* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KBS - teachmath1729
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Pattern recognition wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Time series wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
Multi-armed bandit wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
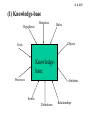
AI & KBS AI & KBS Overview * A brief history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) - requirements of KBS * Introduction to Knowledge-Based Systems (KBS) - definition - architecture - development tools * Examples of some KBS * Characteristics of KBS AI & KBS 1. The Evolution of AI (1) The request of an intelligent machine - early robots ---- electro-mechanical devices - later robots ---- use computers, ‘dumb’ limited and pre-specified tasks - ideal robots ---- intelligent machine combines the memory accuracy, and speed of computers with the intelligence and flexibility of humans. AI - Computer programs that undertake tasks that, if done by people would be described as requiring intelligence. * Can computers think? - Turing Test Imitation game - machine mistaken for a human “Computing machinery and intelligence”, Alan Turing, 1950 Wall AI & KBS In the Turing test a human communicates with an unseen respondent through a terminal, not knowing if the respondent is a person or a machine. If the tester mistakes computer answers for human answers, the computer successfully passes the Turning test. AI & KBS ELIZA • Developed by MIT 1966 • Called ELIZA after Shaws play - it could be taught to speak increasing well • It picked up words from its conversational partner • Transform this into a canned response ELIZA’s opening statement (appears on the terminal screen): Do you have any problems? Human: Yes. I am unhappy. (types response on the terminal screen) ELIZA: Why are you unhappy? Human: My friend is mean to me. ELIZA: Tell me about your friend. (Rogerian Psychoanalyst) It could fool people into thinking it was a real person but it contained no intelligence. AI & KBS (2) Game playing - early AI emphasis - Board games: chess, checkers, & 16-puzzle - No ambiguity in representation of the board configuration - Rules generate large search space: require heuristics Move 1-X 2-O 3-X 4-O 5-X Tic-Tac-Toe game AI & KBS (3) Theorem proving - The proving of mathematical theorems by a computer program - Theorems automatically proven from a given set of axioms - Theorems & axioms expressed in logic and logical inferences applied - First theorem prover developed in mid-50s but breakthrough in 1960s - Breakthrough came after introduction of Resolution inference rule AI & KBS Theorem proving -Resolution All Irish are Europeans. Dave is a Irish. Therefore, Dave is a European AI & KBS (4) Problem solving - GPS (General Problem Solver) focus on systems with general capability for solving different types of problems - Problem represented in terms of initial state, wished-for final state (goal) and a set of legal transitions to transfer states into new states - Using states & operators, GPS generates sequence of transitions that transform initial state into final state AI & KBS - Problems with GPS: * efficiency in choosing path to reach the goal * GPS did not use specific info about problem at hand in selection of state transition * GPS examined all states leading to exponential time complexity * breakthrough in AI towards more specialised problem-solving system, i.e., Knowledge-based systems AI & KBS (5) Other AI fields - a tree representation AI & KBS (6) KBS as real-world problem solvers - Problem-solving power does not lie with smart reasoning techniques nor clever search algorithms but domain dependent real-world knowledge - Real-world problems do not have well-defined solutions - Expertise not laid down in algorithms but are domain dependent rules-of-thumb or heuristics (cause-and-effect) - KBS allow this knowledge to be represented in computer & solution explained AI & KBS 2. Knowledge-based Systems: A definition - A system that draws upon the knowledge of human experts captured in a knowledge-base to solve problems that normally require human expertise. - Heuristic rather than algorithmic - Heuristics in search vs. in KBS general vs. domain-specific - Highly specific domain knowledge - Knowledge is separated from how it is used KBS = knowledge-base + inference engine AI & KBS 3. KBS Architecture Facts Heuristics, etc. Explanation Queries End-user interface Conclusions Expertise Recommendations for action Inference engine Knowledge -base Knowledgerepresentation schema AI & KBS (1) Knowledge-base Hypothesis Heuristics Rules Objects Facts Knowledgebase Processes Attributes Events Definitions Relationships AI & KBS (2) Knowledge representation formalisms & Inference KR * Logic * Production rules * Semantic nets & Frames * Case-based Reasoning Inference Resolution principle backward (top-down, goal directed) forward (bottom-up, data-driven) Inheritance & advanced reasoning Similarity based AI & KBS (3) KBS tools - Shells - Consist of KA Tool, Database & Development Interface - Inductive Shells - simplest - example cases represented as