* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NEUROCHEMICAL TRANSMISSION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
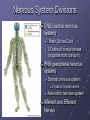
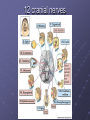
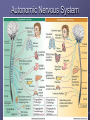
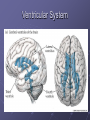
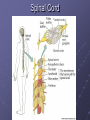
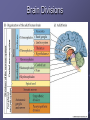
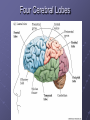
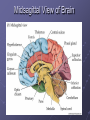
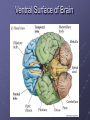
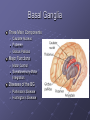
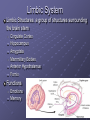
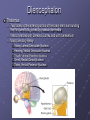
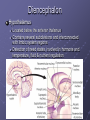
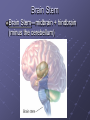
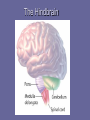
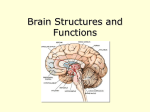
Organization and Functions of the Nervous System Nervous System Divisions CNS (central nervous system) Brain, Spinal Cord 12 pairs of cranial nerves (originate from cranium) PNS (peripheral nervous system) Somatic nervous system 31 pairs of spinal nerves Autonomic nervous system Afferent and Efferent Nerves 12 cranial nerves Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Division Exits Thoracic-Lumbar region of SC Norepinephrine in postganglionic synapses Fight-or-Flight Response Elevated hr, bp Pupil dilation Increased sweat gland activity Dry mouth Increased blood flow to muscles Parasympathetic Division Exits Cranial and Sacral regions of SC Acetylcholine in postganglionic synapses Energy Conservation Decreased hr, bp Pupil constriction Salivation Gastric Secretion Protection of the CNS Meninges (3 protective layers) Dura Mater Arachnoid Membrane Pia Mater Cerebrospinal Fluid Buoyancy and Shock Absorption Ventricles and subarachnoid space Ventricular System Dissection Planes Neuroanatomy Directional Terminology Anterior – Posterior (Front –Back) Dorsal – Ventral (Top – Bottom) Medial – Lateral (Middle –Side) Superior –Inferior (Above – Below) Spinal Cord Brain Divisions Four Cerebral Lobes Midsagittal View of Brain Ventral Surface of Brain Cerebral Cortex Basal Ganglia Three Main Components Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus Major Functions Motor Control Somatosensory-Motor Integration Diseases of the BG Parkinson’s Disease Huntington’s Disease Limbic System Limbic Structures: a group of structures surrounding the brain stem Cingulate Cortex Hippocampus Amygdala Mammillary Bodies Anterior Hypothalamus Fornix Functions Emotions Memory Diencephalon Thalamus Two lobes at the anterior portion of the brain stem surrounding the third ventricle, joined by massa intermedia Interconnected with Cerebral Cortex and with Cerebellum Major Sensory Relay Vision: Lateral Geniculate Nucleus Hearing: Medial Geniculate Nucleus Touch: Ventral Posterior Nucleus Smell: Medial Dorsal Nucleus Taste: Ventral Posterior Nucleus Diencephalon Hypothalamus Located below the anterior thalamus Contains several subdivisions and interconnected with limbic system regions Detection of need states, involved in hormone and temperature, fluid & nutrient regulation Brain Stem Brain Stem—midbrain + hindbrain (minus the cerebellum) Mesencephalon (Midbrain) Tectum (“roof”) relays visual and auditory information and controls simple reflexes, eye and ear orientation movements superior colliculi (“little hills”)—relay visual information inferior colliculi—relay auditory information Mesencephalon (Midbrain) Tegmentum (“floor covering”) Substantia nigra—integration of voluntary movements Red nucleus—controls basic body movements Reticular formation—controls arousal and consciousness Raphé system The Hindbrain The Hindbrain Metencephalon Pons—a “bridge” for many fibers passing from one side of the brain to the other. Contains sensory fibers, fibers from the cortex to cerebellum, and fibers that relay information on sleep, arousal, muscle tone, and dreaming. Cerebellum—involved in the development and coordination of movement Myelencephalon Medulla Oblongata Cranial nerve nuclei Regulates basic life functions (e.g., respiration, heart rate, vomiting, salivation) Cerebellum Components Vermis Lateral zone Flocculonodular lobe Cell Layers Molecular Layer Purkinje Cell Layer Granule Cell Layer Major Functions Balance Motor Coordination Timing and sequencing of rapid movements Sensorimotor Learning Cognition?