* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download s-cheran-g-gargano
Genetic algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model in biology wikipedia , lookup
Hough transform wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Agents, V-ants and
3D Reconstruction
for
Lung CT Imaging
Sorin Cr istian Cheran - ASP, INFN sez. Torino, Università degli Studi di Torino
Gianfranco Gargano - INFN sez. Bari, Università degli Studi di Bari
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Index
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Materials
2D Segmentation
Slides Interpolation
3D Matrix/World Creation
Bronchial Tree 3D Reconstruction
Nodules Detection
Conclusions
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
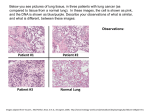
The Lung and The CTs
[LUNG]
1.Either of the pair of organs occupying the cavity of the thorax that effect the aeration of the blood.
2.Balloon-like structures in the chest that bring oxygen into the body and expel carbon dioxide from
QuickTime™ and a
YUV420 codec decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
the body
[TYPES]
1.Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- 20% of all lung cancers
2.Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
(NSCLC) - 80% of all lung cancer
[Risks]
QuickTime™ and a
YUV420 codec decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
In the United States alone, it is
estimated that 154,900 died
from lung cancer in 2002. In
comparison,is estimated that
126,800 people died from
colon, breast and prostate
cancer combined, in 2002.
[LUNG CANCER]
Lung Cancer happens when cells in the lung begin to grow out of control and can than
invade nearby tissues or spread throughout the body; Large collections of this out of
control tissues are called tumors.
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Starting Point
Framework
-pending collaboration’s approving,
discussion, ideas and improvements
-Mapping of the DICOM structure into
classes.
-Tools for manipulating the DICOM Files.
-“We can do it ” experimental GUI
Border Detection
-At the moment two approaches are
available.
-Left the algorithm developed at Pisa
-Right the algorithm developed at
Lecce
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Image Interpolation - Theory
[IDEA]
In order to provide a richer environment we are thinking of using interpolation methods that will
generate “artificial images” thus revealing hidden information.
[RADON RECONSTRUCTION]
Radon reconstruction is the technique in which the object is reconstructed from its projections. This
reconstruction method is based on approximating the inverse Radon Transform.
[RADON Transform]
The 2-D Radon transform is the mathematical relationship which maps the spatial domain (x,y) to
the Radon domain (p,phi). The Radon transform consists of taking a line integral along a line (ray)
which passes through the object space. The radon transform is expressed mathematically as:
{R}( p, )
(x, y)(x cos y sin p)dxdy
[FILTERED BACK PROJECTION - INVERSE R.T.]
It is an approximation of the Inverse Radon Transform.
[The principle] Several x-ray images of a real-world volume are acquired
[The Data] X-ray images (projections) of known orientation, given by data samples.
[The Goal] Reconstruct a numeric representation of the volume from these samples.
[The Mean] Obtain each voxel value from its pooled trace on the several projections.
[Resampling] At this point one can obtain the “artificial slices”
[Reslicing] An advantage of the volume reconstruction is the capability of obtaining new perpendicular slices on the
original ones.
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Image Interpolation - Graphical Representation (I)
y 0 d
(x, y,z )dy
Rz0 (x,90)
0
y0
Rz0 (y,0)
l
(x, y,z )dx
0
0
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Image Interpolation - Graphical Representation (II)
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Agents - Artificial Intelligence
[AUTONOMY] in controlling itself
[REACTIVITY] to the change of the environment
What is an Agent?
[PRO-ACTIVENESS] in taking the initiative to select
adequate behaviour to reach the goal
[SOCIAL ABILITY] of interact with other agents via languages
[AGENTS LANGUAGES]
Are software systems for programming and experimenting with agents.
[AGENTS ARCHITECTURE]
Reactive: Intelligence behaviour arises as a result of agent’s interaction with
environment.
Belief - Desire - Intention: What we want? How can we achieve that?
[TYPE OF AGENTS]
Interface Agents: It act like a filter or interface between the user and a source
of information
Information Agents: It can retrieve information for the user from different
sources (Internet Search Engine)
Believable Agents: It simulates emotions such that can pass as a human
being
Cooperative Problem Solving and Distributed AI: It could do almost anything
like: system management, air-traffic control and CT image processing
[DEFINITION]
An Agent is a computer system situated in an environment and that is able of
autonomous action in order to meet its designed objectives.
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Virtual Ants - Artificial Life
[DEFINITION]
1.Artificial Life is the study of man-made systems that exhibit behaviors characteristic of natural living systems.
2. The goal AL is to provide biological models and also to investigate general principles of life.
[Emergence]
[Self-Organization]
Property of a system as a whole not contained in
any of its parts that results from the interaction of
the elements of such a system, which act
following local, low-level rules.
Spontaneous formation of complex patterns
or complex behavior emerging from the
interaction of simple lower-level
elements/organisms
[Communication]
[Virtual Ants]
V-ants are computer simulated societies
from the insects colonies present in
nature. Thus the behavior of the insects
is mapped onto artificial beings.
Through Stigmergic Interactions
-interactions mediated by modifications of the
[No Mainframe]
No central coordinator is needed to
organize the search for, and storage of
food.
environment (depositing pheromones),
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (LZW) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
[Advantages]
The parallel application of simple local rules solves a complex problem in a much more flexible and efficient way.
Social insects are individuals which “working together in parallel” create a super-organism capable of solving even the most
complex problems without any central organizer. .
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Our Goals - Their Roles
[COMPARISON]
AL is concerned with the generation of lifelike behavior. AI is concerned with generating intelligent behavior. AL and the new approaches in
AI both work bottom-up, combining many simple elements into more complicated ones, looking for emergence and principles of selforganization, using the synthetic methodology.
[GOAL]
Create a Click’n’Clean approach
that will get rid of the Bronchial
Tree after this has been
completely identified with a
simple click.
[WHO]
[ROLES]
Ant world A gent world
-workers
-seekers
-Queens
-mappers
Two approaches might be tried
INTELLIGENT [AGENTS] and
COLONIAL[V-ANTS]
[Algorithm Idea]
1.Ants [Agents] are deployed in the newly constructed World (I.R.T)
2.They have the 2 main degrees of freedom but can gain points according to priorities to move on the third
3.They start moving towards the high intensities under different reasons.
4.Start communicating to others the position of the FOOD/GOAL.
5.Other agents/ants are arriving on the site and try to find the points on the surface of the bronchial tree.
6. These points are passes to mappers/Queens that are mapping around the points a mesh. Thus creating the
surface.
7. The reconstruction is thus done and the bronchial tree.
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
Supporting Algorithms
Problem: They are good but not that good
Solution: Use a series of algorithms than can help the agents/ants during
searching, mapping and also can take their work further
Supporting Algorithms:
Bronchial Tree Reconstruction
Kohonen Self Organized Features Maps (Modeling Bronchial surface)
Active Shape Models (Modeling Bronchial Shape )
Centre of Maximal Balls (Modeling Bronchial Volume )
Skeletonization (Modeling Bronchial Structure)
Nodule Recognition
Centre of Maximal Balls ( pleura attached nodule)
Dot- Enhancement Algorithm
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano
[Questions?]
[Thank you for your
attention]
[Discussion…]
[Suggestions…]
Pisa Meeting, 7 - 9 February 2005
Sorin Cristian Cheran, Gianfranco Gargano