* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
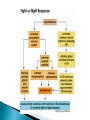
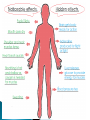
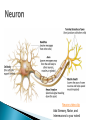
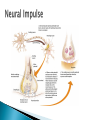
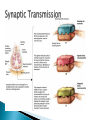
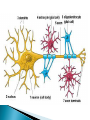
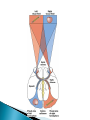
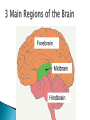
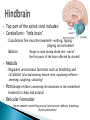
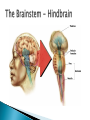
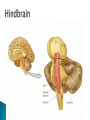
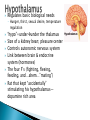
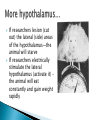
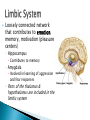
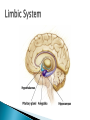
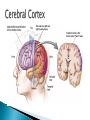
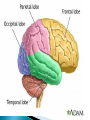
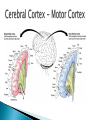
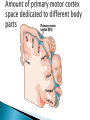
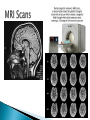
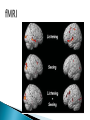
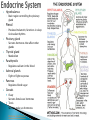
Part ONE AP Psychology ASAP Science: 7 Myths About the Brain You Thought Were True Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral nervous system Somatic Nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Somatic nervous system ◦ Nerves to voluntary muscles and sensory receptors ◦ Controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system ◦ Sympathetic division – mobilizes body resources Internal organs and glands arousing ◦ Parasympathetic division- conserves bodily resources calming Arousing Dilates pupil Accelerates heartbeat Inhibits digestion Stimulates glucose released by liver ◦ Stimulates secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine by adrenal gland ◦ Relaxes bladder ◦ FIGHT or FLIGHT ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Calming ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Contracts pupil Slows heartbeat Stimulates digestion Stimulated gallbladder Contracts bladder Fight or Flight Response ASAP Science: The Science of Goosebumps and Music Chills ASAP Science: Why Do We Get Nervous? With your group, write a short story describing a person in a state of distress. Your story should include descriptions of the effects of the AUTONOMIC nervous system on this person (BOTH sympathetic AND parasympathetic) (Fight or Flight AND Rest & Digest Responses) Highlight key phrases Make it interesting, creative, and exciting! No, it does not have to be totally realistic. I will read them aloud! Automatic inborn response to sensory stimulus ◦ Sensory neurons excited by a stimulus pass a message to interneuron in the spinal cord ◦ The interneuron activates a motor neuron causing a muscle reaction ◦ EX - Finger to a flame – finger moves away before pain registers in the brain Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, & transmit information Soma – Cell Body Dendrites – Branching structures that receive signals from other cells Axon – Fiber that carries signals away from soma to other cells Myelin sheath – Insulating material that encases some axons Terminal buttons – Small knobs at the end of axons that release neurotransmitter at synapses Neuron video clip Add Sensory, Motor, and Interneurons to your notes! Resting Potential – Neuron’s stable, negative charge when inactive Action Potential – Voltage spike that travels along axon Absolute refractory period – brief time after action potential before another action potential can begin All-or-none law – A neuron fires or doesn’t fire Action Potential Video Clip Chemicals that transmit info from one neuron to another. Acetylcholine – ◦ Released by neurons that control skeletal muscles ◦ Enables muscle action, learning and memory ◦ Alzheimer’s disease, Ach- producing neurons deteriorate Dopamine – ◦ Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion ◦ Excess dopamine receptor activity linked to schizophrenia ◦ Starved of dopamine – tremors and decreased mobility , Parkinson’s disease Serotonin ◦ Affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal ◦ Low levels linked to depression and obsessivecompulsive disorder ◦ Prozac and other antidepressant drugs raise serotonin levels Norepinephrine ◦ Helps control alertness and arousal ◦ Undersupply levels linked to depression GABA –gamma-aminobutyric acid ◦ A major inhibitory neurotransmitter ◦ Under supply linked to seizures, tremors and insomnia ◦ Contributes to the regulation of anxiety Glutamate ◦ Major excitatory neurotransmitter ◦ Involved in memory ◦ Oversupply can overstimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures (monosodium glutamate in food) Synthesis and storage of neurotransmitters in synaptic vesicles Release of neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft Binding of neurotransitters at receptor sites lead to excitatory and inhibitory Inactivation or removal – drifting away of neurotransmitters Reuptake or neurotransmitters by presynaptic neuron Video Clip: How neurotransmission occurs Neurotransmitters carry messages from a sending neuron across a synapse to receptor sites on a receiving neuron Agonists molecules excite – mimic neurotransmitters ◦ morphine mimics the action of endorphins Antagonists molecules inhibit – blocks its action ◦ Similar to occupy its receptor site and block its action ◦ Butnot similar enough to stimulate the receptor Create a “family” made up of the following members (give each one a name): Acetylcholine, dopamine twins, serotonin, norepinephrine, glutamate, & GABA Draw each family member and describe their personality ◦ They should clearly represent the functions of that neurotransmitter Make it creative, accurate, and APPROPRIATE! Due Tuesday—2 classwork grades Create a MNEMONIC DEVICE to remember the function of each major brain structure. ◦ Using words and/or pictures ◦ You will need a pack of notecards for this Any size, but bigger is better Left and Right Hemispheres ◦ Contralateral control each hemisphere controls the opposite side of he body ◦ Lateralization Left and right hemispheres have different functions ◦ Left Hemisphere Usually handles verbal processes Language, speech, reading, writing ◦ Right Hemisphere Usually handles nonverbal processing Spatial, musical, and visual recognition tasks Video Clip: Quick Left/Right Brain Test Large band of neural fibers connecting the two brains hemispheres and carrying messages between them. Split-brain surgery--cutting the corpus callosum to reduce epileptic seizures Gazzaniga, Bogen, & Sperry—famous for split-brain studies (1965) ◦ Split brain patients were asked to focus on a dot and then images were shown on both sides of the dots (in their left & right visual fields) ◦ When shown to the right visual field—they could name & describe objects ◦ When shown to the left visual field—they could NOT name it. ◦ Supports the idea that language is controlled by the left side of the brain. Video Clip: Girl with Half a Brain Video Clip: Split Brain Experiments Top part of the spinal cord includes: Cerebellum= “little brain” ◦ Coordinates fine muscle movement—writing, typing, playing an instrument ◦ Balance (finger to nose during drunk test—one of the first parts of the brain affected by alcohol) Medulla ◦ Regulates unconscious functions such as breathing and circulation (also maintaining muscle tone, regulating reflexes— sneezing, coughing, salivating) Pons(bridge of fibers connecting the brainstem to the cerebellum) ◦ Involved in sleep and arousal Reticular Formation Nerve network controlling arousal (also muscle reflexes, breathing, & pain perception) Lies between the hindbrain & the forebrain Involved in locating where things are in space (locating where a sound came from) Dopamine synthesis (creation)—used for voluntary movements Damage to an area of the midbrain linked to Parkinson’s Largest & most complex region of the brain Thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, & more Large in humans ◦ Includes cerebral cortex (outer layer of the brain— wrinkly cauliflower looking part!) and subcortical structures Thalamus ◦ Top of the brainstem ◦ Relay center for cortex ◦ Distributes all incoming sensory signals – except smells Regulates basic biological needs ◦ Hunger, thirst, sexual desire, temperature regulation “hypo”=underunder the thalamus Size of a kidney bean; pleasure center Controls autonomic nervous system Link between brain & endocrine system (hormones) The four F’s (fighting, fleeing, feeding, and…ahem…”mating”) Rat that kept “accidentally” stimulating his hypothalamus— dopamine rich area If researchers lesion (cut out) the lateral (side) areas of the hypothalamus—the animal will starve If researchers electrically stimulate the lateral hypothalamus (activate it) – the animal will eat constantly and gain weight rapidly Loosely connected network that contributes to emotion, memory, motivation (pleasure centers) ◦ Hippocampus Contributes to memory ◦ Amygdala Involved in learning of aggression and fear responses ◦ Parts