* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War I - southsidehistory
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
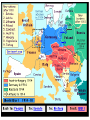
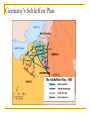
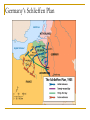
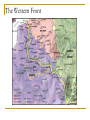
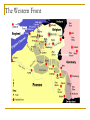
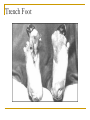
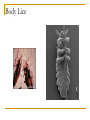
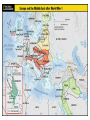
Answer the following questions in your notebook. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What assassination sparked an armed conflict between Austria-Hungary and Serbia that resulted in the First World War? Name at least two factors that may have played a role in starting the First World War. Germany’s Schlieffen Plan called for a two-front war with which two nations? The neutrality of which European state was violated when Germany invaded France in 1914? What was the name of the mutual defensive alliance formed between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy? What was the mutual defense alliance between Britain, France and Russia called? Define Chapter 26 key vocabulary terms (25): alliance, entente, militarism, ultimatum, mobilize, neutrality, stalemate, zeppelin, U-boat, convoy, total war, conscription, contraband, propaganda, atrocity, self-determination, armistice, pandemic, reparations, radicals, collective security, mandate, proletariat, soviet, and commissar Identify the following people, places, and events: Alsace and Lorraine, Dardanelles, Lusitania, Fourteen Points, Treaty of Versailles, Nichols II, Rasputin, Vladimir Lenin, Bolsheviks, and Treaty of Brest Litovsk, WORLD WAR I 1914-1924 Prelude to World War Population Explosion Industrial Revolution Nationalism Militarism Technology Defensive Alliances Military Alliances Triple Alliance (1882)- Germany, AustriaHungary, and Italy Triple Entente (1907)- Great Britain, France, and Russia Tension Leading to War Moroccan Crises 1905 1911 Balkan Crisis WORLD WAR I 1914-1918 Crisis in the Balkans Austria-Hungary (multinational state) Nationalism in the Balkans Pan-Slavism Desire to develop a united Slavic nation (Yugoslavia) A-H annexed Bosnia and Herzegovina, 1908 st 1 Balkan War, 1912 nd 2 Balkan War, 1913 Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife Sophia The Black Hand/Serbian Nationalists Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina, June 28, 1914 Gavrilo Princip Declarations of War A-H wished to take action against Serbia Germany supported A-H A-H declared war on Serbia, July 28, 1914 Russia mobilized against Germany and A-H Germany declared war on Russia and France Germany mobilized against France and violated Belgian neutrality (Schlieffen Plan) Britain declared war on Germany for breaking Belgian neutrality Germany’s Schlieffen Plan World War I Alliances Allied Powers- Great Britain, France, Russia, Serbia, Belgium, and later Japan and Montenegro Central Powers- Austria-Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria, and Ottoman Empire. Italy? World War I and its Destruction 1914-1918 Total War- a war that involves complete mobilization of troops and materials over large areas. The war affects the lives of all citizens in the warring countries, even those remote from the battlefields. Mobilization- the process of assembling troops and supplies and making them ready for war. Germany’s Schlieffen Plan The Battle of the Marne The Germans were advancing NE of Paris The French army organized a force to resist the Germans The Germans retreated (only about 50 miles from Paris) and dug trenches The Western Front was created Trench Warfare war of attrition- a war in which each side tries to wear the other down by constant attack The Western Front The Western Front Trench Warfare Cross-Section of a Trench Life in the Trenches Trench Foot Rats in the Trenches Body Lice The End to War Russia’s withdrawal from the war in 1918 U.S. entry into the war in 1917 Spring 1917- France was weakening, British and German reserves were diminishing March 1918- the Germans launched a final offensive against the Allies, gaining considerable ground July 1918- Second Battle of the Marne With the aid of U.S. troops, the Allies launched an effective counterattack that continued until September, 1918 The resistance of the Central Powers in other areas of the war crumbled November 11, 1918, Germany signed an armistice The Paris Peace Conference January 1919 delegates from 27 nations attended Representatives from the Central Powers and Russia were not included The “Big Four” Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau of France Prime Minister David Lloyd-George of Britain Prime Minister Vittorio Orlando of Italy President Woodrow Wilson of the United States Wilson’s idealism and Europe’s nationalism The Big Four Prime Minister Vittorio Orlando Italy President Woodrow Wilson United States Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau France Prime Minister David Lloyd-George Great Britain Woodrow Wilson and the Restoration of Peace Wilson’s Fourteen Points freedom of the seas and of trade reduction of military weapons an end to all secret alliances self-rule for all nations “general assembly of all nations” “no annexations, no contributions, and no punitive damages” France and Britain demanded reparations WWI Casualties 9 million soldiers killed 21 million soldiers wounded Around 30 million soldiers killed or wounded 13 million civilians died from disease and starvation Armenians? The war destroyed Europe Governments went bankrupt Revolution was rife in Eastern Europe A new Europe had to be formed The Treaty of Versailles June 28, 1919 War Guilt Clause Reduced the size of the German army Prohibited Germany from manufacturing major war weapons Reduced Germany’s territorial size Germany was required to pay extensive reparations Restructuring of Austria-Hungary Restructuring of Europe Germany developed deep resentment in response their loss of the war and Allied treatment after the armistice. The Treaty of Versailles left Germany weak and humiliated. This resentment, which lingered for over two decades, later resulted in even greater violence in the form of German Nazism. The Russian Revolution The First World War and Russia The Russians were not prepared for total war No competent military leaders Russian industry Czar Nicholas II and Czarina Alexandra Gregorian Rasputin *Continued military and economic disasters created tremendous discontent among the people of Russia. The March Revolution Working-class women in St. Petersburg demanded “peace and bread” Provisional Government- March 12, 1917 Nicholas II was encouraged to abdicate Alexander Kerensky 1. 2. Continuation of the war Kerensky made a poor call in continuing the war Problems: Workers and peasants wanted peace soviets (council of workers and soldiers) emerged all over Russia Bolsheviks The Bolsheviks and Vladimir Lenin • • • • Opposed capitalism Advocated violent revolution as a means to effect positive change Lenin’s Promises: Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (March 3, 1918) Assassination of the royal family Civil War (1918-1922) Red Terror Test Preparation Study all of Chapter 26 Be well familiar with Chapter 26 vocabulary words Review and study all notes Review questions from All Quiet on the Western Front The test will be comprised of 50 objective questions (multiple choice, true and false) and four (4) subjective short answer questions.