* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
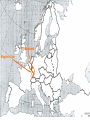
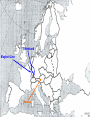
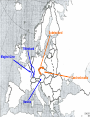
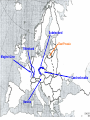
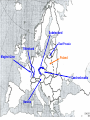
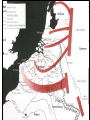
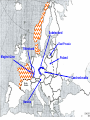
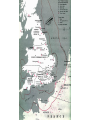
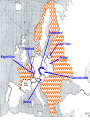
World War II 10.8 Students analyze the causes and consequences of World War II. 10.8.2 - Understand the role of appeasement, nonintervention (isolationism), and the domestic distractions in Europe and the United States prior to the outbreak of World War II. 10.8.3 - Identify and locate the Allied and Axis powers on a map and discuss the major turning points of the war, the principal theaters of conflict, key strategic decisions, and the resulting war conferences and political resolutions, with emphasis on the importance of geographic factors. Nazi aggression Outbreak of War Turning Points I. Nazi Aggression A. Hitler breaks the Versailles Treaty 1. By 1935 the German army is rebuilding 2. In 1936 the German troops reoccupy a 30 mile wide zone between Germany and France called the Rhineland a. French and British stunned, but do nothing b. Allies rely on the policy of appeasement Rhineland Maginot Line I. Nazi Aggression A. Hitler breaks the Versailles Treaty 3. In March of 1937, Hitler sends his army into Austria and annexes it (called the Anschluss) a. British and French ignore pledge to keep Austrian Independence b. Many Austrians supported the unity with Germany Rhineland Maginot Line Austria I. Nazi Aggression B. Hitler and the Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia) 1. 3 million German people live in the land bordering Czech and Germany 2. Sept. 1938 Hitler demands that it be handed over to Germany a. Czechs refuse and ask France for help b. Czechs have a defense treaty with France Sudetenland Rhineland Maginot Line Czechoslovakia Austria I. Nazi Aggression B. Hitler and the Sudetenland (Czechoslovakia) 3. The Munich Conference, Sept. 1938 a. British and French give in to Hitler’s demand, hoping for peace b. Czechs not invited c. Hitler promised to respect the new borders 4. British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain believed that he had achieved “Peace in our time” 5. Hitler took the rest of Czech 6 months later II. Outbreak of War A. Hitler looks towards Poland 1. Hitler wants Poland next a. Polish corridor be returned to Germany, including the city of Danzig 2. Britain and France promise to aid Poland 3. German Non-Aggression Pact with Soviets a. No threat of Soviet attack b. Poland split in half Sudetenland East Prussia Rhineland Maginot Line Czechoslovakia Austria II. Outbreak of War A. Hitler looks towards Poland 4. Sept. 1, 1939 – Germans attack Poland a. Hitler uses his blitzkrieg tactics – “lightning war” b. 1.5 Million men are carried by truck into Poland c. Warsaw is overwhelmed, Poland falls in a matter of weeks 5. WWII has begun Sudetenland East Prussia Rhineland Maginot Line Poland Czechoslovakia Austria II. Outbreak of War B. The Battle for France and Britain 1. On Sept. 3, 1939, France and Britain declare war on Germany 2. The Phony War – 7 month pause in fighting 3. In May of 1940, Hitler attacks Holland, Belgium, and Luxembourg a. The Germans “squeezed between” the Maginot Line and reached the coasts of France in 10 days II. Outbreak of War B. The Battle for France and Britain 4. May 26, 1940 – The miracle at Dunkirk a. 338,000 soldiers are trapped and surrounded on the coast b. 850 ships (navy and civilian) rescue them across the English Channel 5. On June 14, Paris falls to the Germans a. On June 22, 1940, France surrenders b. Puppet gov. set up in Vichy France (South) Sudetenland East Prussia Rhineland Maginot Line Poland Czechoslovakia Vichy France Austria II. Outbreak of War B. The Battle for France and Britain 6. Britain stands alone against the Nazis a. b. c. d. German invasion plan Operation Sea Lion RAF vs. Luftwaffe – “Battle of Britain” Germans target airbases first, then turn on British cities Hitler hoped to break the British morale 7. Battle of Britain lasts until May of 1941 when Hitler finally calls off the attacks III. Turning Points A. Hitler and Operation Barbarossa 1. Early June 22, 1941, Hitler’s tanks roll into the Soviet Union 2. Soviets have the largest army in the world, but are completely unprepared 3. Within a few months Hitler drove 500 miles into Russia a. Russians retreat, burning everything behind them b. Russians held out until the Russian winter stopped the German divisions Sudetenland East Prussia Rhineland Maginot Line Poland Czechoslovakia Vichy France Austria III. Turning Points A. Hitler and Operation Barbarossa 4. The Battle of Stalingrad a. Russians ordered to “hold at all costs” b. Nov. 1942, Germans own 90% of the city c. Russians counterattack during winter (they were more prepared for it than the Germans) d. 1-2 million Russians, 260,000 Germans casualties III. Turning Points B. North Africa 1. Afrika Corps defeated at El Alamein a. British Montgomery or “Monty” vs. German Rommel or “the Desert Fox” 2. American troops land in Morocco 3. British and American troops drive Nazis off the continent in May of 1943 American Troops landing El Alamein III. Turning Points C. June 6, 1944 – Allies land in France: D-Day 1. Operation Overlord – 3.5 million troops, thousands of planes, trucks, tanks, etc. 2. 60 miles of beach were invaded by American, British, and Canadian forces. 3. Paris was liberated by August of 1944. III. Turning Points D. December 16, 1944 – The Battle of the Bulge 1. Hitler tries one last blitzkrieg 2. Hitler attacked the allies in a hope to split the British and American forces 3. The offensive fails 4. The Germans are no longer able to mount any offensive actions III. Turning Points E. March 1945 – Allies march into Germany 1. By April of 1945, Soviet troops surrounded Berlin 2. Hitler commits suicide on April 29, 1945 3. May 8, 1945 – German unconditional surrender a. V-E Day (Victory in Europe) IV. Pacific War A. Japanese Expansion 1. 1931 – Japanese invade Manchuria 2. 1937 – Japanese invade the mainland of China a. Japanese atrocities: Rape of Nanking 3. In order to get more resources and raw materials, the Japanese invade the rest of Southwest Asia IV. Pacific War B. Dec. 7, 1941 1. Japanese surprise attack Pearl Harbor, over 2,000 men die 2. America declares War on Japan C. The Japanese push out 1. They take Guam, the Philippines, and pushed all they way to India IV. Pacific War D. The Tide Turns 1. Japanese are defeated at the battles of Coral Sea and Midway in early 1942 a. The Americans go on the offensive 2. American’s begin an “island hopping” campaign E. Americans drop the Atomic Bomb 1. Japan surrenders Sept 2, 1945