* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II Notes
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Germany wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
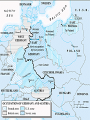
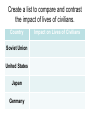
Home Front and the Aftermath of War Chapter 26 Section 4 How did World War II contribute to racial tensions in the United States? How did WWII end in Europe? • Allies divide Germany up between them. – This helps start the Cold War. • Trials are held in Germany (and Japan) to try the people responsible for the war. – Many are executed and jailed for war crimes. What was the intended effect of bombing German Cities? How did WWII end in the Pacific? • “Island-Hopping” – Invading throughout the pacific Island by Island – Costly in lives, resources; bloody battles – Battle of Midway – US destroys Japanese fleet [turning point in the pacific] – Japan continues to fight despite losses – Truman doesn’t want to invade mainland Japan (projected too costly in lives) – Aug. 6 Hiroshima; Aug 9. Nagasaki Why were Civilian populations bombed? Quick Facts • War Costs – US Debt 1940 - $9 Billion – US Debt 1945 - $98 Billion • WWII cost $330 billion – 10 times the cost of WWI & equivalent to all previous federal spending since 1776 Losses of the Major Wartime Powers in WWII, 1939-1945 • Germany – 4.5 million military – 2 million civilian • Japan – 2 million military – 350,000 civilians • Italy – 400,000 military – 100,000 civilian • China – 2.5 million military – 7.4 million civilians • USSR – 10 million military – 10 million civilians • Great Britain – 300,000 military – 50,000 civilians • France – 250,000 military – 350,000 civilian • United States – 274,000 military Postwar Efforts at Revenge • The Nuremberg Trials of 1945-46 – After, WWII the Allied powers decided to place on trial the highest-ranking Nazi officers for “crimes against humanity” – Allied forces had attempted to do this after WWI, but had released them on the grounds that they “were just following orders” – Hitler, Goebbels, and Himmler were dead; but, 22 Nazi leaders (including Goring) were tried at an international military tribunal at Nuremburg, Germany. 12 were sentenced to death. Similar trials occurred in the east and throughout the world. • The Tokyo Trial (1946-48) Postwar Efforts at Peace • The United Nations – There was some hope when, in 1945, the United Nations was created; an organization to promote international stability – A General Assembly where representatives from all countries could debate international issues. – The Security Council had 5 permanent members – U.S., Soviet Union, Britain, France, and China could veto any question of substance. There were also 6 elected members. – Key: the U.S. joined [in contrast to League of Nations] Wartime Agreements • Unlike WWI, there was no Peace of Paris to reshape Europe. – Instead, the Yalta agreement of February 1945, signed by Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin, turned the prevailing military balance of power into a political settlement. – Potsdam Conference, in suburban Berlin (July 1945)—Truman, Stalin, Churchill – Finalized plans on Germany. Germany would be demilitarized and would remain divided. Postwar Reality: Soviet Control of Eastern Europe • Europe was politically cut in half; Soviet troops had overrun eastern Europe and penetrated into the heart of Germany. • During 1944-1945, Stalin starts shaping the post-war world by occupying SE Europe with Soviet troops that should have been on the Polish front pushing toward Berlin. • Roosevelt did not have postwar aims because he still had to fight Japan; Stalin did have postwar aims. Postwar Reality • Consequences of World War II – Soviet Union with agenda – Unlike the isolation after WWI, the U.S. was engaged in world affairs – The triumph of Communists in China – Decolonization • The independence of nations from European (U.S. & Japan) colonial powers. What caused the major split between the United States and the Soviet Union following World War II? Create a list to compare and contrast the impact of lives of civilians. Country Soviet Union United States Japan Germany Impact on Lives of Civilians