* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 : Cognitive Neuroscience
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
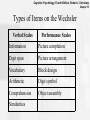
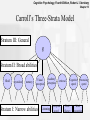
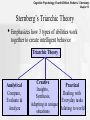
Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Chapter 13: Human and Artificial Intelligence Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 What Do You Consider Intelligence? Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Intelligence Is… • Capacity to learn from experience • Ability to adapt to different contexts • The use of metacognition to enhance learning Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Emotional Intelligence • Mayer & Salovey (1997) “The capacity to reason about emotions, and of emotions to enhance thinking. It includes the abilities to accurately perceive emotions, to access and generate emotions so as to assist thought, to understand emotions and emotional knowledge, and to reflectively regulate emotions so as to promote emotional and intellectual growth” Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Social Intelligence • Ability to get along with others • Knowledge of social matters • Insight into moods or underlying personality traits of others Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Artificial Intelligence • The computational part of the ability to achieve goals in the world Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Historical Trends • Emphasize psychophysical abilities – Galton – Examine relationships of sensory abilities • Emphasize on judgment – Binet (1904) – Identify children needing special instruction – Compared child’s abilities to what the average child at that age could do Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Historical Trends • Terman (1900s) – Created an English version of Binet’s test (called it the Stanford-Binet) – Created the intelligence quotient (IQ): divide mental age by chronological age then multiply by 100 – Became the first modern “intelligence” test Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Types of items on the Stanford-Binet Age 4 9 Task Fill in the missing word when asked, "A puppy is a dog, a kitten is a _______. Answers correctly when the examiner says, “Yesterday, the scientist went into the swamp to capture a dinosaur. What is foolish about that? Fills in the missing words of sentences like "The 12 rivers are flooding because…." Can describe the difference between happiness and Adult elation, and virtue and morality. Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Wechsler Intelligence Scales • Wechsler created scales for adults, children, and preschoolers • Yield 3 scores – Verbal score – Performance score – Overall score • Most widely used intelligence test Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Types of Items on the Wechsler Verbal Scales Performance Scales Information Picture completion Digit span Picture arrangement Vocabulary Block design Arithmetic Digit symbol Comprehension Object assembly Similarities Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Measurement or Process? • Measurement structure – Identify most relevant factors • Process emphasis – Identify and examine the speed and accuracy of mental manipulations Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Nature, Nurture, or Both? • Is intelligence genetic? • Is intelligence acquired? • Is intelligence a combination of both? Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Factor Analysis • Primary method used to describe intelligence • • structure Correlations among many dependent variables are examined with the goal of discovering something about the nature of the factors that affect them How many different factors are needed to explain the pattern of relationships among these variables? Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Factor Analysis Matrix Paragraph comprehension Sentence completion Word meaning Counting dots Identifying shapes Multiplication Paper folding Block patterns Series completion Reading Numerical Visual 0.84 0.10 0.06 0.86 -0.05 -0.01 0.81 0.04 -0.02 0.08 0.91 0.04 0.02 0.82 0.10 -0.24 0.87 -0.02 0.05 0.20 0.77 -0.03 -0.01 0.65 0.02 0.04 0.57 Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Number of Factors in the Structure of Intelligence • Spearman says two • Thurstone says seven • Guilford says 150 • Cattell, Vernon, and Carroll propose hierarchical models Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Spearman’s “g” Factor • Two-factor theory of intelligence – All intellective functioning was due to an overall mental ability – “g” – Accompanied by specific abilities for differing mental tasks Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Thurstone’s 7 Primary Mental Abilities • Verbal comprehension • Verbal fluency • Inductive reasoning • Spatial visualization • Number • Memory • Perceptual speed Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Guilford • SOI Model – Structure of Intelligence – Each cube represents an intersection of operations, products and contents to create 150 components of intelligence Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Cattell’s Fluid and Crystallized Intelligence • Fluid intelligence – Ability to reason and use information – Peaks approximately at age 20 • Crystallized intelligence – Acquired skill and learned knowledge – Continues to increase into old age Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Carroll’s Three-Strata Model Stratum III: General g Stratum II: Broad abilities fluid crystalized memory Visual perception Stratum I: Narrow abilities Auditory perception Listening retrieval Perceptual speed Cognitive Processing speed speed Word fluency Word recognition Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Historical Trends & Intelligence • In the past, focus was on the product, • • identify aptitudes, measure, and create models based on data During 1960’s & 1970’s conceptualization changed to what are the processes involved? Information processing models focus on the processes that are involved in intelligence Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Information Processing & Intelligence • Inspection time – How long a stimuli has to be viewed before an accurate judgment can be made – How quickly a