle ear Transformation and gain Structure for sound transmission and transformation: tympanic membrane and ossicular chain Physiological functions of the tympanic membrane Valid area of vibration : 55 mm2 Area of the footplate: 3.2 mm2 17times Function Middle ear—amplification from area ratio •Pressure = Force/area •Area of tympanic membrane ~17 > area stapes •Gain of area ratio ~24 dB Physiological functions of the ossicular chain Lever manubrium of malleus long crus of incus 1.3×17=22.1 27dB 1.3:1 Function of Middle ear—pressure amplification-ossicles Energy loss at air-fluid interface-99.9% loss (-30 dB) •Malleus longer than incus-amplify pressure ~1.7X (+2 dB) Physiological functions of muscles in the tympanic cavity stapedial muscle: decreasing pressure of perilymph Physiological functions of muscles in the Eustachian tube Keeping balance of pressure in the middle ear Drainage Prevention of retrograde infection Noise abatement Auditory physiology Transmission Sensation Basilar membrane displacement for a 250 Hz tone Basilar membrane displacement for a 1 kHz tone Basilar membrane displacement for a 4 kHz tone Cochlear mechanical response due mass and stiffness gradient •Mass & stiffness gradient gives rise to a so-called “traveling wave” •Characteristic frequency—frequency which produces the largest amplitude of response •Apex-maximum response to low frequencies •Base maximum response to high frequencies Envelope of traveling wave Characteristic frequency 1 2 3 4 Mass-increases from base (stapes) to apex Stiffness-increases from apex to base Stereocilia on OHCs attached to tectorial membrane Stereocilia on IHCs free standing Motion of basilar membrane towards scala vestibuli deflects stereocilia in excitatory direction Tectorial membrane deflects OHC stereocilia Viscous fluid drag of fluid deflects IHC stereocilia Model of organ of Corti Responds to OHC Electromotility •Model: OHC contraction cause organ of Corti to distort as shown herer •Cell motility feeds back enhancing basilar membrane motion thereby increasing traveling wave amplitude and making the “cochlea active” OHC contracts in-phase with deflection of the hair bundle toward the tallest stereocilia. The current through the cell increases with deflection in this direction. If the current is modulated slowly (compared to 1 kHz), then the voltage across the lateral membrane will be in-phase with the current. Conformational changes in many voltage sensitive molecules situated within the lateral membrane cause the length of the cell to change. The diameter of the cell increases slightly as the cell contracts to maintain constant cell volume. Balance physiology Semicircular canal: Perception of positive or negative angular acceleration Saccule and utricle : Perception of linear acceleration Macula sacculi: Perception of static balancing and linear acceleration on the coronal plane Macula utriculi: Perception of static balancing and linear acceleration on the vertical plane