* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing343 - UAA College of Business and Public Policy
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Competitive intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
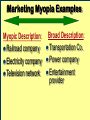
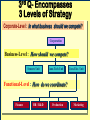
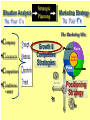
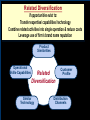
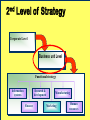
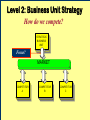
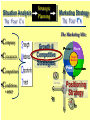
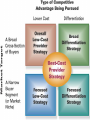
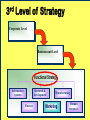
BA343 Week#4 Strategic Planning 2 weeks ago started the Situation Analysis— …w/ the Environmental Scan Environmental Scanning= The process of identifying the nature & magnitude of Uncontrollable forces in the external (macro) environment exerting significant influence on our strategies… So far…determined Consumer Competitors Conditions How to segment the consumer market, measure demand & relevant factors that influence consumers’ purchasing decisions Your competitors relative market positions, competencies & advantages Macro-E political-legal, economic, sociocultural & technological trends relevant to your organization Final Component of Strategic Situation Analysis Marketing Strategy Planning Situation Analysis P’s The Marketing Mix: •Company G Growth, Competitive Service & Positioning Strategies N C •Consumers Product Place Target Market TGT •Competitors •Conditions • PEST E D Price Promotion WM F Company Considerations History / Culture Resources Existing portfolio Existing customer base – characteristics – loyalty Experience – w/markets – w/ marketing Company Portfolio Analysis Analyze company’s products w/ respect to: How good your product is…. How good the market you sell it in is… G.E Strategic Planning Model Business Strength Strong Average Weak High Industry Attractiveness Low Business Strength Index Industry Attractiveness Index * Market Share * Price Competitiveness * Product Quality * Customer Knowledge * Sales Force and Effectiveness * Geographic Advantage * Market size * Market Growth * Industry Profit Margin * Amount of Competition * Seasonality * Cost Structure Boston Consulting Group’s Growth-Share Matrix High Product-Market Growth (%) STARS Low PROBLEM CHILD CASH COWS 10x 4x High DOGS 2x 1.5x 1x Relative Market Share .5x Low .2x .1x BCG Portfolio Matrix MARKET SHARE DOMINANCE High growth Market leaders Require cash Large profits HIGH LOW MARKET GROWTH RATE HIGH LOW High growth Low market share Need cash Poor profit margins $ Low growth High market share High cash flow Low growth Low market share Minimal cash flow Strategic Planning Situation Analysis Marketing Strategy P’s The Marketing Mix: •Company G Growth, Competitive Service & Positioning Strategies N C •Consumers Product Place Target Market TGT •Competitors •Conditions • PEST E D Price Promotion WM F SWOT Analysis S W O T Things the company does well. Things the company does not do well. Conditions in the external environment that favor strengths. Conditions in the external environment that do not relate to existing strengths or favor areas of current weakness. SWOT Analysis Strengths and Weaknesses (INTERNAL) ● Production Costs ● Marketing Skills ● Employee Capabilities ● Financial Resources ● Available Technology ● Company/Brand Image SWOT Analysis Opportunities And Threats EXTERNAL ●Social ●Demographic ●Economic ●Technological ●Political/Legal ●Competitive Situation Analysis 1st Step Marketing Strategy P’s The Marketing Mix: •Company Growth & Competitive •Consumers Product Place Target Market Strategies •Competitors •Conditions nd • PEST 2 Strategic Planning G Price Promotion N C Service Step TGT Positioning Strategy D E WM F Definition: Strategic Planning= A series of goaldirected decisions & actions matching your skills & resources (strengths & weaknesses) w/ market threats & opportunities Strategic Planning EVOLVING MARKET OPPORTUNITIES and/or threats RESOURCES & OBJECTIVES LONG RUN PROFITABILITY AND GROWTH Strategic Planning answers the 3 Big Questions: 1.Where are we now? 2.Where do we want to go? 3.How do we get there? Company Consumer Competitors Conditions Org. goals & objectives encapsulated in Mission & Vision Statement answers 2nd Question: 2. Where do we want to go? – – – – What business(es) should be in Market positions to stake out? Consumer needs & segments serve? Outcomes to achieve? Mission or Purpose is a precise description of what an organization does. It should describe the business the organization is in. It is a definition of “why” the organization exists A vision is a statement about what your organization wants to become … A compelling description of the state and function of the organization once it has implemented and achieved the strategic plan… Valuable Build a Strategic Framework: Mission Statement Vision >Part 1: Strategy & Vision Statements >Part 2: Mission Statements Mission