person gives their answer is irrelevant, participants are encouraged to take their time Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Inspection Time Demonstration * Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Inspection Time and IQ • Nettlebeck & Lally (1976) – First to note the relationship • Nettlebeck (1987) – Inspection time accounts for 25% of IQ variance (r = -.5) – The higher the IQ, the less stimulus time needed to accurately inspect the stimuli – Big issue now is direction of causation between the two variables Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Intelligence and Other Processes • The speed at which we process thought can explain why one individual is more intelligent than another • Choice Reaction Time – Jensen • Lexical Access Speed – Hunt – Speed of word retrieval Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Working Memory & Intelligence • Being able to store and manipulate information in working memory is related to level of intelligence Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Componential Analysis • This approach involves identifying the steps in complex • information-processing tasks and seeing how each process contributes to the decision Sternberg’s componential analysis on solving analogies Red : Stop :: Green : ____ Graceful: Clumsy :: late : _____ – – – – Encode - Identify each term of the problem Inference - Discover rule between 1st two terms Mapping - Map rule to second set of terms Application - Apply relationship and generate final term Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Sternberg’s Findings • Measured amount reaction time for each step • Found more intelligent participants took longer to encode, but less time to complete the remaining steps • Global versus local planning Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Contextualist View of Intelligence • Culture and definition of intelligence are intertwined • Differs from one culture to another • Critical in one culture may be unimportant in another culture • Measurement of intelligence will be influenced by culture Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Culture Differences • Western cultures view intelligence as a means for individuals to devise categories and to engage in rational debate • Eastern cultures see it as a way for members of a community to recognize contradiction and complexity and to play their social roles successfully Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Evidence Supporting Cultural Influences • Kpelle tribe in Africa – Prefer functional sorting – In Western society, seen as less intelligent – Westerners prefer hierarchical sorting • Italian Americans’ IQ study – First generation median = 87 – Ceci (1996) Italian Americans scores were slightly above average (above 100) – Cultural assimilation is the explanation Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences • Eight types of abilities that are independent of one another – – – – – – – – Visual / Spatial Intelligence Musical Intelligence Verbal Intelligence Logical/Mathematical Intelligence Interpersonal Intelligence Intrapersonal Intelligence Bodily / Kinesthetic Intelligence Naturalist Intelligence Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Gardner’s Theory • Is modular, each type is independent of another • Allows for existence of savants Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory • Emphasizes how 3 types of abilities work together to create intelligent behavior Triarchic Theory Analytical Compare, Evaluate & Analyze Creative Practical Insights, Dealing with Synthesis, Everyday tasks Adapting in unique Relating to world situations Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory • Intelligence involves not merely adapting to one’s • • environment but in some cases modifying the environment or selecting another Intelligences are developing abilities not fixed characteristics of an individual; Traditional definitions conceptualize intelligence to remain essentially constant throughout an adult life Intelligence means adapting using your strengths and improving or compensating for your weaknesses Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Artificial Intelligence • The Turing test – Used to refer to a proposal made by Turing (1950) as a way of dealing with the question whether machines can think – Can an observer who has a conversation with a computer and a human figure out which conversationalist is the computer? – Computer passes Turing test if the person cannot Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Computer Programs Better than Humans • Deep Blue and Chess – 1,000,000,000,000 positions/sec – 100 - 200 billion moves considered – Able to evaluate moves • Beat world champion Kasparov in 1997 match Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Psychotherapy AI • ELIZA • PARRY – Weizenbaum (1966) created this program to engage in a dialogue imitative of the style favored in Rogerian psychotherapy – The program can successfully emulate human conversation to a degree that humans often assumed they were communicating remotely over teletype with another human – ELIZA's technique of responding to keyword-matching demonstrated the plausibility of natural language understanding by computers – Colby (1963) created a computer simulation of a paranoid human – Psychologists reliably judged PARRY's interactive output as being paranoid schizophrenic and were unable to distinguish transcripts of a session with PARRY from that of a session originating from a human patient Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Expert Systems • Telephone network maintenance • Credit evaluation • Tax planning • Detection of insider securities trading • Mineral exploration • Irrigation and pest management • Predicting failure of diesel engines • Medical diagnosis • Class selection for students Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Limitations of Expert Systems • Can handle only narrow domains • Do not possess common sense/intuition • Have a limited ability to learn Cognitive Psychology, Fourth Edition, Robert J. Sternberg Chapter 13 Summary • To date, no computer AI can match all dimensions of human intelligence • For algorithmic problems, computers can perform faster, however humans still write the programming