* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Imperialism-Power-Point
German colonial empire wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Japanese militarism wikipedia , lookup
Neocolonialism wikipedia , lookup
Decolonization wikipedia , lookup
Colonialism wikipedia , lookup
Scramble for Africa wikipedia , lookup
Western imperialism in Asia wikipedia , lookup
American imperialism wikipedia , lookup
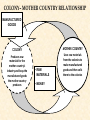
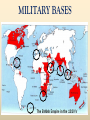
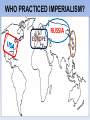
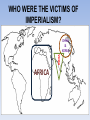
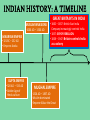
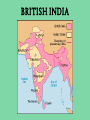
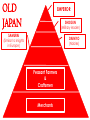
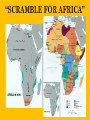
THE AGE OF IMPERIALISM EUROPEAN IMPERIALISM IN CHINA, INDIA, AND AFRICA VOCABULARY OF IMPERIALISM IMPERIALISM – THE PRACTICE OF ACQUIRING COLONIES FOR THE BENEFIT OF THE MOTHER COUNTRY MOTHER COUNTRY – A state that controls colonies COLONY – An area controlled by another country for that country’s benefit VOCABULARY OF IMPERIALISM RAW MATERIALS – Natural material that can be manufactured into a more valuable product • For ex: rubber is a cheap natural resource necessary for manufacturing tires MANUFACTURED GOODS – Products made in a factory from raw materials that can be sold to consumers • For ex: tires are a manufactured good that can be sold to consumers at a higher price than rubber COLONY– MOTHER COUNTRY RELATIONSHIP MANUFACTURED GOODS COLONY MOTHER COUNTRY Produces raw materials for the mother country’s industry and buys the manufactured goods the mother country produces Uses raw materials from the colonies to make manufactured goods and then sells them to the colonies • RAW MATERIALS • MONEY CAUSES OF IMPERIALISM ECONOMIC • Because of the Industrial Revolution many European countries produced a surplus of manufactured goods • Factory owners also needed raw materials for factories • Factory owners needed places to sell the goods they produced • European countries acquired colonies to gain raw materials and sell manufactured goods CAUSES OF IMPERIALISM POLITICAL • NATIONALISM – Countries competed to acquire colonies to show their power and show up their rivals • PRESTIGE – Honor and respect – More colonies = more prestige from other countries • These two ideas caused European countries to acquire colonies in Asia and Africa CAUSES OF IMPERIALISM MILITARY • NAVAL BASES – European countries built advanced and large navies – They needed bases to supply their ships all over the world – Europeans took colonies to serve as bases – Great Britain, Germany, Japan, the USA, Italy, and France all did this • MANPOWER – European countries used the population of their colonies as soldiers MILITARY BASES CAUSES OF IMPERIALISM RACIAL • SUPERIORITY – Europeans were technologically superior to all other parts of the world – They viewed all other peoples as inferior to them • THE WHITE MAN’S BURDEN – Europeans felt it was their duty to “civilize” non-Europeans – They wanted to make nonEuropeans more like them – They conquered Asians and Africans • • • • Forced natives to speak their language Changed native customs Spread Christianity Westernization WHO PRACTICED IMPERIALISM? RUSSIA EUROPE J A P A N WHO WERE THE VICTIMS OF IMPERIALISM? INDIA CHINA & KOREA AFRICA IMPERIALISM IN INDIA INDIAN HISTORY: A TIMELINE GREAT BRITAIN’S IN INDIA MUSLIM INVASIONS • 1000 AD – 1500 AD MAURYAN EMPIRE • 321 BC – 232 AD • Emperor Asoka • 1600 – 1857: British East India Company increasingly controls India • 1857: SEPOY REBELLION • 1858 – 1947: Britain controls India as a colony GUPTA EMPIRE • 320 AD – 535 AD • Golden Age of Hindu culture MUGHAL EMPIRE • 1526 AD – 1857 AD • Muslim dominated • Emperor Akbar the Great BRITISH IMPERIALISM IN INDIA THE SEPOY REBELLION: 1857 – 1858 • Many Indians were unhappy w/ the British East India Company’s rule of India • East India Company went too far by giving bullets to their Sepoys greased w/ cow and pig fat This violates the beliefs of Muslims and Hindus The Sepoys rebelled against the British East India