* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geocentric Model of the Solar System
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
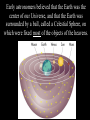
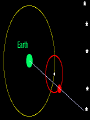
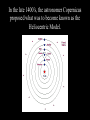
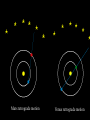
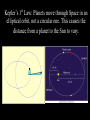
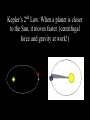
Chapter 26.2: Observing the Solar System Early views of the organization of Space were much different than ours. Early astronomers believed that the Earth was the center of our Universe, and that the Earth was surrounded by a ball, called a Celestial Sphere, on which were fixed most of the objects of the heavens. This interpretation of our solar system is called a Geocentric Model, meaning Earth-centered. Early astronomers noticed groups of stars that were visible at the same time every year. These were named constellations, and were used as a basis for calendars. The Orion Constellation Astronomers noticed that some celestial bodies did change position relative to the constellations. They called these “wandering stars” planets. Notice the planet Mars moving across the constellations Gemini and Leo over the course of 11 months. Astronomers also noted that, periodically, these planets which normally moved eastward, moved backward for a few weeks, then resumed their path eastward. In 200 A.D., the Greek astronomer Ptolemy explained this “retrograde’ motion by stating that the planets orbited the Earth in a circle, but also orbited another point in a circle, what he called an epicycle. In the late 1400’s, the astronomer Copernicus proposed what was to become known as the Heliocentric Model. Copernicus stated that the Sun was the center of the Solar System, the Earth was a planet, and that it orbited the Sun. And, here is how he explained retrograde motion. Mars retrograde motion Venus retrograde motion In the 16th –century, the astronomer Johannes Kepler developed three laws to describe the way in which planets move through Space. Kepler’s 1st Law: Planets move through Space in an elliptical orbit, not a circular one. This causes the distance from a planet to the Sun to vary. Kepler’s 2nd Law: When a planet is closer to the Sun, it moves faster. (centrifugal force and gravity at work!) Kepler’s 3rd Law states that the further a planet is from the Sun the longer its period of revolution (its year) will be. In the 1600’s, Isaac Newton stated that a force called gravity was causing the planets to behave as Kepler had observed. He stated that all objects with mass exerted a force of attraction on other objects with mass, and that the strength of that force is proportional to the mass of the objects and their distances from one another.