* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From the USSR to Russia
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Background of the occupation of the Baltic states wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
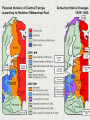
THE HOUSE THAT STALIN BUILT Kievan Rus • First great civilization of the Eastern Slavs. • Centred on Kiev and Novgorod on trade routes between Scandinavia and Black Sea – Constantinople. • Grand Prince Vladimir imposes Orthodox Christianity in 988: religion, alphabet. • Rus becomes part of the Eastern sphere. What is Russia? • Approximately 1240 Mongols conquer Rus, rule for 200 years. • Western area (now Ukraine) largely absorbed into Polish kingdom. • Beginning in around 1320 Moscow becomes the centre of a new state: Muscovy. • 1556 Ivan IV takes Kazan, headquarters of Mongols. Ivan IV (“The Terrible” 1533-1554) The dynamic of expansion • Muscovy grows to absorb the surrounding lands. • Late 16th century reaches across Siberia to the Pacific. • 17th century absorbs eastern part of Ukraine from Poland. The Russian Empire • Peter I decides to bring Russia into European sphere. • moves capital to St Petersburg in 1703. • Builds a strong navy and military. • Fights Swedes and Turks. Peter I (1682-1725) Battle of Poltava against Sweden (1709) Growing the Empire • Catherine II (17621796) continues Peter’s program of expansion. • Expands to the south to absorb Crimea. • Division of Poland between Russia, Prussia and Austria. • The power structure of the Russian State The Tsar The Boyars (chiefs of bureaucracy) The intelligentsia (middle class, small layer) The Narod (Common People) The Origin of the Soviet Union • First World War: Russia fights against Germany and Austria. • Russia becomes exhausted, the last Emperor Nicholas II abdicates. • Lenin’s Bolshevik party overthrows the provisional government on 25th October / 7th November 1917. Vladimir Lenin (1917-1924) What was Bolshevism? • 1903 Lenin splits the Socialist movement: instead of working through parliamentary means (menshevism or Social Democracy), he advocates a dictatorship of the proletariat. • The Russian revolution was the first proletarian revolution. The Bolshevik party renamed Communist. • Lenin unleashes terror in the name of class warfare. • In 1921, with the Civil War over, Lenin announces the New Economic Plan, allows small business to thrive. The poet Vladimir Mayakovsky’s call to revolution Let’s march ! Let’s fly ! Let’s sail ! Let’s roll ! Checking the list of all creation. That thing is necessary – Fine, keep it. Unnecessary ? To the devil ! A black cross. We’ll destroy you, old romantic world ! In place of faith in our soul we have electricity and steam. In place of misery, pocket the riches of all worlds ! The old men ? Kill them. And use the skulls for ashtrays! The Soviet Empire? • USSR occupies most of territory of the former Russian Empire. • Exceptions: Finland, Poland, Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania) which become independent in 1918 (and were reabsorbed after 1945). • 1924 Lenin dies, Georgian Bolshevik Josef Stalin consolidates power. Josef Stalin (1924-1953) JOSEPH STALIN: BIOGRAPHY - born Dec. 21, 1879, Georgia, Russian Empire - expelled from the seminary for revolutionary activities in 1899 - served in minor party posts and was appointed to the first Bolshevik Central Committee in 1912 - served as commissar for nationalities and for state control in the Bolshevik government (1917–23). - overcame his rivals and took control of Soviet politics after Lenin's death (1924) - radically altered the economic and social structures leading to millions of deaths and the rise of Soviet Union as a world super power. What was Stalinism? • 1920s saw rise of Fascism in Germany, Italy: war inevitable to defend the only communist country • Socialism in one country meant building a powerful industrial state • 1928 First Five-Year Plan to raise production. • Millions arrested, used as slave labour in construction • Electrification of the country: dams and canals Collectivization of Agriculture • Decision to sell grain abroad to purchase industrial equipment • Peasants forced into collectives, contributing their own livestock, land, equipment • Industrialization of agriculture: tractors and combines • Partly class war against peasants “Holodomor” • In 1933 the crops fail, Soviets confiscate grain • Millions die of starvation in the villages, especially in Ukraine • Was it genocide by Russians against Ukrainians? Collectivization Theory: • increased output possible due to concentration, mechanization Doubtful results: • eradication of peasants’ motivation • Millions of people are starved to death when land and food is confiscated • Soviet agriculture permanently disabled Industrialization Introduction of ambitious 5-year plans: • Successful development of heavy industry. • Tractors, trucks, planes, Moscow metro • Soviet Union becomes a sophisticated industrial power • Massive exploitation of prisoners’ work. Labour camps. • Stalin’s utopian projects: White (Belomor) Sea Canal THE NEW SOVIET MAN • Socialist state requires the support of a man of a new social and psychological type: • devoted to the ultimate goal of building communism, an ideal society on earth • capable of shifting from words to deeds • represents the mass • In post-Soviet Russia despised as “homo sovieticus” Voloshyn, Reconstruction of Dnieper Hydro Plant, 1947 Gulags: Labour camps 3,000,000 2,500,000 2,000,000 Camps Colonies Total 1,500,000 1,000,000 500,000 0 1945 1948 1951 1953 Official police data. Reported to Stalin by Minister Kruglov. Source: Ahlberg 1992 PURGES: THE GREAT TERROR Elimination of political rivals: • murder of Kirov (1934) • show trials of fellow Bolsheviks • the Great Terror (peak in 1937) • Millions arrested, shipped to Siberia, worked to death in the GULAG camps Why the Terror? • Stalin falsified history to eliminate Trotsky from the history books • Wrote his own History of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union exaggerating his own role • Feared a coup d’état and his own replacement by Trotsky, in exile in various countries • Trotsky finally murdered in Mexico City by a Soviet agent in 1940 Why the Terror? The external situation • Poland: invaded Soviet Russia in 1920, reached Kiev before being driven back to the gates of Warsaw; in 1930 plotted a second invasion with Japan; in 1939 negotiated with Hitler, broke off negotiations in April • Japan defeated Russia in 1903-5; had designs on Siberia; invaded Mongolia in 1939 • Germany had controlled large chunk of Ukraine in 1918; Hitler hated Bolshevism, fought proxy war with USSR in Spain (1936) The most important victory of the war? Khalkin Gol • August 23-30, 1939 • Soviet forces under General Zhukov surround and annihilate Japanese force in Mongolia. • Japan signs treaty with USSR, turns to the Pacific • Stalin gains time for war with Germany, does not have to fight on two fronts • USSR declares war on Japan August 8, 1945, occupies Kuril Islands The Prelude to War Molotov-Ribbentrop pact 23 August 1939. Germany and USSR: secret protocols divide Eastern Europe into “spheres of interest.” USSR granted Eastern Poland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Finland and Bessarabia (Moldavia). Execution of Polish Officers • Some 20,000 Polish officers surrendered to Soviets • In 1940 Stalin gives the order for them to be eliminated • Why? – they pose a risk in case of invasion; they represent a hostile force • Falsification of history: Soviets claim they were murdered by the Germans THE SECOND WORLD WAR (THE GREAT PATRIOTIC WAR) • June 22, 1941 Germany invades USSR. • Defence of Moscow and Leningrad • July 1942 - February 1943 the Battle of Stalingrad • “Generals win battles, economies win wars.” Spoils of war • Victory and the division of Europe • Growth of Stalin’s popularity at home. Soviet Union becomes a a world superpower. • In 1945 USSR is superpower. • Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Ukrainian-speaking part of Poland, Moldavia (part of Romania) all absorbed into USSR. • Part of German East Prussia around Königsberg (Kaliningrad) becomes Soviet. • “Soviet bloc” of occupied countries is formed: East Germany (GDR), Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria. “Personality Cult” • • • • • • Stalin as an Icon People cried when he died Religious-style indoctrination Forged history Stalin=Motherland Denounced by Nikita Khrushchev on 25 February1956 at 20th Communist Party congress. • Most popular leader in Russia today Question • Was Stalin inevitable, i.e., would another leader (for example, Leon Trotsky) have acted in the same way?