Company and tried to drive the British out of India (very violent and brutal) • The rebellion failed, Britain’s Parliament took away the East India Company’s power and ran India as a colony until 1947 BRITISH EAST INDIA COMPANY TAKES CONTROL: 1750 – 1857 • Mughal Empire was very weak and was losing control of India • As a result the British East India Company took control over much of India • The East India Company controlled these areas like a government: Collected taxes, built roads and schools, spread Christianity Created an westernized army using native Indian soldiers called SEPOYS BRITISH EAST INDIA COMPANY COMES TO INDIA: 1600 – 1750 • Private company given control over trade w/ India by the British government in 1600 • Established trading posts and traded tea and other luxuries w/ Europe THE SEPOY MUTINY BRITISH INDIA THE RISE OF JAPAN MEIJI RESTORATION OF 1868 OLD JAPAN EMPEROR SHOGUN (Military leader) SAMURAI (Similar to knights in Europe) DAIMYO (Nobles) Peasant Farmers & Craftsmen Merchants JAPAN MODERNIZES: 1853 – 1905 1853 PERRY EXPEDITION • USA sends a naval expedition to force Japan to trade with America • Japan is threatened into agreeing to give up isolation and trade with Europe & America 1904 – 1905 RUSSO – JAPANESE WAR • Japan & Russia both wanted Korea as a colony and to use China as a market for goods and source of raw materials • Japan shocks the world and defeats Russia, a major European power • Treaty of Portsmouth: gives Japan control of Korean and spheres of influence in China 1868 MEIJI RESTORATION • Emperor Meiji and his supporters force the conservative shogun out of power • Create a limited monarchy based on Germany’s government • Reduced the power of daimyo & samurai • Immediately westernized Japan’s military, government, economy, and society 1894 – 1895 SINO – JAPANESE WAR • Japan fights a war with China over control of Korea • Japan’s westernized army defeats China easily • Japan begins to acquire colonies throughout Asia PERRY EXPEDITION MEIJI RESTORATION A SCENE FROM A NEW MODERN JAPAN AFTER THE REFORMS OF THE MEIJI RESTORATION JAPAN BECOMES A MODERN NATION-STATE How did they do it? • POLITICAL REFORMS – MEIJI CONSTITUTION (1889) • Emperor held most political power in Japan • Established equality of all men before the law • Created an elected legislature with limited powers • Only wealthy men had the power to vote – Created a strong government to implement reforms JAPAN BECOMES A MODERN NATION-STATE How did they do it? • ECONOMIC REFORMS – Government helps business • Builds railroads and ports • Sets up banks & factories – Wealthy families buy factories from the government and set up their own businesses – Japan quickly goes through an Industrial Revolution – The Japanese economy is westernized and modern JAPAN BECOMES A MODERN NATION-STATE How did they do it? • SOCIAL REFORMS – Established equality between social classes • Took away some of the privileges of the daimyo and samurai, but they still held political power – Built schools and universities • Increased education • Students sent to Europe to study western ideas – Adopted western dress, customs, and culture – Women had few rights and were left out of government JAPAN BECOMES A MODERN NATION-STATE How did they do it? • MILITARY REFORMS – Main goal of Japan’s plans for westernization – Wanted a strong to resist western imperialism – Copied western armies and navies • Used guns and cannons • Built modern warships • Created large armies using peasant manpower – Built a very strong military based on the Prussian army SINO-JAPANESE WAR RUSSO – JAPANESE WAR JAPAN BUILDS A COLONIAL EMPIRE THE DECLINE OF THE CHINESE EMPIRE & IMPERIALISM IN CHINA CHINESE DECLINE: mid 1800s TAIPING REBELLION • Peasant rebellion in the mid 19th century • Caused by peasants’ desire for their own land • Killed millions of Chinese • Eventually stopped by the government • Caused massive chaos and destruction OPIUM WARS • British government sold opium (an addictive drug) to the Chinese people • Chinese government tried to stop the drug trade • Britain declared war and used modern