* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Corporate Creativity
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Morgenthau Plan wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
May 1940 War Cabinet Crisis wikipedia , lookup
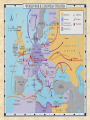
World War II Europe in the 1930’s • Adolph Hitler – Rise because of WWI – Criticized rather than submitted a plan for progress – Forced his way into the chancellorship Europe in the 1930’s • Austria – Hitler threatened invasion – Merged with Germany • Czechoslovakia – German-speaking area turned over – Meeting in Munich • Peace declared – Non-aggression pact with Stalin Germany’s Attack in Europe • Polish invasion – Sept. 1, 1939 – Blitzkrieg – Warsaw Ghetto "The Nazi occupation of Poland was horrific. Twenty percent of the Polish people died in forced labor, of hunger, or from fighting. Resistance was impossible. Even the feeblest opposition brought devastating, over-whelming reprisals. Drs. Lazowski and Matulewicz decided to resist anyway, and their solution was brilliant. They knew that the Germans were terrified of a typhus outbreak. So they injected dead typhus bacteria into various patients, then sent blood samples to the German authorities. The blood tested positive for typhus. The Germans conducted more tests, and most were also positive. The occupation authorities quarantined the area. The people were not deported for slave labor and German troops stayed away. Drs. Lazowski and Matulewics spared their neighbors the worst of World War II, because even impossible problems have solutions." – Thorpe, Scott, How to Think Like Einstein, Barnes & Noble Books, Inc., 2000, p. 127. Germany’s Attack in Europe • Denmark, Holland • Norway (Quisling) • Belgium and France – Dunkirk • Britain – Winston Churchill Dunkirk “...We shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end...We shall fight in the seas and oceans...We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landinggrounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender...” — Winston Churchill “We have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat.” — Winston Churchill “Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will say, ‘This was their finest hour.’” — Winston Churchill “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.” — Winston Churchill Germany’s Attack in Europe • Balkans • Russia • US isolation Maximum Axis Control (Sept 1942) Allied Counterattacks in Europe • Soviet • North Africa • Italy • Normandy • Battle of the Bulge Allied Counterattacks in Europe • Surrender – Stalin, Churchill, Roosevelt • The Marshall Plan "Men occasionally stumble over the truth, but most of them pick themselves up and hurry off as if nothing happened." – Churchill, Winston, quoted in Thorpe, Scott, How to Think Like Einstein, Barnes & Noble Books, Inc., 2000, p.119. Japan’s Invasion • China – Blockade • Pearl Harbor • Southeast Asia Allied Counterattacks in the Pacific • Midway • Southeast Asia • Island hopping • Japanese main islands Pacific War Creativity • How was creativity affected by the war? • What was the center of creativity? "I am tired and sick of war. Its glory is all moonshine... War is hell." – William Tecumseh Sherman (quoted in John Keegan, A History of Warfare, 1993, 6) “If a man does his best, what else is there?” -General George S. Patton (1885-1945)