* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
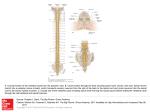
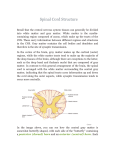
The Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) Brain 脑 Telencephalon 端脑 Diencephalon 间脑 Cerebellum 小脑 Brain stem 脑干 Midbrain 中脑 Pons 脑桥 Medulla oblongata 延髓 Spinal cord 脊髓 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Cranial n. (12 pairs) 脑神经 Spinal n. (31 pairs) 脊神经 Visceral n. 内脏神经 Visceral sensory n. Visceral motor n Sympathetic part 交感神经 Parasympathetic part 副交感神经 Cellular organization Neurons 神经元 Cell body 胞体 Axon 轴突 Dendrites 树突 Neuroglia -glial cell胶质细胞 Structural classification Bipolar neuron 双极神经元 has an axon and a dendrite Pseudounipolar neuron 假单极神经元 has a central branch and a peripheral branch Multipolar neuron多极神经元 has an axon and two or more dendrites Functional classification Sensory (efferent) neuron Motor (afferent) neuron Association neuron 联络神经元 感觉神经元 运动神经元 Reflex and reflex arc Reflex: a reaction of the organism by the nervous system in response to a stimulus Reflex arc: has 5 basic components Receptor ↓ Sensory neurons ↓ CNS ↓ Moter neurons ↓ Effector Basic terminology in nervous system In the CNS Gray matter 灰质: collection of nerve cell bodies and their dendrites, gray color during fresh condition Cortex皮质: the outermost layer of gray matter in cerebrum and cerebellum White matter白质: collection of nerve fibers, white color during fresh condition Medulla髓质: a central core of white matter beneath cortex of cerebrum and cerebellum Nucleus神经核: a collection ( group ) of cell bodies which have the same shape and function Fasciculus 纤维束 ( tract ): a bundle of nerve fibers which have the same origin, termination, pathway and function Reticular formation 网状结构: an admixture of cross-crossing fibers with larger or smaller groups of nerve cells occupying the meshes In the PNS Ganglion 神经节: a collection of neuronal cell bodies outside the CNS Nerve 神经: a bundle of nerve fibers held together by connective tissue sheath The Spinal Cord 脊髓 Position Lies in vertebral canal Continuous above with medulla oblongata at level of foramen magnum Ends below at lower border of L1 in adult; at birth at level of L3 External features A long cylindrical structure and slightly flattened anteroposteriorly, Conus medullaris (脊髓圆锥) Filum terminale (终丝) Cauda equina (马尾) Two enlargements Cervical enlargement (颈膨大): corresponds to the C4 to the T1 segments Lumbosacral enlargement (腰骶膨大): corresponds to the L2 to the S3 segments Fissure and sulci Anterior median fissure 前正中裂 Posterior median sulcus 后正中沟 Anterolateral sulcus 前外侧沟-anterior (motor) roots emerge serially Posterolateral sulcus 后外侧沟-posterior (sensory) roots enter spinal cord, each bear a spinal ganglion which constitutes the first cellstation of the sensory nerves Relationship of segments of spinal cord to vertebrae A portion of the cord that gives rise to a pair of spinal nerve constitutes a segment. There are 31 segments 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal Relationship of segments of spinal cord to vertebrae Spinal segments Vertebral levels (spines) Upper cervical region (C1~C4) = C1 ~ C4 Lower cervical and upper thoracic region (C5~T4) — 1 = C4 ~ T3 Middle thoracic region (T5~T8) — 2 = T3 ~ T6 Lower thoracic region (T9~T12) — 3 = T6 ~ T9 Lumber segments = T10 ~ T12 Sacral and coccygeal segments = L1 Internal structures Central canal 中央管 Gray matter Anterior horn (column) 前角(柱) Posterior horn (column)后角(柱) Intermediate zone 中间带 Lateral horn (column) 侧角(柱) Anterior gray commissures 灰质前连合 Posterior gray commissures 