* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War I The Great War
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
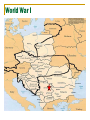
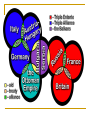
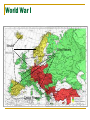
World War I The Great War 1914- 1918 1: World War I Five Causes of World War I A – Alliances Triple Alliance (Central Powers) – Germany, AustriaHungary, & Italy Triple Entante (Allied Powers) – France, Great Britain and Russia P – Propaganda to persuade public opinion A – Arms Build Up (Weapons) I – Imperialism by European nations N – Nationalism – pride in one’s country World War I World War I Otto Von Bismarck unified Germany watchful of France because of the Franco-Prussian War allied with Austria-Hungary, later joined by Italy Kaiser Wilhelm II power hungry signed a treaty with France planned a strong navy World War I Serbia Wanted to ally Slavic people in the region including Bosnia & Herzegovina Austria was determined Not to lose any land they had previously claimed Not to allow take over Not to allow creation of a Slavic nation Franz Ferdinand & Wife, Sophie Planned a visit to Sarajevo, Bosnia Promote good will between the people and Austria-Hungary World War I Powder Keg on the Balkan Peninsular Political tension in the Balkans was referred to as The Powder Keg World War I Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand 1914 – Franz Ferdinand & his wife were on a good-will mission to Bosnia – they were killed Princip – a 19 year old Serbian nationalist was the assassin Member of the Black Hand, A nationalist group wanting to rid Bosnia of Austrian rule Did not want to be Austrian Did not want alliance with Austria-Hungary World War I Murders Gave Austria-Hungary and excuse to punish Serbia German offered to support Austria-Hungary Austria sent Serbia and ultimatum Serbia Agreed to some demands Others would be settled on the international level Austria Must end all anti-Austrian activity Must allow Austria to investigate the assassination Rejected Serbia’s offer and declared war on Serbia Russia mobilized troops to support Serbia 2: World War I Alliances Complex alliances drew most of the countries of Europe into war. Germany, Austria-Hungary, & Italy (Ottoman Empire & Bulgaria) -vsRussia, France, & *Britain (Japan, many others including U. S.) World War I Neutral Allied Powers Central Powers World War I Schlieffen Plan – Germany’s quick victory plan Large portion of German army would go west to quickly defeat France Then quickly east to defeat Russia Germans decided to take the short cut through Belgium World War I Belgium A Neutral Nation Germany Belgium Refused to let Germany through Great Britain, ally of Belgium, pledged support Germany Demanded that troops be allowed through Belgium Forced their way through Belgium Causing Great Britain to declare war on Germany Italy pulled out because of the actions of Germany World War I Western Front With a German victory almost certain the French intercepted the German plan of attack Allies attacked the Germans north of Paris 600 taxis were used to transport French soldiers to the battlefield Allies won Schlieffen Plan failed WHY DID THE SCHLIEFFEN PLAN FAIL? World War I Trench Warfare – deep ditches from which the battles occurred. Troops from both sides would eat, drink, and sleep in the trenches. No man’s land – space between the trenches World War I Advanced Weapons of WW I Machine Guns Poison Gas Armored Tanks Advanced Artillery Submarines Millions of lives were lost because of the advances in weapons. World War I The Eastern Front Area along the German/Russian border Russia & Serbia -vs- Germany, Austria & The Ottoman Turks The Russian army was weakening Although Russia had the early victories, Germany eventually gained ground. The Eastern and Western Fronts were not Germany’s only problems. Oh, the snowflakes fell in silence Over Belleau Wood that night For a Christmas truce had been declared By both sides of the fight As we lay there in our trenches The silence broke in two By a German soldier singing A song that we all knew Though I did not know the language The song was "Silent Night" Then I heard my buddy whisper, "All is calm and all is bright" Then the fear and doubt surrounded me 'Cause I'd die if I was wrong But I stood up in my trench And I began to sing along Then across the frozen battlefield Another's voice joined in Until one by one each man became A singer of the hymn Then I thought that I was dreaming For right there in my sight Stood the German soldier 'Neath the falling flakes of white And he raised his hand and smiled at me As if he seemed to say Here's hoping we both live To see us find a better way Then the devil's clock struck midnight And the skies lit up again And the battlefield where heaven stood Was blown to hell again But for just one fleeting moment The answer seemed so clear Heaven's not beyond the clouds It's just beyond the fear No, heaven's not beyond the clouds It's for us to find it here Garth Brooks - Belleau Wood World War I No Man’s Land World War I Trench Warfare 3: World War I Global Conflict In hopes on ending the stalemate of war - the Allies attacked the Dardanelles - considered the gateway to Constantinople - called the Gallipoli Campaign - the Allies made repeated assaults - became a stalemate, finally the Allies gave up With the help of the Arabs - Allied forces took control of Baghdad, Jerusalem, & Damascus Other places - Germany’s colonial possessions came under assault World War I The United States Enters the War 1. unrestricted submarine warfare (Germany) +Germany established a blockade around Britain +promised to sink any ship,without warning near Britain +sank British passenger ship Lusitania, killing over 1,000 people including 128 Americans THE AMERICAN PUBLIC WAS OUTRAGED, SOME DEMANDED THAT AMERICA ENTER THE WAR World War I World War I 2. Zimmermann Note + British intercepted a note from the Germans to the ambassador in Mexico, promising to help Mexico get back land lost to the U.S. for Mexico’s help against the U.S. America Declared War on Germany- April 2, 1917 World War I Total War Devoting all of the nation’s resources to war Rationing of goods Limit on use of products Women and War Women went to work in the factories Worked the farms Kept troops supplied with basic needs World War I Russia Withdraws From WW I Total loss in life was over 5 million Lenin insisted that Russia pull out Offered Germany a truce Signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk Surrender lands that included parts of Finland, Poland, Ukraine, Latvia, Lithuania, & Estonia World War I AFTER RUSSIA PULLED OUT Most German soldiers were sent to the Western Front Pushed within 40 miles of Paris Allies launched a massive counter attack Second Battle of the Marne Allies were victorious. Nov. 11, 1918 an armistice was signed 4: World War I Paris Peace Conference Delegates from 32 nations met Key players Woodrow Wilson – U. S. George Clemenceau – France David Lloyd George – Gr. Britain Vittorio Orlando of Italy World War I Wilson’s Plan - FOURTEEN POINTS A plan for lasting peace in Europe 1-4 –end to secret treaties, freedom of the seas, free trade, and reduction in military forces 5 – adjustment of colonial claims with fairness to colonial people 6-13 – specific suggestion for border changes and the creation of new nations 14 – League of Nations – international organization to keep world peace Self-determination – allowing the people to decide under which type of government they would live World War I Treaty of Versailles signed June 28, 1919 Punishment for Germany Lost territory & restrictions placed on the military, “War Guilt Clause” – Germany would take blame for the war and be required to pay reparations to the Allies Overseas territories would be governed by the League of Nations until they could function independently World War I The U. S. ultimately rejected the treaty Germany American’s rejected the League of Nations Believed the best hope for peace was to stay out of the affairs of Europe Angry over the war guilt clause Angry over loss of land Other Nations Italy and Japan did not get the land they wanted World War I LEGACY War of new and deadly technology War of extreme costs 8.5 million soldiers killed 21 million wounded Drained the treasuries of Europe Destroyed acres of farmland as well has homes, villages and towns Survivors Insecurity and despair Shown in art and literature following the war World War I Posters World War I Posters World War I Posters World War I Posters World War I Posters