of the thalamus & hypothalamus are included in the limbic system Cerebrum -Handles complex mental activities Sensing, learning, thinking, planning Divided into two cerebral hemispheres (left/right brains) Fissures—grooves in the brain; corpus callosum in the fissure separating the halves, connecting the two hemispheres Each cerebral hemisphere has 4 lobes: Frontal Lobe Located behind the forehead Speaking and muscle movements Making plans and judgments Prefrontal cortex – relational reasoning, working memory Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Motor Cortex ◦ Located at the top of the head ◦ Somatosensory cortex – touch and body sensation ◦ Located at the back of the head ◦ Visual areas that receive visual information form the opposite visual field ◦ Located above the ears ◦ Includes auditory areas primarily from the opposite ear ◦ Located at the rear of the frontal lobes ◦ Controls voluntary movement Aphasia – impaired use of language due to damage to any one of several cortical areas Broca’s Area – controls speech muscles via the motor cortex Wernicke’s Area- Interprets auditory code Angular Gyrus – transforms visual representations into an auditory code Visual Cortex – receives written words as visual stimulation Clinical Observations ◦ Observe effects of brain disease and injuries Manipulating the Brain ◦ Electrically, chemically or magnetically stimulate parts of the brain and study the effects Record Electrical Activity ◦ EEG – electroencephalogram Use electrodes on the head to record electrical activity Line tracings called brain waves Measures brain waves Lesioning ◦ Destroying a piece of the brain to learn about its function Electrode inserted deep into brain, passes electric current, burns tissue & disables brain structure Neuroimaging Techniques ◦ PET scans – positron emission tomography scan Chemical Activity Detects radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a given task Like radar shows which areas of the brain are most active while performing a task ◦ MRI – magnetic resonance imaging Images of Brain Structure Uses a strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce a computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of tissue See the structures within the brain, brain anatomy ◦ fMRI – functional MRI Brain Function Reveals blood flow and brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans The brains ability to modify and reorganize following damage (especially in children) NPR audio article ◦ “The Face Of A Famous Skull Found On Flickr” Be ready to share with the class 3 details from the story. Phineas Gage LEGO creation -Damaged frontal lobe & prefrontal cortex -Found that it affected both his decision making and personality The body’s slow chemical communication system Glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream Chemical messengers ◦ Mostly manufactured by the endocrine glands that are produced in one tissue and affect another including the brain ◦ When they act on the brain they influence our interest in sex, food and aggression ◦ Some are chemically identical to neurotransmitters ◦ Effects usually outlast the effects of neural messages Endocrine glands – ◦ above kidneys ◦ Secrete Epinephrine (adrenaline) Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) ◦ Help to arouse the body in times of stress Pituitary gland ◦ Most influential gland- hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland ◦ Regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands Hypothalamus ◦ Brain region controlling the pituitary gland ◦ Pineal ◦ Produced melatonin; functions in sleep & circadian rhythms Pituitary gland ◦ Secretes hormones that affect other glands Thyroid gland ◦ Metabolism Parathyroids ◦ Regulates calcium in the blood Adrenal glands ◦ Fight or flight responses Pancreas ◦ Regulates blood sugar Gonads ◦ ◦ Ovary Secretes female sex hormones Testis Secretes male sex hormones Hormone Crash Course Brain Pituitary Other glands Hormones Brain With your partner(s), develop a scenario in which a person may have damaged, injured, or developed some kind of abnormality to the part(s) of the brain you have been assigned. Describe what symptoms/difficulties a person injured in that region(s) of the brain may face. Describe your scenario and present your symptoms to the class The class will determine what brain part(s) were affected. *Turn in ONE copy of your scenario/symptoms and affected brain parts.