matrix of known data (premises) and resulting effects (conclusions) - matrix converted into decision tree or IF-THEN statements - examples selected for the tool - Rule-based shells - simple to complex - IF-THEN rules AI & KBS - Hybrid shells - sophisticate & powerful - support multiple KR paradigms & reasoning schemes - generic tool applicable to a wide range - Special purpose shells - specifically designed for particular types of problems - restricted to specialised problems -Scratch - require more time and effort - no constraints like shells - shells should be investigated first AI & KBS 4. Some example KBSs (1) DENDRAL (chemical) - Pioneering work developed in 1965 for NASA at Stanford University by Buchanan & Feigenbaum - DENDRAL infers the molecular structure given mass spectral data - Traditional method of generate-and-test, difficulty: millions of possible structures might be generated to account for data - Experts used rules-of-thumb to weed-out structures that are unlikely to account for the data - Encoded this expertise & produced program which performed as well as an expert chemist AI & KBS (2) MYCIN (medicine) - Developed in 1970 at Stanford by Shortcliffe - Assist internists in diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases: meningitis & bacterial septicemia - When patient shows signs of infectious disease, culture of blood and urine set to lab (>24hrs) to determine bacterial species - Given patient data (incomplete & inaccurate) MYCIN gives interim indication of organisms that are most likely cause of infection & drugs to control disease - Drug interactions & already prescribed drugs taken into account - Able to provide explanation of diagnosis (limited) (3) XCON/RI (computer) AI & KBS - Configures DEC’s VAX, PDP11 and VAX - DEC offers the customer a wide choice of components when purchasing computer equipment, so that client achieves a custom-made system - Given the customer’s order, configuration is made, perhaps involving component replacement or addition - Problem: information subject to rapid change & configuring a computer system requires skills and effort - Since 1981, XCON with XSEL assists DEC agents in drawing up orders. AI & KBS (4) DRILLING ADVISOR (industry) - Developed in 1983 by Teknowledge for oil company to replace human drilling advisor - Problem:drill bits becoming stuck - Difficulty: lack of subsurface information on location & condition on end of drill - (scarcity) expert examines rock pieces, mud, lubricant brought up by drilling to determine cause - Drilling Advisor uses geological site information, conditions of problem, historical information about other problems experienced in the past - Provide recommendation to correct problem & advice on how to change current practices to avoid problem AI & KBS (5) Human Resource Management HRM facilitates the most effective use of employees to achieve organisational and individual goals HRM KBS forms part of overall strategy (includes DSS & EIS) KBS helps decision making for HRM managers with heuristic knowledge in unstructured & semi-structured problems (job placement & pay rises) Using semantic nets & Prolog, illustrates use of KBS in HR planning, recruiting, compensation & labourmanagement relations (see Human resource management expert systems technology, Byun & Suh, ES, May 94, 11:2) AI & KBS 5. Typical tasks of KBS (1) Diagnosis - To identify a problem given a set of symptoms or malfunctions. e.g. diagnose reasons for engine failure (2) Interpretation - To provide an understanding of a situation from available information. e.g. DENDRAL (3) Prediction - To predict a future state from a set of data or observations. e.g. Drilling Advisor, PLANT (4) Design - To develop configurations that satisfy constraints of a design problem. e.g. XCON (5) Planning - Both short term & long term in areas like project management, product development or financial planning. e.g. HRM AI & KBS (6) Monitoring - To check performance & flag exceptions. e.g., KBS monitors radar data and estimates the position of the space shuttle (7) Control - To collect and evaluate evidence and form opinions on that evidence. e.g. control patient’s treatment (8) Instruction - To train students and correct their performance. e.g. give medical students experience diagnosing illness (9) Debugging - To identify and prescribe remedies for malfunctions. e.g. identify errors in an automated teller machine network and ways to correct the errors AI & KBS 6. Advantages & Limitations (1) Advantages - Increase availability of expert knowledge expertise not accessible training future experts - Efficient and cost effective - Consistency of answers - Explanation of solution - Deal with uncertainty AI & KBS (2) Limitations -Lack of common sense -Inflexible, Difficult to modify - Restricted domain of expertise - Lack of learning ability - Not always reliable AI & KBS Overview - Traditional AI & its limitations for real-world problem solving - KBS emergence in 60’s emphasis on specific domain-knowledge rather than GPS separation of knowledge and reasoning - KBS basic components: knowledge-base, inference engine & user-interface - Examples - Advantages & limitations