* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Foundations of AI and Intelligent Agents
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model in biology wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
How to Create a Mind wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Agent (The Matrix) wikipedia , lookup
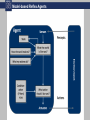
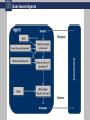
Computer Science & Engineering, University of Nevada, Reno CS482/682 Artificial Intelligence Lecture 1: The Foundations of AI and Intelligent Agents 25 August 2009 Instructor: Kostas Bekris 482/682 What is AI? Humanly vs. Rationally Thinking “The automation of activities that “The study of mental faculties we associate with human thinking, through the use of computational activities such as decision-making, models.” problem solving, learning” (Winston, 1992) (Bellman, 1978) vs. “AI is concerned with rational “The art of creating machines that action... and studies the design of perform functions that require rational agents. A rational agent intelligence when performed by acts so as to achieve the best people” expected outcome” (Kurzweil, 1990) (S.R. & P.N., 1995) Acting 482/682 What is AI? Humanly vs. Rationally Thinking “The automation of activities that “The study of mental faculties we associate with human thinking, through the use of computational activities such as decision-making, models.” problem solving, learning” (Winston, 1992) (Bellman, 1978) vs. “AI is concerned with rational “The art of creating machines that action... and studies the design of perform functions that require rational agents. A rational agent intelligence when performed by acts so as to achieve the best people” expected outcome” (Kurzweil, 1990) (S.R. & P.N., 1995) Acting 482/682 Acting Humanly 482/682 What is AI? Humanly vs. Rationally Thinking “The automation of activities that “The study of mental faculties we associate with human thinking, through the use of computational activities such as decision-making, models.” problem solving, learning” (Winston, 1992) (Bellman, 1978) vs. “AI is concerned with rational “The art of creating machines that action... and studies the design of perform functions that require rational agents. A rational agent intelligence when performed by acts so as to achieve the best people” expected outcome” (Kurzweil, 1990) (S.R. & P.N., 1995) Acting 482/682 Thinking Humanly 482/682 What is AI? Humanly vs. Rationally Thinking “The automation of activities that “The study of mental faculties we associate with human thinking, through the use of computational activities such as decision-making, models.” problem solving, learning” (Winston, 1992) (Bellman, 1978) vs. “AI is concerned with rational “The art of creating machines that action... and studies the design of perform functions that require rational agents. A rational agent intelligence when performed by acts so as to achieve the best people” expected outcome” (Kurzweil, 1990) (S.R. & P.N., 1995) Acting 482/682 Thinking Rationally 482/682 What is AI? Humanly vs. Rationally Thinking “The automation of activities that “The study of mental faculties we associate with human thinking, through the use of computational activities such as decision-making, models.” problem solving, learning” (Winston, 1992) (Bellman, 1978) vs. “AI is concerned with rational “The art of creating machines that action... and studies the design of perform functions that require rational agents. A rational agent intelligence when performed by acts so as to achieve the best people” expected outcome” (Kurzweil, 1990) (S.R. & P.N., 1995) Acting 482/682 Acting Rationally 482/682 Intelligent Agents 482/682 Environments and their properties 482/682 Environments and their properties 482/682 Structure of the Course Part 1. Decision-Making in Deterministic Environments • Single-agent: Dynamic programming and search, informed search and heuristics, randomized search, genetic algorithms, constraint satisfaction and path planning • Multi-agent: Adversarial search (mini-max and expecti-mini-max) Part 2. Decision-Making in Stochastic Environments • Single-agent: Bayesian networks, Hidden Markov Models, Kalman and Particle filters, Decision and Utility theory, Markov Decision Processes • Multi-agent: Introduction to Game Theory Part 3. Learning in Unknown Environments • Supervised learning: Decision trees, Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks • Unsupervised learning: Introduction to Reinforcement Learning 482/682 482/682 Where are we now? 482/682 What are my personal interests? Physicall yGrounde d Agents Robotics Computer Games Human Assistants Agents that must and do appropriately model and reason about the physical properties of their environment: • algorithmic generation of motion (motion planning) • state estimation problems given noisy sensors • and distributed message-passing coordination 482/682 How do agents work? 482/682 Reflex Agents 482/682 Model-based Reflex Agents 482/682 Goal-based Agents 482/682 Utility-based Agents 482/682 Learning Agents