* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology - CHOW
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
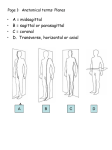
Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology • Anatomy – Structural organization of living things • Physiology – Basic processes that occur in the human body Anatomical Position • • • • Upright, standing position Face & feet pointing forward Arms at side Palms facing forward (supinated) Why do we care? Universal starting point from which to describe anatomical features and positions Consistency of description ability to communicate with each other *structures will always be described as they are to the subject rather * Anatomical Terms of Location • • • • • Anterior/Posterior Superior/Inferior Proximal/Distal Medial/Lateral Superficial/Deep Pg. 6 in textbook Refers to a part of the body in relation to another TERM MEANING EXAMPLE Anterior Towards the front of the body The knee cap is on the anterior side of the leg Posterior Towards the back of the body The shoulder blades are posterior to the ribs Superior Towards the head The heart is superior to the stomach Inferior Towards the feet The chest is inferior to the neck Medial Towards the midline of the body The big toe is medial to the 5th toe Lateral Away from the midline of the body The thumb is on the lateral side of the hand Proximal Closer to the trunk or point of origin The hip is proximal to the knee Distal Further from the trunk or point of origin The wrist is distal to the elbow Superficial Closer to the surface of the body Skin is superficial to the muscle Deep Further from the surface The lungs are deep to the ribs Examples: ANTERIOR to the ears. The nose is ____________ SUPERFICIAL to the skin. The fingernails are ____________ MEDIAL to the thumb. The pinky is __________ Anatomical Planes Frontal Relate to positions in space and are at right angles to one another Transverse Sagittal 1. Frontal (coronal) plane – Divides body into front & back segments 2. Transverse (horizontal) plane – Divides body into upper & lower segments 3. Sagittal (median) plane – Divides body into right & left segments Frontal Transverse Sagittal Anatomical Axes An axis is a straight line around which an object rotate Movement at the joint take place in a plane about an axis Horizontal Longitudinal Antero-posterior 1. Horizontal axis – East-west in relationship to anatomical position 2. Longitudinal axis – North-south in relationship to anatomical position 3. Antero-posterior axis – Front to back in relationship to anatomical position Describing Position & Movement • A body movement can be described in terms of the anatomical plane through which it occurs and the anatomical axis around which it rotate RULE: The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of movement Longitudinal Sagittal Plane Frontal Plane AnteroPosterior Horizontal Transverse Plane Axis of Rotation Horizontal Plane of Motion Example Sagittal Walking Squatting Cycling Longitudinal Transverse Twist Pirouette Antero-posterior Frontal Jumping Jacks Side Bend Types of Body Movement pg. 4-5 in textbook Retraction/Protraction Abduction/Adduction Flexion/Extension Pronation/Supination Dorsiflexion/Plantar Flexion Depression/Elevation Reposition/Opposition Inversion/Eversion External Rotation/Internal Rotation Circumduction External Rotation Internal Rotation Thumb Reposition Movements in Anatomical Planes What types of movement occur on these planes? • Sagittal Plane • Frontal Plane • Transverse Plane