* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
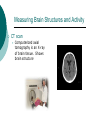
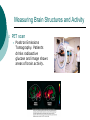
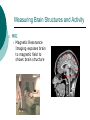
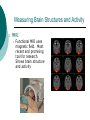
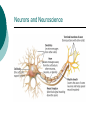
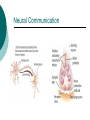
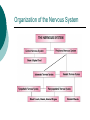
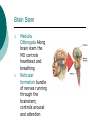
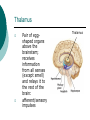
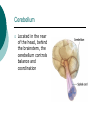
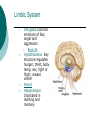
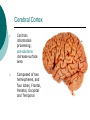
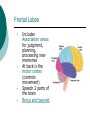
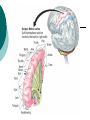
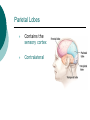
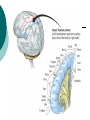
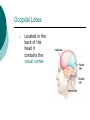
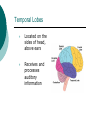
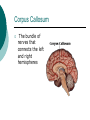
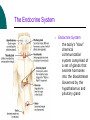
Biological Psychology Branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior Areas of study include neuroscience (functions and structures of the brain), nervous system, endocrine system and the relative contribution of evolution and genetics Phrenology The science which studies the relationships between a person's character and the morphology of the skull. It is a very ancient object of study. Discovered by the Austrian physician Franz Joseph GALL (1758-1828). Brain Teaser Time!!! 1. Johnny’s mother had three children. The first child was named April. The second child was named May. What was the third child’s name? 2. A clerk at a butcher shop stands five feet ten inches tall and wears size 13 sneakers. What does he weigh? 3. Before Mt. Everest was discovered, what was the highest mountain in the world? 4. How much dirt is there in a hole that measures two feet by three feet by four feet? 5. What word in the English language is always spelled incorrectly? 6. Billie was born on December 28th, yet her birthday always falls in the summer. How is this possible? 7. In British Columbia you cannot take a picture of a man with a wooden leg. Why not? 8. If you were running a race and you passed the person in 2nd place, what place would you be in now? 9. Which is correct to say, “The yolk of the egg is white” or “The yolk of the egg are white?” 10. A farmer has five haystacks in one field and four haystacks in another. How many haystacks would he have if he combined them all in one field? Measuring Brain Structures and Activity Electroencephalogram Or EEG measures electrical currents across the brain. Intended to measure brain activity. Measuring Brain Structures and Activity CT scan Computerized axial tomography is an X-ray of brain tissue. Shows brain structure Measuring Brain Structures and Activity PET scan Positron Emissions Tomography. Patients drinks radioactive glucose and image shows areas of brain activity. Measuring Brain Structures and Activity MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging exposes brain to magnetic field to shows brain structure Measuring Brain Structures and Activity fMRI Functional MRI uses magnetic field. Most recent and promising tool for research. Shows brain structure and activity Neurons and Neuroscience Neuron A nerve cell. The building blocks of the nervous system. Trillions of nerve cells are in the brain (neurons and neuroglia) Dendrite Extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body Axon The extension of a neuron, ending in terminal branches, through which messages are sent to other neurons or to muscles or glands Myelin Sheath Layer of fatty cells encasing the fibers of many neurons enabling greater transmission speed of neural impulses Neurons and Neuroscience Neural Communication Synapse The area between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap is called the synaptic gap. Neurotransmitters Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. These travel across the synapse and bind to specific receptor sites on the receiving neuron. Excess neurotransmitters are enzymatically broken down or reabsorbed by receptors in a reuptake process. Neural Communication Some Important Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Learning, memory and muscle control. Deficit present in Alzheimer’s disease. Endorphins Opiate-like action linked to pain control and to pleasure. Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline Related to arousal and state of alert (fight or flight). Serotonin Mood, sleep, arousal, pain sensitivity and hunger regulation. Implicated in depression. Antidepressants raise levels. Dopamine Movement, learning and attention. A deficit seen in Parkinson’s disease. An excess in schizophrenia. Neural Communication Action Potential A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. Threshold The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. All or Nothing (None) response Like it sounds. Neurons on the basis of “all or nothing”. Refractory period The period of rest following a neural impulse Cool Research in Neural Communication Neural plasticity and Synaptic pruning Neurogenesis Article on Neuroplasticity Article on Adult Neurogenesis Mirror neurons Organization of the Nervous System Brain Stem Medulla Oblongata Along brain stem the MO controls heartbeat and breathing Reticular formation bundle of nerves running through the brainstem; controls arousal and attention Thalamus Pair of eggshaped organs above the brainstem; receives information from all senses (except smell) and relays it to the rest of the brain: afferent/sensory impulses Thalamus Cerebellum Located in the rear of the head, behind the brainstem, the cerebellum controls balance and coordination Limbic System Amygdala Controls emotions of fear, anger and aggression Brain 24 Hypothalamus Key structure regulates hunger, thirst, body temp, sex, fight or flight, reward center Mind 6 Hippocampus Implicated in learning and memory Cerebral Cortex Controls information processing; convolutions increase surface area Composed of two hemispheres, and four lobes, Frontal, Parietal, Occipital and Temporal Frontal Lobes Includes Association areas for judgment, planning, processing new memories At back is the motor cortex (controls movement) Speech 2 parts of the brain Broca and beyond Parietal Lobes Contains the sensory cortex Contralateral Occipital Lobes Located in the back of the head it contains the visual cortex Temporal Lobes Located on the sides of head, above ears Receives and processes auditory information Corpus Callosum The bundle of nerves that connects the left and right hemispheres Name that brain part Split Brain Research Sperry and Gazzaniga’s research The Brain: Split Brain Split Brain NP.Org Scientific American excerpt The Endocrine System Endocrine System the body’s “slow” chemical communication system comprised of a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream Governed by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland Hormones- chemical substances that carry messages through the body in blood. Hormones affect behavior, body structure, metabolism, energy, and personality. Heredity- is the transmission of characteristics from parents to children. Genes are the basic building blocks of heredity. Identical twins- develop from a single fertilized egg and share the same genes. Fraternal twins- develop from two fertilized eggs and genes are no more similar than those between a brother and sister. All the effects that genes have on behavior occur through their role in building and modifying the physical structures of the body.