* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01-Introduction2008-10
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
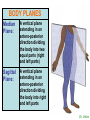
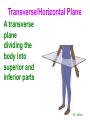
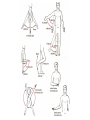
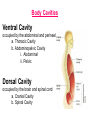
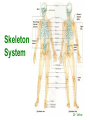
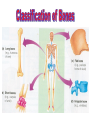
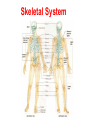
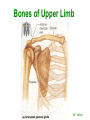
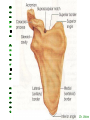
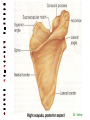
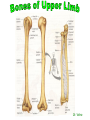
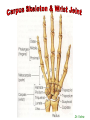
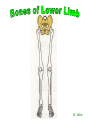
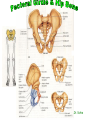
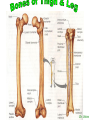
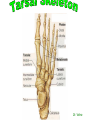
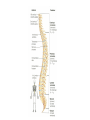
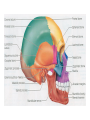
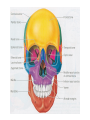
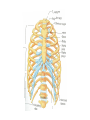
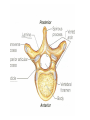
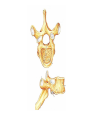
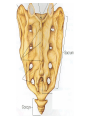
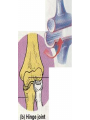
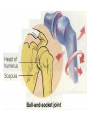
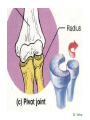
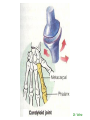
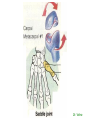
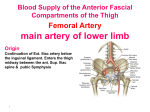
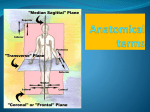
http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/v ohra/default.aspx By Dr. Saeed Vohra Let us wish you the best for your studies in Anatomy and in your other courses. We hope that you will enjoy this course, as well as learn some morphology and histology. If you have any problems with the course work, please come and see one of us right away: we can often help you find a solution The Chairman Dr. Musaed Alfayez Ph.D. Glasgow UK MBBS PhD Japan Assistant Professor What is anatomy? Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body with relation to each other. Derived from the Greek to cut up: the Latin 'to cut up' gives us dissect. To avoid confusion, it is always assumed that the body is in a standard position called Anatomical Position Dr. Vohra In anatomical position •the body is standing erect •the feet parallel •the face facing forward •the arms hanging at the sides •the palms facing forward Dr. Vohra Directional Terms Superior/Cranial A term indicating that a given structure lies above another (towards the head) Inferior/Caudal Away from the head end or towards the lower part of the body Anterior/Ventral Towards the front of the body Posterior/Dorsal Relating to the back or the dorsal aspect of the body Medial Situated close to or at the midline of the body or organ Lateral Located away from the midline Intermediate Between the medial & lateral structure Proximal Close to the point of attachment of a structure Distal Away from the point of attachment of a structure (as opposed to proximal) Superficial On or near the body surface Deep: Away from the body surface BODY PLANES Median Plane: A vertical plane extending in an antero-posterior direction dividing the body into two equal parts (right and left parts) Sagittal Plane: A vertical plane extending in an antero-posterior direction dividing the body into right and left parts Dr. Vohra Frontal/Coronal Plane A vertical plane at right angles to the sagittal plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts Dr. Vohra Transverse/Horizontal Plane A transverse plane dividing the body into superior and inferior parts Dr. Vohra TERMS OF MOVEMENTS Flexion: A movement, in the sagittal plane, that decreases the angle of the joint, and brings two bones closure Extension: A movement, in the sagittal plane, that increase the angle, or distance between two bones ( opposite of flexion) Abduction: A movement away from midline or median plane of the body Adduction: A movement toward midline (opposite of abduction) Rotation: Movement of bone around a fixed axis Circumduction: Combination of flexion, extension, abduction & adduction Pronation: Moving the palm from an anterior position to posterior position Supination: Moving the palm from a posterior position to anterior position Inversion: Turning the sole of the foot medially Eversion: Turning the sole of the foot laterally Dorsiflexion: Movement of foot up towards the leg (standing on heels) Planter flexion: Movement of toes towards the ground (standing on toes) Origin: The proximal point of muscle attachment that is fixed or less moveable during the muscle contraction Insertion: The distal point of muscle attachment that is moveable during the muscle contraction Dr. Vohra Body Cavities Ventral Cavity occupied by the abdominal and perineal a. Thoracic Cavity b. Abdominopelvic Cavity i. Abdominal ii. Pelvic Dorsal Cavity occupied by the brain and spinal cord a. Cranial Cavity b. Spinal Cavity Skeleton System Dr. Vohra Classification of Bones According to the basic types of bone tissue 1. Compact bone 2. Spongy bone According to the shape There are four types 1. Short bones 2. Long bones 3. Flat bones 4. Irregular bones Functions of the bones 1. Support & Shape Supports & anchors all soft organs Bones of the legs act as pillars to support the body trunk when we stand Without bones, our body will not be having any shape 2. Protection Brain is protected by the skull and rib cage protects the lungs heart & liver 3. Movement 4. Storage 5. Blood cell formation Skeletal System Dr. Vohra Bones of Upper Limb Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Classification of Joints 1- Fibrous Sutures of the skull 2-Cartilaginous Intervertebral, pubic symphysis 3- Synovial Plane Hinge Ball & Socket Condyloid Saddle Pivot Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra Dr. Vohra