* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositiva 1 - a4academics.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Seminar on,
Applications of Artificial
Intelligence in Safe
Human-Robot Interactions
Contents
Introduction
Human Modelling
Prediction of the Human Trajectory
Reactive Control Scheme
Conclusion
References
2
Introduction
Integration of both Robot’s and Human’s
workspace.
A new sensory system for
modelling,tracking & predicting human
motions within a Robot workspace
Obtain a superquadric-based model of
human using SOM.
Assess the danger of the robot operations.
A new reactive control scheme.
3
Human modelling
Sensory system for modelling and tracking human
motion.
Safety mat.
Data processing using SOM.
Obtain body orientation and location.
Model of the human body.
4
Four steps in Human modelling
Step 1: The safety mat consists of a number of pressureactivated nodes.Each node on the mat has fixed
coordinates. Under the human body weight, a set of
nodes F = {(xj, yj)|j = 1, . . . , n} are activated across the
mat.
Step 2:This set is then clustered into two subsets F1 and
F2, corresponding to each foot using a SOM network .
Step 3: Using these subsets, the human body orientation
and its location are derived .
Step 4: This information along with average human body
dimensions is then used in order to obtain a model of the5
human .
Safety mat
Detects obstacles.
Constructed using 2 rubber sheets having
parallel wires.
Pressure activated nodes.
Each node on the mat has fixed
coordinates.….
6
Data processing using SOM
Activated node set F needs to be first divided(clustered) into two
subsets,F1 and F2 corresponding to each foot.
SOM network seems a suitable candidate for clustering the data
representing human footprints.
Input to the SOM network is (xj, yj) pairs and produce output as
(f1, f2)
7
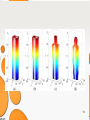
Data processing using SOM
Correct clustering
TYPE A
Incorrect clustering
TYPE B
8
Connectivity of the Laplacian matrics of the
given sample set.
Type A sample set have 2 zero eigen values in its Laplacian matrics…
9
To convert type B to type A, uncertain nodes are need to
be removed.
l1 and l2 corresponding to the outer borders and
orientation of each soles.
lavg represents inner border of the two soles.
10
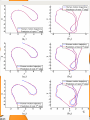
Obtaining body orientation
It can be obtained from 2 subsets F1 & F2
α- average of sole orientation
Centre of the body
These values used to obtain human model
Lines lL and lR lines connecting the centers of
the forefoot to the heel in each sole, respectively.
11
Model of the human body
Unduloidlike structure
Variable cross section at various heights.
12
13
Prediction of the human
trajectory
Motivated by ordinary human-human
interaction.
Observe the pattern of the motion and
predict the motion using ANN.
14
15
Reactive control
Formulation of the Danger Index.
DI(κ, v) = fD(κ)fV(v)
Impedence based Reactive Control
Strategy.
-Threshold value for DI.
-Repulsive force
-Virtual damping torque.
Cumulative PDI method
Fp = kpPDI(n0, dp)up
16
17
Conclusion
Study on a sensory system and reactive
control scheme.
SOM network and superquadric functions
are used for human modelling.
Human motion predicted using ANN.
Reactive control scheme is developed.
18
References
Nima Najmaei and Mehrdad R. Kermani “Applications of
Artificial Intelligence in Safe Human–Robot Interactions”,
April 2011.
A. De Santis, B. Siciliano, A. De Luca, and A. Bicchi, “An
atlas of humrobot interaction,” Mech. Mach. Theory, vol.
43, pp. 253–270, 2008.
R. Bischoff and V. Graefe, “Hermes—A versatile
personal robotic assistant,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 92, no. 11,
pp. 1759–1779, Nov. 2004.
American Nat. Standard for Indus. Robots—Safety
Requirement, RIA/ANSI R15.06—1999, 1999.
19