* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The War Ends
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Resistance in the German-occupied Channel Islands wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
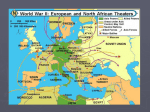
The War Ends The Third Reich Collapses • Well before the war ended the allies were aware that the Germans were committing atrocities • Roosevelt felt the best way to put an end to the concentration camps was to destroy the Nazi regime • To do that they would have to break out of Normandy, liberate France and conquer Germany • • • • D-Day had been a major success, but the surrounding fields of Normandy were hedgerows-dirt walls several feet thick covered in shrubbery-they were built for livestock but allowed Germans to fiercely defend their positions The battle of the hedgerows ended on July 25, 1944 when 2,500 American bombers blew a hole in German lines and American tanks rushed through As the Allies broke out of Normandy the French resistance-citizens who organized a resistance, staged a rebellion On August 25, the streets of Paris were filled with citizens as the city was liberated-three weeks later American troops were only 20 miles from the German border Battle of the Bulge • As the Allies closed in on Germany, Hitler decided to stage one last desperate offensive. His goal was to cut off Allied supplies coming through the port of Antwerp, Belgium. • December 16,1944 the battle began with six inches of snow on the ground and bitter cold-German soldiers caught Americans by surprise-as the Germans moved west their lines bulged outward-the attack became known as the Battle of the Bulge Battle of the Bulge • Part of the German plan called for the capture of the town of Bastogne, where several important roads converged. If the Allies held Bastogne, it would greatly delay the German advance. • At this town Germans surrounded the American forces that refused to surrender-Eisenhower sent Patton to rescue themIn three days-through a snowstorm-Patton’s troops slammed into German lines-when the weather cleared Allied aircraft began hitting German depots • On Christmas Eve out of fuel and weakened by heavy lossesthe Germans were forced to stop their move towards Antwerp. Two days later Patton’s troops were in Bastogne. The United States won the Battle of the Bulge and with the German arm being weakened there was little to stop the Allies from entering Germany V-E Day: The War Ends in Europe • While the Americans and British were liberating France the Soviets began a massive attack on the Germans in Russia. By the time the Battle of the Bulge ended the Soviets had driven Hitler’s forces back across Poland. By February of 1945, they were only 35 miles from Berlin. • Germany was now under attack from the East and West. Soon the Americans would cross the last line of defense-the Rhine River and enter the heart of the Nazi war machine. The Death of Hitler (?) • As German defenses crumbled-Americans closed in on Berlin. • Deep inside a Berlin bunker, Adolph Hitler knew the end was near. On April 30, 1945, he put a pistol in his mouth and pulled the trigger. His secretary carried his body outside and burned it. • The United States ordered an unconditional surrender. On May 7, 1945 Germany surrendered. The next day May 8, 1945 was declared V-E Day-the war in Europe was over Japan is Defeated • Sadly Franklin Roosevelt would not live to see the defeat of Germany-On April 12, 1945 while vacationing in Warm Springs, Georgiahe suffered a stroke and died • Vice President Harry S. Truman was now president ( quote pg 767 ). He at once began making decisions. Truman would have to make some of the most difficult decisions of the war. Island Hopping in the Pacific • To defeat the Japanese the United States would have to take back Japanese controlled islands one by one. This strategy was referred to as island hopping. • Fighting in the Pacific Theater was terrible and extremely costly. One reason was the terrible weather conditions-at times weeks of monsoon like rain, volcanic ash on islands, and thick rainforests. • On each island we faced an enemy that had been preparing defenses for years and that refused to surrender. Often fighting did not end until almost every Japanese soldier was killed or committed suicide. • Islands like Peleliu and Guadalcanal were death traps. Allied forces would fight for weeks and months to control the island only to develop a false sense of security before fighting would erupt after short periods of stoppage. Civilian casualties were high in many of these locations and soldiers were faced to make gut-wrenching decisions during combat. Uncommon Valor on Iwo Jima • On November 24, 1944 bombs began falling on Tokyo for the first time since the Doolittle raid. Unfortunately the bombing was ineffective because the bombs kept missing their targets. Japan was to far away and by the time the bombers got there coordinates were inaccurate due to changes in winds or navigational errors. • It was determined that the best solution was to invade a nearby island-they chose Iwo Jima Uncommon Valor on Iwo Jima • • • • The island was perfectly located, but was covered with rocky terrain, caverns, and dozens of caves, as well as a dormant volcano Mount Surabachi The Japanese had built a network of tunnels on the island and concrete bunkers On February 19, 1945- 60,000 U.S. Marines landed on Iwo Jima. As the troops left there amphtracs they sank up to their ankles in soft ash as Japanese artillery began to pound the invaders ( quote pg. 768 ) The Marines would crawl inch by inch, fighting their way with flamethrowers and explosives destroying Japanese bunkers-6,800 Marines would die on Iwo JimaAdmiral Chester Nimitz would say “ uncommon valor was a common virtue” Firebombing Devastates Japan • Curtis LeMay-the commander of the B-29’s-decided to use a new strategy to help the bombers hit their targets-they dropped bombs filled with napalm-a kind of jellied gasoline-even if they missed the fire would spread to the targets • The use of these firebombs was very controversial-the fires would kill civilians-but there was seemingly no other way to destroy Japanese production facilities-strong winds spread the fires and thousands asphyxiated-80,000 would die and 250,000 buildings were sestroyed-67 cities were bombed (quote pg. 768 ) The Invasion of Okinawa • Despite the bombing by the spring of 1945 there were no signs that Japan was ready to surrender-It became clear Japan would have to be invaded • Okinawa was chosen as the site-Japanese soldiers took positions in the mountains of Okinawa-facing constant machine and artillery fire, American soldiers fought there way up steep slopes and by June 22, 1945 the island was captured at the expense of 12,000 soldiers The Terms of Surrender • Shortly after Okinawa was captured the emperor urged the government to find a way to end the war. The problem is that America was demanding an unconditional surrender. The Japanese were willing to surrender, but the emperor would have to stay in power. Most Americans blamed the emperor for the war and demanded he be removed. Truman did not wish to go against public opinion. He also knew that the United States was developing a new weapon that would force Japan to surrender-the weapon was the atomic bomb. The Manhattan Project • In 1939 Leo Szilard, one of the worlds top physicists, learned that German scientist had split the uranium atom. He believed that this could release an enormous amount of energy. • Worried that the Germans were gone to develop a weapon using this energy, he asked the worlds most famous physicists Albert Einstein to sign his letter to President Roosevelt warning that by using uranium-” extremely powerful bombs of a new type may be constructed.” The Manhattan Project • Roosevelt responded by setting up a scientific committee to study the issue. They were skeptic until they met with British scientists and 1941 that were already working on the bomb-they were sop impressed they began to work on building a bomb. • The American project was called the Manhattan Project and was headed by General Leslie R. Groves. After the first nuclear reactor was built at Chicago University-Groves organized a team of engineers and scientists to build and test an atomic bomb at a secret lab in Los Alamos, New Mexico-the team was lead by Robert Oppenheimer-On July 16, 1945-they detonated the worlds first atomic bomb near Alamogordo, New Mexico. • “I have become death, the destroyer of worlds.”-from the Mayan Book of Death • J Robert Oppenheimer Japan Surrenders • Faced with such massive destruction and the shock of the Soviets entering the war-Japan surrendered-August 15, 1945-V-J Day • On the other side of the world Americans celebrated. Quote pg. 771 • The long war was finally over • Outline the following two topics: • The Nuremberg Trials • The Creation of The United Nations