* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US Involvement in World War 2
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
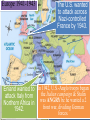
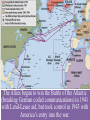
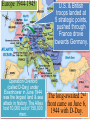
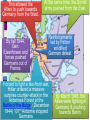
■Essential Question: –What role did the U.S. play in winning the wars in Europe & the Pacific? ■Warm-Up Question: –What other major American war is most similar in its resemblance to the U.S. entrance into WW2? Germany, using When the U.S. entered WW2 in The late Japanese 1941, blitzkrieg tactics, victory seemed remote dominated Asia, controlled almost all crippled of Europe the U.S. navy after the Pearl Harbor attack, Beginning in 1940, & seized most In 1941,Hitler broke England was wounded Western colonies in the from German attacks in the Pacific. Nazi-Soviet the Battle of Britain. Nonaggression Pact & marched into The German & Italian Russia. FDR & Churchill agreed that defeating Hitler was the top armies dominated Northern Africa, troops would be deployed to fight priority, but American threatened the Japan Suez at the same time. Canal & the oil fields in the Middle East. And over the next 2 years, the U.S. & the Allies began to win the wars in Europe & the Pacific Europe 1941-1943 The U.S. wanted to attack across Nazi-controlled France by 1943. Enland wanted to In 1942, U.S.-Anglo troops began the Italian campaign & Stalin attack Italy from To win the European was ANGRY bc he wanted a2 Northern Africa in different frontcampaign, war, dividing2 German 1942. plansforces. were proposed The Allies began to win the Battle of the Atlantic (breaking German coded communications) in 1941 with Lend-Lease aid, but took control in 1943 with America’s entry into the war. U.S. and British troops forced Germans into Tunisia. Despite U.S. On Nov. 8, 1942, General POINT: Forces loss at Kasserine Eisenhower landed on coastPass,TURNING led by British General of Morocco and Algeria. the Axis army was forced Montgomery stopped German forces led by to surrender in May Rommel (The Desert 1943. Fox.)The Allies finally defeated Germany at the Battle of El Alamein on Nov. 4, 1942 & then pushed the Axis Powers out of Africa. Britain & USA agreed to fight the Axis Powers in North Africa. When Italians surrendered, Germans took over defense. Allies seized Rome in 1944, and in April 1945, the Germans finally surrendered. American & British troops invaded Italy. General Patton decided to take Southern Italy and Sicily in 1943. In 1945, Mussolini was captured & executed by the Italian resistance. The Soviets defeated the German army atpoint the The Soviet victory at Stalingrad was a turning Battle of Stalingrad Meanwhile, the II Soviet armythe Russians in World War because began in Feb. 1943 . stopped the German attack at pushing towards Germany from the East by 1943. Moscow & Leningrad in 1942. The USSR was able to “free” Poland, Hungary, Romania. Results of Stalingrad ■ Stalin began demanding the Allies invade Western Europe to relieve pressure on the Eastern front. ■ Russia developed perception that the West did not care about their suffering. This would help fuel the Cold War later. • U.S. lost 400,000 in WWII • Russia lost 18 million. • Before the Battle of Stalingrad, nearly 500,000 lived in the city; after battle, only 1,500 still lived in the city. • More Russian forces died at Stalingrad than all U.S. forces combined during the entire war. Tehran Conference, 1943 By agreeing to “Operation Overlord” (D- FDR proposed a future United Nations ■ In Day), 1943,the FDR, Stalin met AlliesChurchill, would divide the Axis dominated by “4 policemen” (USA, Britain, military across twofirst fronts in Tehran, Iran for the of three China, & USSR) with power to “deal immediately conferences: withwartime any sudden emergency which requires action” USSR –The USA, Britain, coordinated their war strategy –FDR & Churchill finally committed to Stalin’s demands to open a western front (D-Day) –Discussed plans to create a “general internat’l organization” to promote “peace & security” (UN) Europe 1944-1945 Operation Overlord (called D-Day) under Eisenhower in June 1944 was the largest land & sea attack in history. The Allies lost 10,000 out of 150,000 men. U.S. & British troops landed at 5 strategic points, pushed through France drove towards Germany. The long-awaited 2nd front came on June 6, 1944 with D-Day. The Normandy invasion was deadly, but the Allied victory created a Western Front… America: Story of Us: D- This allowed the Allies to push towards Germany from the West. By fall 1944, Gen. Eisenhower and forces pushed Germans out of France. At the same time, the Soviet army pushed from the East. Reinforcements led by Patton solidified German defeat. Forced to fight a two-front war, Hitler ordered a massive surprise counter-attack in the Ardennes Forest at the Battle of the Bulge. (December 1944) 101st Airborne stopped Germans. By March 1945, the Allies were fighting in Germany & pushing towards Berlin. Results of Battle of the Bulge • This was the largest battle in Western Europe during WWII and the largest battle the U.S. fought in the War. • The U.S. lost 80,000 and the Germans lost 100,000. • This last attack by Hitler reduced the remaining strength of the German army, which significantly weakened the defense of Germany on both fronts. Yalta Conference in February 1945 To recognize the independence ■The “Big 3” met at Yalta to & sovereignty of nations in Eastern Europe discuss post-war Europe given They also agreed to the eminent defeat of Germany: occupy –Stalin up Germany afterrefused to give And they agreed theEastern war. Europe but did& join a to he create United Nations. agree to “self-determination” –Stalin agreed to send Soviet troops to the Pacific after the German surrender if the USSR could keep Manchuria As the Allies pushed into Germany & Poland, troops discovered & liberated concentration & death camps. Liberation of Nazi Concentration Camps (2.16) Soon after the Yalta Conference in Feb 1945, FDR died…and Harry Truman became president In late April 1945, the Allies broke through the Eastern & Western Fronts forcing both Italy & Germany to surrender In April 1945, the Soviet army captured Berlin. On April 30, 1945, Hitler committed suicide. On May 9, 1945, the German government signed an unconditional surrender to the Allies. The world celebrated V-E Day (Victory in Europe). The United States & the Holocaust ■ Examine the timeline “Stages of the Holocaust” & read “Response to the Holocaust from the U.S.” ■ With a partner, answer the 3 discussion questions & prepare for a class discussion