* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E4 Neurotransmitters and synapses trs
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
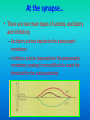
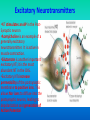
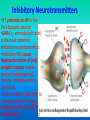
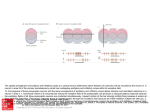
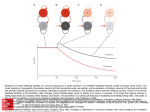
E4 Neurotransmitters and synapses Ms. TRS E.4.1 State that some presynaptic neurons excite postsynaptic transmission and others inhibit postsynaptic transmission. E.4.2 Explain how decision making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. At the synapse… • There are two main types of actions, excitatory and inhibitory. – Excitatory actions depolarize the postsynaptic membrane. – Inhibitory actions hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane, making it more difficult to reach the threshold for the action potential. Excitatory Neurotransmitters •NT stimulates an AP in the PostSynaptic neuron •Acetylcholine is an example of a generally excitatory neurotransmitter. It is active in muscle contraction. •Glutamate is another important excitatory NT; it is the most abundant NT in the CNS. •Excitatory NTs increase permeability of the postsynaptic membrane to positive ions. This allows Na+ ions to diffuse into the postsynaptic neuron, leading to depolarization and generation of Action Potential Inhibitory Neurotransmitters •NT prevents an AP in the Post-Synaptic neuron •GABA (-aminobutyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. •Inhibitory NTs cause hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron (makes neuron more negative), thereby inhibiting action potentials. •When inhibitory NTs bind to receptors, either K+ ions move out of the cell, or Clions move in. Decision making in the CNS • At any given time, a neuron may receive both inhibitory and excitatory signals. • If summation of these signals is inhibitory, then it will not fire an action potential. If it is excitatory and reaches the required threshold, then an action potential will fire. Summation Psychoactive drugs • E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. • E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of inhibitory psychoactive drugs. Psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing post synaptic transmission Excitatory Drugs • Increase synaptic transmission • Includes many (but not all) stimulant drugs – Nicotine, cocaine, amphetamine Inhibitory Drugs •Decrease synaptic transmission •Includes many (but not all) depressant drugs –Benzodiazepines (Valium), alcohol, THC Psychoactive drugs Effects of THC and Cocaine • E.4.5 Explain the effects of THC and cocaine in terms of their actions at synapses in the brain. • E.4.6 Discuss the causes of addiction, including genetic predisposition, social factors and dopamine secretion. Effects of Cocaine Normal conditions: Dopamine acts as an excitatory T. Re absorbed into the pre-synaptic neuron after timulation With Cocaine: Cocaine blocks receptors on euptake pump, dopamine is not reabsorbed, so emains in the synaptic cleft. his increases post-synaptic transmission hanges on mood: Dopamine is a pleasure NTnhances feeling of pleasure, feelings last longer as opamine is not taken back to the pre-synaptic euron ffect on behaviour: eelings of Euphoria ncreased energy and alertness ddictive ssociated with depression(dopamine production by ody is reduced). Effects of THC Normal: GABA HAS AN INHIBITORY EFFECT ON THE RELEASE OF DOPAMINE. With THC: THC inhibits GABA Release by binding to Cannaboid receptors, so GABA cannot inhibit dopamine. Therefore more dopamine is released. Effect on mood: Higher levels of Dopamine stimulate reward centres – increase feelings of pleasure Effect on behaviour: -Intoxication(drunk feeling) -- hunger -- memory impairment Causes of Addiction • What is it?? Is a nuerological disorder with genetic, social and environmental characteristics • Addiction often involves actions of dopamine neurons – This is part of why so many psychoactive drugs have the common factor of acting on the dopaminergic system Social factors Peer pressure and age: Strong peer pressure especially during adolescence increases chance of using drugs. Availability: Easy access to drugs increases chances of addiction. Legality and religion: In countries where use of drugs is prohibited by the law and culture, use of drugs and addiction is rare. Family and community: Relaxed attitudes to drugs can encourage addiction Mental health: depression, abuse and low self esteem can lead to drug use and addiction.