* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The USSR in World War II
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
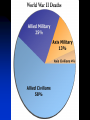
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
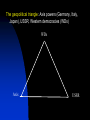
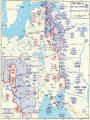
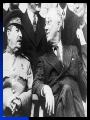
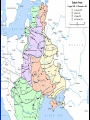
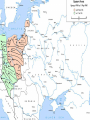
The USSR in World War II London: monument to Roosevelt and Churchill The Big Three: Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin at Yalta, Feb.1945 The ultimate test of the Russian battle order has usually been war The Romanov Empire failed that test in WWI – and fell By the time of the next test – WWII, the Russian state was transformed into a more formidable machine The “socialist” organization of the country was aimed at making the state more militarily capable A similar logic unfolded in Italy and Germany under different forms of “socialism” They talked of “socialism”, but they meant winning world wars If the essence of War Communism was to win the Russian civil war, the essence of Stalinism was to win in World War II Belief in the inevitability of war – of one kind or another The slide to war Forced modernization The Great Terror of 1937-38 Skirmishes in the 1930s: China, Spain Diplomatic maneuvers in 1934-39: attempts to contain the fascist powers, then a non-aggression pact with Hitler Global civil war and interstate conflict Fierce Left-Right struggles in European countries since WWI, the lure and fear of revolution Stalinism in Russia as a new stage in the Russian civil war: forced modernization to strengthen the state and make it fit for the next round of interstate wars Fascism as a new stage in European Left-Right conflict: to defeat the Left internally and externally Projection of the internal conflicts on interstate relations The Spanish Civil War Appeasement: betrayal of Czechoslovakia The fall of democracies across Europe due to both internal (Left vs. Right) and external (actions of Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union) The geopolitical triangle: Axis powers (Germany, Italy, Japan), USSR, Western democracies (WDs) WDs Axis USSR As a state committed to world revolution, the Soviet Union was viewed as a threat by Western elites The rise of fascism was partly a response to the threat – and anticommunism was one of the motives of Western appeasement of Hitler But the Axis powers were also challenging other Great Powers in Europe and Asia – the continuing conflict between empires In the 1920s-early 1930s, before Hitler’s coming to power in Germany, USSR cooperated with Germany against Britain and France When Germany became a radical anticommunist force, USSR and Western democracies discussed “collective security” arrangements to prevent Hitler’s aggression – without success Then Britain, France and the USSR made their separate deals with Hitler, which enabled him to start World War II Britain and France hoped to channel Hitler’s aggression to the East, toward conflict with Russia – reluctant to fight Germany Hitler was determined to prevent Western democracies and USSR from joining forces: beat them one by one Stalin was determined to avoid war with Germany as long as possible – but convinced that such a war was inevitable 1939: A divergence of interests between USSR and Western democracies – and a convergence of interests between Germany and USSR The unexpected deal was logical – but only temporary Moscow, August 23, 1939: German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop signs non-aggression pact with Russia Hitler and Mussolini in Munich, June 1940 1939-1941: growing tensions between USSR and Germany At first: division of the spoils. But then: Germany’s unexpected triumph in the West emboldens Hitler Hitler’s strategic goal of conquering the USSR was never abandoned – for geopolitical and ideological reasons Stalin expected the new war to generate a new wave of revolutions – and intended to get involved By 1941, his fear of German power became the overwhelming factor He was appeasing Hitler – and preparing for war against him at the same time Each of the two intended to strike first Hitler preempted Stalin and delivered a crushing blow Operation Barbarossa June 22, 1941 Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along an 1,800 mile front Goals: Total destruction of the Soviet state Colonization of the Soviet territory, together with allies – Japan especially Enslavement of the