* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internet Marketing Concepts
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Web analytics wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ad blocking wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
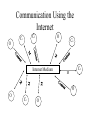
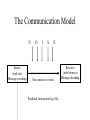
Internet Marketing Concepts Part 2 Objectives • • • • The new communication medium The Internet and the marketing mix Key elements of effective web site designs Internet marketing versus conventional marketing The Internet as a New Communication Medium • Digital, interactive, and a greater depth of information can be published • Demographics may be different • Culture of purchasers may be different • Markets may be different The Digital Medium of the Internet • Predominantly a pull medium • Enables interaction • Potential for one-to-one or many-to-many communication • The medium changes the nature of advertising • Changes to the distribution channel and marketplace enabled by the digital media Communication Using the Internet C5 C1 O C4 O Internet Medium C2 M O O C3 O The Communication Model N Source (web site) Message encoding O I S E Site content or e-mail Feedback (transaction log file) Receiver (web browser) Message decoding Cultural Difference • Uses of the Internet in the UK (1998) includes: – – – – – – – Sending email (72 %) Research (63%) Education (58%) Seeking information on products and services (53%) Hobbies and interests (53%) Games playing (32%) Planning holidays (24%) Web reference: NOP Research Group (www.nopres.co.uk) In Europe and the USA • Average age of user is 35.7 years old • 38.5 % female and 61.5% male (22%, 72% Europe) • 65% access the Web from home (29% Europe) • Average household income $53,000 Web reference: KPMG (www.kpmg.co.uk), GVU (www.gvu.gatech.edu/user_surveys) Cultural Difference • Techno_lusters – focused in the culture and technology • Academic buffs – originally on of the main types of users • Techno-boffins – similar to the techno-lusters, but make more directed use of the technology for business • Get aheads – use the Internet as a lifestyle accessory, use email and Internet for product selection • Hobbyists – people with specialist interests who use the Internet for purchase selection (golfers…) • Knowledge traders – business oriented users who turn to the Internet for news services and information on best business practice • Business bods – general business users in management roles • Home users – members or families looking for education or purchases Internet and Marketing Mix Using the Internet to vary the marketing mix Product • Quality • Image • Branding • Features • Variants • Mix • Support • Customer service • Use occasion • Availability • Warranties Price • Positioning • List • Discounts • Credit • Payment methods • Free or valueadded elements Promotion • Marketing communica tions • Personal promotion • Sales promotion • PR • Branding • Direct marketing Place • Trade channels • Sales support • Channel number • Segmented channels People • Individuals on marketing activities • Individuals on customer contact • Recruitment • Culture/ima ge • Training and skills • Remuneration Processes • Customer focus • Businessled • ITsupported • Design features • Research and developme nt The buying Process on the Internet Stages in buying process 1. Unaware 2. Aware of product need, develop specification 3. Suppliers search Communications objectives Generate awareness Internet marketing techniques Banner advertising, PR, links Position Features, benefits and brands Web site content (Plus search support) Lead generation (from range of customers) Search engines, Intermediaries 4. Evaluate and select Assist purchase decision 5. Purchase Facilitate purchase 6. Post-purchase evaluation and feedback Support use and retain business Web site content, Intermediaries Web site content Personalized web Site content and interaction Key Elements of Effective Web Site Design • • • • • • Capture Content Community Commerce Customer orientation Credibility Alternative Factors • Attract users • Engage users’ interest and participation • Retain users and ensure that they return to the site • Learn about customer preference • Relate back to customers with customized interactions Internet Marketing vs Conventional Marketing • It is a many-to-many medium • Consumers can interact with the medium • Consumers can provide commercially oriented content to the medium