* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 26 - Cengage Learning
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Wang Jingwei regime wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
American mutilation of Japanese war dead wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
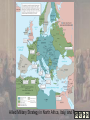
CHAPTER 26 The Second World War, 1940 - 1945 Web War in Europe Hitler-Stalin Pact (1939) Germany blitzkriegs Poland in September 1939 Britain and France declare war on Germany Germany invades Belgium, Holland, Luxembourg France falls June 22, 1940 Dunkirk flotilla Winston Churchill FDR wins third term as president Wendell Wilkie The End of Neutrality Lend-Lease program begins in 1941 USS Reuben James Germany breaks pact, invades Russia, June 1941 Churchill and FDR sign Atlantic Charter Japanese aggression in Pacific escalates Gunboat Panay Pearl Harbor 18 warships, 300 planes, and 2,400 Americans lost U.S. suffers early defeats while gearing up for war Japanese took Guam, Wake Island, and Philippines Douglas MacArthur The Homefront War ends Depression Americans go to work in defense industries War Production Board Revenue Act of 1942 17 million new jobs created during war Americans were “making do” now that “We’re all in this together” Rationing leads to shortages Baseball became part of war effort Opportunity and Discrimination Women and minorities fill traditional men’s roles and new work roles 6 million women took defense jobs “Rosie the Riveter” becomes American icon “Double-V Campaign” is adopted by blacks Fair Employment Practices Committee Executive Order #8802 bars discrimination in federal jobs, but discrimination continues Japanese-American internment Executive Order 9066 Hirabayashi v. United States Japanese American Relocation ©2002 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning ™ is a trademark used herein under license. The Grand Alliance Russian army fights virtually alone against Germany Stalingrad Western Allies concentrate on North Africa and Italy Mussolini killed in April, 1945 Tehran Conference Normandy invasion begins in June 1944 3 million men in Operation Overlord Omaha Beach Paris liberated in August, 1944 Germans counter-attack in Battle of the Bulge The Grand Alliance (cont.’d) Allies converge on Berlin Discovered extermination camps 6 million Jews and 4 million others killed Dachau and Auschwitz War Refuge Board Hitler committed suicide in his Berlin Bunker, April 20, 1945 War in Europe ends May 7, 1945 Allied Military Strategy in North Africa, Italy, and France Allied Advances and the Collapse of German Power The Pacific War Battle of Coral Sea halts Japanese invasion of Australia Battle of Midway U.S. forces retake territory America remains on offensive for rest of war Leapfrogging across Pacific islands Guadalcanal secured February 1943 Retook Gilberts, Marshals, Guam, Tinian, Saipan, and Marianas Philippines liberated October 1944 Battle of Leyte Gulf Brutal fighting on Iwo Jima and Okinawa Japanese Expansion and Early Battles in the Pacific Pacific Theater Offensive Strategy and Final Assault Against Japan A Change in Leadership Roosevelt meets with Churchill and Stalin at Yalta Plan for post-war Germany FDR dies April 12, 1945, of severe stroke, is replaced by Harry Truman Truman learns of Manhattan Project Web Enola Gay and Bock’s Car Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki Japanese surrendered September 2, 1945 aboard USS Missouri Discussion Questions What were the major events in Europe between 1933 and 1939 that led to war? How did FDR mobilize the U.S. economy to support the war effort? Examine the Allied strategy for winning the war. How was it implemented? What were the major problems? How did the U.S. and its allies defeat the Japanese in the Pacific? How was this war different than the war in Europe?