population, turning the territory into a resource base for the Third Reich The Nazi invasion : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= StYywx7Uzok&feature=related BBC, “War of the Century”, Parts 2,3,4 Hitler explaining the future war against Russia, March 1941: “It is a struggle between two ideologies… Communism presents an enormous danger for the future. A communist has never been and never will be our comrade. It is a struggle for annihilation. If we think otherwise, then, even if we should crush the enemy, the communist threat will rise again in 30 years… This war will be vastly different from the onw in the West. In the East, brutality is a benefit for the future. Commanders must be ready for sacrifice and overcome their doubts.” From the diary of General F. Halder, Chief of Staff, Land Forces, Germany German poster depicting Soviets: “The lower race” STAKES IN THE BATTLE FOR RUSSIA Will the Soviet state survive? Will Soviet society as a product of the transformations since 1917 be crushed? Will the Soviet Union become a German colony? How many Soviet citizens will survive? Will genocide become a new global norm? What will become of the world? In the first 10 days, German armies moved 550 km into Soviet territory In the first 20 days of the war, the Red Army lost 1/5 of its manpower – 600,000 men By July, 20 mln. Soviets found themselves under occupation. Nazi terror began. Resistance Redeployment of industry to the East Victims of German occupation Japanese terror in occupied China Resistance http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4IAfigTgzmU&feature=re lated The Battle of Moscow: September 1941 – January 1942 Moscow, October 1941 Women digging anti-tank moats near Moscow Antitank barriers in downtown Moscow November 7th, 1941: military parade in Red Square Marshal Georgi Zhukov, commander of Soviet forces in the Battle of Moscow Women in the war: medics Women in the war: pilots Children workers assembling weapons Partisans Partisans The Battle of Moscow was the first Soviet victory over Nazi Germany. Casualties in the battle of Moscow: 250,000 – 400,000 German 600,000 – 1,300,000 Soviet The Siege of Leningrad September 1941 – November 1943 The Germans and Finns failed to take the city The cost to Soviet population: About 1.4 million people were rescued by military evacuation from the besieged city of Leningrad in two years between September 1941 and November 1943. Another 1.2 million civilians perished in the city. In 1939-41, states of the Global Right attacked the world order, aiming at global primacy Western democracies joined forces with the communist state in a defensive Center-Left coalition against the Right The battle for Russia became decisive for the defeat of the Global Right US and British aid to the Soviet ally, 1941-45: Food - $1.5 bln. in Automobiles – 427,000 Warplanes – 22,000 Tanks – 13,000 Warships – over 500 Explosives – 350,000 tons Other supplies Total estimated cost of Allied aid to USSR in contemporary prices – $100 bln. America at war: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G5u8 E4s57I0&feature=related The turning point of World War II: Stalingrad http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G5u8 E4s57I0&feature=related The Battle of Stalingrad claimed over two million casualties, more than any other battle in human history It was also one of the longest: it raged for 199 days Killed, wounded or captured at Stalingrad: Soviets: 1,290,000 Germans and allies: 850,000 Red flag over Berlin, May 1945 Checking out Hitler’s headquarters, May 1945 Berlin, 1945: surrender of German High Command Ovens in Buchenwald concentration camp Survivors of a Nazi concentration camp June 24, 1945: Marshal Zhukov leads Victory Parade in Red Square Victory Parade in Red Square, June 24, 1945: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QDQ2 gQttPBs&NR=1 Soviet losses in World War II Over 27 mln. killed (13.6% of the population) Of those who survived, 29 mln. took part in the fighting (including 0.8 mln. women) Battlefield losses – est. 8 mln. (Germany lost 4 mln.) 5 mln. POWs (of them 3 mln. died in concentration camps) US and British POWs – 232,000 (8,500 died) German POWs – 2.4 mln (0.45 mln. died) 1710 cities and 70,000 villages completely or partially destroyed 40,000 hospitals, 84,000 schools, 43,000 libraries destroyed Historically unprecedented level of damage suffered by any country The war took all nine of her sons http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=da1e9Sz8I8k&feature=related