* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Slides
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
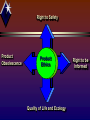
Chapter 10 Strategies for New Products and the Product Life Cycle Objectives Define “newness” ID elements of successful new products Overview stages of new product development Understand possible reasons for new product failure Introduce the product life cycle Objectives - cont’d Relate new product diffusion to consumer adoption patterns ID ways to modify existing products Explore total quality management Review product line management Discuss ethical considerations of product strategy Management Perspectives on “New” Products New-to-the-world Product category extensions Product line extensions Product modifications Consumers’ Perspectives on “New” Products Discontinuous Innovation Breakthrough Dynamically Continuous Innovation Continuous Innovation Major change Ongoing alteration New Product Failures New Products That Succeed New Products That Fail After Introduction 80%: New Product Ideas That Fail Characteristics of Success Relative advantage Lower costs Faster Easier Longer lasting More fun Characteristics of Success Compatibility with existing habits and behaviors Characteristics of Success Trialability Easily tested Low risk Inexpensive No special equipment Free samples or coupons Sample size Demo days Characteristics of Success Observability Visible cues Communicate hidden qualities Characteristics of Success Simplicity User friendly Understandable Logical extension Easy to grasp New Product Development IDEA GENERATION SCREENING BUSINESS ANALYSIS DEVELOPMENT COMMERCIALIZATION NEW PRODUCT New Product Development Idea generation Ongoing ID target market needs Technology driven Marketing research Global vision New Product Development Screening Reasonable Pertinent Appropriate Real consumer need Magnitude of potential Corporate criteria / hurdle rates New Product Development Business analysis Qualitative evaluation Features Resource needs Basic marketing plan Quantitative evaluation Market demand Costs Investment Competitive activity Break-even analysis New Product Development Product development Prototype Total product (packaging, branding, etc.) Preliminary testing Concept Testing Present product to potential customers Test Marketing Field testing Laboratory testing New Product Development Commercialization Launch decision Marketing mix Establish production capacity Supply chain & partner relationships New Product Failure Insufficient superiority or uniqueness Inadequate/inferior planning Poor execution Technical problems Poor timing Product Life Cycle S a l e s Introduction Growth Maturity Time Decline Product Life Cycle Introduction Slow sales Low revenue Promote to gain awareness Varied length Product Life Cycle Growth Increasing sales Increasing profits Increasing competition Product refinement Profits peak Promote to create brand preference Product Life Cycle Maturity Sales from increase to decline Intense competition Prices and profit margins decrease Profits often still high Product Life Cycle Decline Falling industry sales & profits Industry shakeout Stimulating Adoption Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Adoption TIME Diffusion Process INNOVATORS (2.5%) Venturesome Inner directed Risk takers Younger, better educated & financially stable Buy during introduction stage Diffusion Process Early Adapters (13.5%) Similar to innovators Often buy during growth stage Opinion leaders Well educated Important promotional target BUY X Diffusion Process BUY X Early & late majority (68%) mass market buying cues from early adopters Average SES Fairly risk averse OK, we will buy X Diffusion Process OK, we will Laggards buy X. If I have to buy it I will. Resist change Conservative Like tradition Nonadopters Refuse to change No way! Strategies to Modify Existing Products Product Modification Cost Reductions Repositioning Total Quality Management Product Line Strategies Full Line Strategy Limited Line Strategy Single-Product Strategy Modifying Products for International Markets Standardization Globalization Strategy •Electronics •McDonalds Adaptation Customization Strategy •Post-It Notes •Consumer goods Right to Safety Product Obsolescence Product Ethics Quality of Life and Ecology Right to be Informed Review Define “newness” ID elements of successful new products Overview stages of new product development Understand possible reasons for new product failure Introduce the product life cycle Review - cont’d Relate new product diffusion to consumer adoption patterns ID ways to modify existing products Explore total quality management Review product line management Discuss ethical considerations of product strategy