Statement We will produce outstanding financial returns by providing totally reliable, competitively superior, global, air-ground transportation of high-priority goods and documents that require rapid, time-certain delivery." “PepsiCo’s overall mission is to increase the value of our shareholders’ investment. We do this through sales growth, cost controls and wise investment of resources. We believe our commercial success depends upon offering quality and value to our consumers and customers; providing products that are safe, wholesome, economically efficient and environmentally sound; and providing a fair return to our investors while adhering to the highest standards of integrity.” Avoid Corporate Myopia Short sightedness by firms that define their business too narrowly Marketing Myopia Examples Myopic Description: Railroad company Electricity company Television network Broad Description: Transportation Co. Power company Entertainment provider Market Oriented Vision / Missions COMPANY PRODUCT-ORIENTED MARKET-ORIENTED VISION/MISSION STATEMENTS VISION/MISSION STATEMENTS Revlon We make cosmetics. We sell hope…we accent a lifestyle & self expression; Disney We run theme parks. We make people happy.. by providing fantastic experiences & entertainment Philip Morris We Sell Cigarettes We provide “Life's Simple Pleasures. Final Question answered by Strategic Planning: 1.Where are we now? 2.Where do we want to go? 3.How do we get there? *Growth, Competitive & Functional Strategies “If you don’t know where you are going any route will get you there.” Chris Bartlett, Harvard Business School 3rd Q- Encompasses 3 Levels of Strategy Corporate-Level : In what business should we compete? Corporation Business-Level : How should we compete? Sensors Unit Nano-Tech Unit Cons.Elec. Unit Functional-Level : How do we coordinate? Finance HR / R&D Production Marketing Level 1 Corporate Strategy In which businesses should we compete? Corporation Corporation STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT #1 MARKET COMPETITOR A COMPETITOR B STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT #3 STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT #2 COMPETITOR C COMPETITOR D COMPETITOR E ? MARKET MARKET COMPETITOR F COMPETITOR G COMPETITOR H COMPETITOR I Once decided what businesses to compete in –need to decide - what Products & Markets to compete w/& in= Growth Strategy Situation Analysis •Company •Consumers •Competitors Strategic Planning Marketing Strategy P’s The Marketing Mix: Growth & Competitive Product Place Target Market Strategies G Price Promotion N •Conditions C Service TGT • PEST Positioning Strategy D E WM F Growth Strategies PRODUCT Present Present Market Penetration New Product Development MARKET New Market Development Diversification To Concentrate or Diversify… that is the question… Concentrate on your primary line of business look for ways to meet growth objectives thru increasing your level of operation in your primary business Market Penetration Increase market share among existing customers. Market Development Attract new customers to existing products Product Development Create new products for present markets Or Diversify… Diversification new products… new markets… new alliances Or Diversify… P R O D U C TS Present Present New Market Penetration Product Development Market Development Diversification M A R K E TS New Related Diversification if opportunities exist to: Transfer expertise/ capabilities/ technology Combine related activities into single operation & reduce costs Leverage use of firm’s brand name reputation Product Similarities Operational Skills-Capabilities Related Diversification Similar Technology Customer Profile Distribution Channels Examples of Related Diversification Darden Restaurants – – – Johnson & Johnson – – – – Olive Garden Red Lobster Bahamas Breeze Prescription drugs Non-prescription drugs (Tylenol, pepcid AC) Band-aids Baby products PEPSICO – – – Soft drinks Fruit Juices Snack foods (Fritos, Lays, Cracker Jacks) Unrelated Diversification Involves diversifying into businesses with – No strategic fit – No meaningful value chain relationships – No unifying strategic theme Approach is to venture into “any business in which we think we can make a profit” Firms pursuing unrelated diversification are often referred to as conglomerates Diversification viaMerger & Acquisition A popular approach to diversification- altho only ~20% succeed --M&A activity in 2004 was worth more than $1 trillion Advantages Quicker entry into target market Easier to hurdle certain entry barriers – – – – Technological inexperience Gaining access to reliable suppliers Being of a size to match rivals in terms of efficiency and costs Getting adequate distribution access Diversification via- Joint Ventures & Strategic Alliances Good way to diversify when: Uneconomical/ risky to go it alone Pooling competencies for more competitive strength Foreign partners needed to