灰质后连合 White matter Anterior funiculus 前索 lateral funiculus 外侧索 Posterior funiculus 后索 Anterior white commisure 白质前连合 Posterior horn (column): Marginal layer (缘层) Substantia gelatinosa (胶状质) Nucleus proprius (后角固有核) Nucleus thoracicus(胸核) in segments C8~L3 Intermediate zone Intermediaolateral nucleus (中间外侧核)(lateral horn or column): lies in segments T1~L3, containing sympathetic preganglionic neurons Sacral parasympathetic nucleus (骶副交感核): lies in segments S2~S4, containing parasympathetic preganglionic neurons Intermediomedial nucleus (中间内侧核) : for sensation of viscera Anterior horn (column): contain motor neurons Three kinds of neuron α-motor neuron: larger multipolar neuron, innervates extrafusal fibers of skeletal m., producing contraction of m. γ-motor neuron: smaller neuron, innervates intrafusal fibers regulating muscular tonus Renshaw’s cell: negative feedback mechanism Two groups of nuclei Medial nuclear group: present in most segments of spinal cord, innervating axial muscles Lateral nuclear group: present only in cervical and lumbosacral enlargements, innervating limb muscles Rexed’s lamina 板层 posterior horn is formed by lamina Ⅰ to Ⅵ; Intermediate zone corresponding to lamina Ⅶ; Anterior horn is composed laminae Ⅷ and Ⅸ; lamina Ⅹ is the gray matter surrounding the central canal. Important Subdivision of Spinal Cord Gray Matter Region Lamina Nucleus Posterior horn Ⅰ Marginal layer Ⅱ Substantia gelatinosa Ⅲ, Ⅳ Nucleus proprius Ⅶ Nucleus thoracicus (C8~L3) Ⅶ Intermediolateral nucleus (T1~L3) Ⅶ Sacral parasympathetic nucleus (S2~S4) Ⅶ Intermediomedial nucleus Ⅸ Motor neuron Intermediate zone Anterior horn Ⅲ) White matter White matter contains three kinds of fibers: ascending, descending, and fasciculus proprius Ascending tracts Fasciculus gracilis(薄束) Fasciculus cuneatus (楔束) Posterior spinocerebellar tract (脊髓小脑后束) Anterior spinocerebellar tract (脊髓小脑前束) Spinothalamic tract (脊髓丘脑束) Ascending tracts Tract Site of origin Funiculus Termination Fasciculus gracilis Spinal ganglia Posterior below segment T5 Gracile nucleus Fasciculus cuneatus Spinal ganglia above segment T4 Cuneate nucleus Posterior spinocerebellar Homolateral nucleus thoracicus Anterior spinocerebellar Contralateral Laminae Ⅴ~Ⅶ Spinothalamic Laminae Ⅰ, Ⅳ~Ⅶ Function Convey proprioceptive and fine touch sensation of trunk and limbs Lateral Cerebellum Unconscious proprioception from lower limb and lower portion of trunk Lateral and anterior Dorsal thalamus Pain, temperature and simple touch sensation of trunk and limbs Descending tracts Fasciculus proprius (固有束) Lateral corticospinal tract (皮质脊髓侧束) Rubrospinal tract (红核脊髓束) Reticulospinal tract (网状脊髓束) Vestibulospinal tract (前庭脊髓束) Tectospinal tract (顶盖脊髓束) Medial longitudinal fasciculus (内侧纵束) Anterior corticospinal tract (皮质脊髓前束) Descending tracts Tract Site of origin Funiculus Termination Function Lateral corticospinal Cerebral cortex Lateral Voluntary movement Anterior corticospinal Cerebral cortex Anterior Laminae Ⅳ~Ⅸ anterior horn Rubrospinal Red nucleus Lateral Laminae Ⅶ~Ⅶ Excitatory of flexors Vestibulospinal Homolateral vestibular nuclei Anterior Laminae Ⅶ~Ⅷ Excitatory of extensors Reticulospinal Reticular formation Anterior and lateral Laminae Ⅶ~Ⅷ Voluntary movement Medial longitudinal fasciculus Vestibular nuclei Anterior Laminae Ⅶ~Ⅷ Coordinate neck with eye movement Tectospinal Superior colliculus Anterior Laminae Ⅵ~Ⅷ Fasciculus proprius Spinal cord Anterior, lateral and posterior Spinal cord Intrinsic reflex mechanism of spinal cord Main functions of spinal cord Conduction of excitations Reflex activity