* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
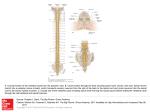
Anatomy Nervous System Lab Divisions of the Nervous System Central nervous system – brain & spinal cord Peripheral nervous system – cranial nerves & spinal nerves The Brain Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) Cerebrum pons midbrain Diencephalon T H M thalamus PP hypothalamus midbrain Cerebellum mamillary bodies epithalamus (pineal gland) pons m.o. Cerebrum Cerebellum The Brainstem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain – cerebral peduncle cerebral aqueduct of midbrain corpora quadrigemina pons superior colliculi Cerebral peduncle Cerebral aqueduct of midbrain m.o. inferior colliculi The Diencephalon thalamus hypothalamus mamillary bodies T H M infundibulum P connects to pituitary gland via infundibulum epithalamus (pineal gland) The Diencephalon Intermediate mass of Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Infundibulum Pituitary gland Cerebrum convolutions gyrus sulcus (separated from cerebrum by transverse fissure) 4 lobes per hemispherefrontal, parietal, temporal, occipital The Cerebrum corpus callosum septum pellucidum fornix The Cerebellum gray matter “folia” white matter “arbor vitae” separated from cerebrum by transverse fissure Transverse fissure 2 hemispheres connected by “vermis” The Spinal Cord Begins at foramen magnum & ends at L2 vertebral level by forming conus medularis Has 2 thickened areascervical enlargement - supplies nerves to upper extremity lumbar enlargement - supplies nerves to lower extremity Made up of 31 spinal cord segments Cross Sectional Anatomy of the Spinal cord segments Posterior median sulcus Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Posterior column Posterior gray horn sensory Central canal Lateral column Gray commissure Anterior column Lateral gray horn (T1-L2, S2S4) - autonomic Anterior gray horn motor Spinal nerve Ventral root Anterior median fissure The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves • Each spinal cord segment gives off a pair of spinal nerves • each spinal nerve forms from union of dorsal/ventral root of spinal cord segment & exits between vertebra at IVF • 8 pair cervical spinal nerves – 1st cervical nerve exits between occipital bone & C1, 8th cervical nerve exits the IVF between C7-T1 • 12 pair thoracic spinal nerves • 5 pair lumbar nerves • 5 pair sacral nerves • 1 pair coccygeal nerves Below the conus medularis, spinal nerves must angle downward (in the subarachnoid space) before exiting their IVF. These spinal nerves make up the cauda equina Cauda equina The Central Nervous System CNS well protected by bones (cranial & vertebrae), CT meninges, & cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Meninges – Connective tissues that surround and protect the brain and spinal cord (CNS) 3 layers: • Dura Mater • Arachnoid • Pia Mater Meninges 2 layers thick around brain with creation of dural sinuses between layers; dural folds into fissures of brain Dura Mater – tough, fibrous outer layer Dural folds and dural sinuses Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Inferior sagittal sinus Tentorium cerebelli Straight sinus Confluence of sinuses Transverse sinus Sigmoid sinus Dural folds and dural sinuses Superior sagittal sinus Falx cerebri Inferior sagittal sinus Straight sinus Confluence of sinuses Transverse sinus Meninges- Dura mater 1 layer around spinal cord with epidural space external Meninges Arachnoid – “spidery” web-like middle layer Pia Mater – delicate, thin inner layer; filum terminale - extension of pia mater extends from tip of cord to coccyx to anchor cord in place; denticulate ligaments anchor cord laterally Meninges Subarachnoid space – between arachnoid & pia mater; contains cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) Subarachnoid space (blue space) Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) clear, colorless fluid formed by filtration of blood plasma by choroid plexuses within ventricles of the brain. functions in protection of CNS, support, nutrient supply, waste removal CSF Circulation Lateral ventricle (behind septum pellucidum) Third ventricle Aqueduct of midbrain Fourth ventricle Lateral ventricles (in cerebral hemispheres) interventricular foramen third ventricle (in diencephalon around thalamus) cerebral aqueduct of midbrain fourth ventricle (between pons/cerebellum) subarachnoid space & central canal of SC Reabsorption of CSF through arachnoid granulations (arachnoid villi) of dural sinuses (superior sagittal sinus) into cerebral veins (space around & within thalamus & hypothalamus) Cranial Nerves 12 pairs of nerves that connect to the brain; provide motor, sensory &/or autonomic (parasympathetic) function Spinal nerves & Plexuses (Intercostal nerves) (Common peroneal nerve)