technology to defeat the Chinese army & navy • Unequal treaties favored Britain, forcing China to trade with Europe TAIPING REBELLION OPIUM WARS EUROPE COMES TO CHINA: Spheres of Influence • “Sphere of Influence” – An area of one country unofficially controlled by another country • Britain, Russia, France, Germany, and Japan divide China into “spheres of influence” – They each wanted raw materials, markets, naval bases, prestige, and to spread Western culture • Europe now controlled much of China WHAT DID CHINA DO ABOUT IT? FAILURE TO REFORM • Conservatives controlled the Chinese government • They did change China to meet the European threat • China failed to westernize or modernize its military, economy, or society BOXER REBELLION • In 1899, Chinese nationalists rebelled to kick foreigners out of China • They were called Boxers • The Boxers hated foreigners and attacked Europeans all over China • European countries & the USA teamed up and crushed the rebellion FAILURE OF THE BOXER REBELLION •The Boxers tried to drive “foreign devils” from China •The Boxers used martial arts and believed they were immune to bullets, they were wrong •Europeans crushed the rebellion and established stronger control over China IMPACT OF IMPERIALISM ON CHINA BEFORE IMPERIALISM CHINA WAS: • A powerful empire • United under a strong central government • The most powerful empire and culture in Asia AFTER IMPERIALISM CHINA WAS: • Weak & divided • Controlled by European states • 2,000 year old Chinese empire collapsed in 1911 IMPERIALISM IN AFRICA WHY COLONIZE AFRICA? • NATIONALIST CAUSES – Nationalist feelings led to competition between European countries to gain colonies in Africa – European states all wanted the PRESTIGE increase that came from gaining colonies – Europeans took over most of Africa for this reason • ECONOMIC CAUSES – Africa was rich in natural resources • Gold, coffee, silver, rubber, copper, diamonds, etc. – Colonies in Africa provided raw materials and were a market for European manufactured goods “SCRAMBLE FOR AFRICA” • Before 1878 most of Africa was free • Between 1878 and 1914 European states acquired colonies over almost all of Africa • Only two African states (Liberia & Ethiopia) were not colonies of Europe in 1914 • CONGRESS OF BERLIN – In 1884, the countries of Europe met and started to divide up Africa between them – After this meeting European countries “scrambled” to take as many colonies in Africa as they could “SCRAMBLE FOR AFRICA” • FRANCE – Conquered a large empire in west Africa • BRITAIN – Conquered the largest empire in Africa – Controlled South Africa, Egypt, and most of the land in between • OTHER EUROPEAN STATES – Belgium, Germany, Italy all acquired a few colonies to add to their prestige “SCRAMBLE FOR AFRICA” “SCRAMBLE FOR AFRICA” SCRAMBLING FOR AFRICA 1. How does this cartoon reflect the idea of a “scramble” for Africa? 2. Why were European countries interested in acquiring colonies in Africa? POSITIVES AND NEGATIVES OF IMPERIALISM FOR COLONIES & MOTHER COUNTRIES POSITIVES OF IMPERIALISM • MOTHER COUNTRY – – – – Access to raw materials & markets Increased political power and prestige Naval bases and ports for fueling ships Spreading their culture, language, and way of life • COLONY – Political Unity • Ex) India, under British rule, became united for the 1st time ever – Westernization • Increased education, literacy, medicine, and disease prevention – Economic development • Europeans built roads, railroads, telegraph lines, mines, sewers NEGATIVES OF IMPERIALISM • MOTHER COUNTRY – Competition for colonies led to war & conflict with other European countries – Cost of maintaining & defending colonies was high – Opposition by natives to being controlled by Europe • COLONY – Lack of political freedom – Artificial borders • Europeans created colonies with groups of people living together that historically didn’t get along – Lack of economic development • Colonies relied on Europeans for ALL manufactured goods – Suppression of native culture • Europeans restricted the culture, religion, and customs of people they controlled in colonies