* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit VIII: Prelude to Another World Conflict
India in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
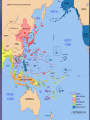
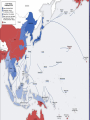
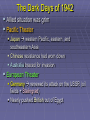
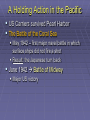
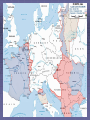
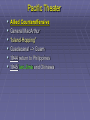
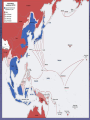
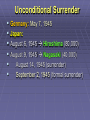
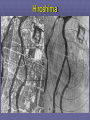
US Response to German Aggression Neutrality a heated issue in US Britain & France in desperate need of US airplanes & other material Neutrality Acts set restrictions 1935 & 1936: outlawed arms sales or loans to nations @ war 1937: passed in response to Spanish Civil War Banned arms sales & loans to nations undergoing civil wars US Response to German Aggression FDR calls Congress into a special session; wants them to lift the arms embargo After 6 weeks Neutrality Act of 1939 Ability for belligerents to purchase war materials; ONLY “cash and carry” FDR authorized to declare “danger zones” Hurts China; Helps Britain & France American Preparedness and Aid to the Allies (1939-1941) Changes in Public Opinion FDR awakens Americans to national security threat The Fall of France - Britain alone Congress “all measures short of war” American Preparedness and Aid to the Allies (1939-1941) Military Preparedness Congress (1940) (1) two-ocean navy and a huge air force (2) Selective Service Act Destroyer-Naval Base Deal of 1940 50 “over age” destroyers –> bases in W. Hemisphere Lend Lease Act of 1941 UK cash nearly exhausted; FDR new leg. US –> “arsenal of democracy”; Lend-Lease Act (aid to England) Merchants convoyed part way by US Navy American Preparedness and Aid to the Allies (1939-1941) Embargo on Strategic Materials Japan US - Open Door Policy protests against occupation of French Indochina (1940-1941) Embargo: gasoline, scrap iron, etc.; assets in US “frozen” The Pacific Theater US – Japanese Relations 1940-1941 Embargo Against Japan Spring 1940 – France and the Netherlands fall to Germany (colonies in Asia vulnerable) Before the month ended, Vichy France agrees to cede control of French Indochina US responds w/ an embargo (scrap metal, oil, and aviation fuel) US – Japanese Relations 1937-1941 (cont’d) Japan dependent on US for: 90% of its scrap metal 60% of its oil The following day Japan announced it formed a military alliance with Germany and Italy July 1941, Japan occupied French Indochina US Response froze all Japanese accounts in American banks prevents Japan from buying any goods from the US Later US-Japanese negotiations fail Pearl Harbor 7:55 a.m. on Sunday, Dec. 7, 1941: Japan attacks while Japanese diplomats were meeting with Hull US military had been warned of an attack but expected it in SE Asia Most of the fleet caught at anchor – only the carriers were not docked A catastrophe for the US 19 ships destroyed (6 battleships) 180 aircraft destroyed 2,300 killed + 2,000 wounded Pearl Harbor on October 30, 1941 President Roosevelt, wearing a black armband, signs the Declaration of War against Japan on December 8, 1941 Three days later, Germany and Italy declare war on the US – US responds in kind Japanese Offensives 1941-1942 Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Japanese launched offensives against Allied forces in South East Asia Also launched simultaneous attacks on Hong Kong, British Malaya and the Philippines. Battle of Bataan – General MacArthur forced to flee (one of the worst US defeats) over 70,000 US and Filipino POWs Fall of Singapore - Largest surrender of British-led military personnel in history The Dark Days of 1942 Allied situation was grim Pacific Theater Japan western Pacific, eastern, and southeastern Asia Chinese resistance had worn down Australia braced for invasion European Theater Germany renewed its attack on the USSR (oil fields + Stalingrad) Nearly pushed British out of Egypt World War II (animated) The Allies Look for an Effective Military Strategy Admiral Ernest King (US) and General Douglas MacArthur proposed the US focus on the defeat of Japan FDR accepted the British view that the Allied prime target should be Germany and Italy General George Marshall and Dwight Eisenhower urged an Allied invasion of France by spring 1943 The War in North Africa Jan.-July 1942: Erwin Rommel and the Afrika Korps win victories El Alamein Operation Torch November 1942: US and British North Africa and easily defeat Vichy forces there By May 1943 Axis forces surrender A Holding Action in the Pacific US Carriers survived Pearl Harbor The Battle of the Coral Sea May 1942 – first major naval battle in which surface ships did not fire a shot Result: the Japanese turn back June 1942 Battle of Midway Major US victory Air War Over Germany Allies attack German cities “to disrupt the German war machine” Increased intensity 1943-1945 (day & night) The Invasion of Italy Mussolini’s government fails unconditional surrender & German occupation The Eastern Front A New German Blitzkrieg: May – Nov. 1942 success Battle of Stalingrad - Hitler’s order: “no retreat” German 6th Army: 300,000 men trapped 30 January 1943 F.M. Paulus surrenders The USSR turns the tide US Lend-Lease Marshal Zhukov - “defense in depth” Stalin - scorched earth; industry in Urals and Siberia Battle of Stalingrad German 6th Army Surrender Battle of Kursk D-Day and the Liberation of France D-Day Invasion Liberation of Paris The Battle of the Bulge German objectives of the Ardennes Offensive Red Army victorious in Berlin Pacific Theater Allied Counteroffensive General MacArthur “Island-Hopping” Guadacanal –> Guam 1944 return to Philippines 1945 Iwo Jima and Okinawa General Douglas MacArthur wading ashore at Leyte Unconditional Surrender Germany: May 7, 1945 Japan: August 6, 1945 Hiroshima (80,000) August 9, 1945 Nagasaki (40,000) August 14, 1945 (surrender) September 2, 1945 (formal surrender) HIROSHIMA & Little Boy Hiroshima Fat Man A mushroom cloud from the nuclear explosion over Nagasaki rising 60,000 feet (18 km) into the air on the morning of August 9, 1945. Representatives of Japan stand aboard the USS Missouri prior to signing of the Instrument of Surrender. Huge formation of American planes over USS Missouri and Tokyo Bay celebrating the signing, September 2, 1945.