surmount – – – – Import quotas and Tariffs Nationalistic political interests Cultural roadblocks Lack of knowledge about markets in particular countries nd 2 Level of Strategy Corporate Level Business unit Level Functional strategy Information systems Research & development Finance Manufacturing Marketing Human resources Level 2: Business Unit Strategy How do we compete? STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT Quality? Focus? Cost? MARKET COMPETITOR A COMPETITOR B COMPETITOR C Situation Analysis •Company •Consumers •Competitors Strategic Planning Marketing Strategy P’s The Marketing Mix: Growth & Competitive Product Place Target Market Strategies G Price Promotion N •Conditions C Service TGT • PEST Positioning Strategy D E WM F Competitive Strategy is the creation of a unique & valuable position- The position is based on– Performing the same activities as competitors, but differently --or performing a different set of activities Generic Competitive Strategies Cost: Design, produce, market more efficiently than competitors Differentiation: Deliver unique & superior value in terms of product quality, features, service Focus = Competitive Scope/ Breadth of company’s target market 5-50 Cost Leadership Strategic Choices A cost leader does not try to be industry innovator A cost leader positions products to appeal to mainstream customers The overriding goal isincreased efficiency & lower costs relative to rivals Generic Business-Level Strategy:Cost Leadership Advantages If rivals charge similar prices, a cost leader achieves superior profitability – A cost leader is able to charge a lower price than competitors – Cost Leadership Disadvantages Competitors may lower their cost structures Competitors may imitate the cost leader’s methods Cost reductions can impact demand- product-service performance drop below threshold acceptability… Generic Business-Level Strategy: Differentiation Create a product that customers perceive as different or distinct in an important way Advantages – Premium price – Increased revenues = superior profitability Competitive Strategies; Focused Differentiation: Focus on particular group or geographic market – – Seek differentiation in targeted market segment Serve special needs of narrow target market Differentiation Advantages Customers develop brand loyalty: The greater the loyalty.. The less the price sensitivity… Differentiators can pass price increases on to customers Differentiation and brand loyalty are barriers to entry Differentiation: Disadvantages Difficulty in maintaining long-term distinction in customers’ eyes – Agile competitors can quickly imitate – Patents & first-mover advantages are limited Difficulty/expense of maintaining premium pricing– requires greater marketing costs Best-Cost Provider Strategies Combine a strategic emphasis on low-cost with a strategic emphasis on differentiation Make an upscale product at a lower cost Give customers more value for the money Objectives Deliver superior value by meeting or exceeding buyer expectations on product attributes and beating their price expectations Be the low-cost provider of a product with good-toexcellent product attributes, then use cost advantage to underprice comparable brands 5-58 rd 3 Level of Strategy Corporate Level Business unit Level Functional Strategy Information systems Research & development Finance Manufacturing Marketing Human resources Level 3 Functional Strategy STRATEGIC BUSINESS UNIT FINANCE R&D PRODUCTION INVENTORY MARKETING /SALES PURCHASING How do we coordinate? Getting In-Sync w/ Functional Planning Finance Production Marketing R&D HR The goal of functional planning is to achieve a state of Internal Strategic Alignment INTERNAL STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT Achieved when : 1. 2. All functional areas in sync w/ one another, As well as with the overall strategic direction of the firm. For INTERNAL STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT to occur: Marketing/R&D must be operating in a manner that is complementary to Production Which is complementary to Human Resources Which is complementary to Finance. Even after divining & aligning strategy still have problem of implementation & performance Marketing Strategy Organizational Structure Training & Reward Programs Human Resources Communicate Implementation Motivate Coordinate Marketing Performance Climate and Culture The Only Problem… Only 5% of workforce gets the strategy Only 25% of managers have incentives linked to strategy 60% of organizations don't link budgets & strategy 85% of executive teams spend <1 hour/ month discussing strategy 90% fail to execute strategy successfully Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton The Strategy-Focused Organization, 2000 The Marketing Implementation Process Problem: Separation of Strategic Planning & Marketing Implementation Very Much Strategic Planning Time Spent Marketing Implementation Very Little Chief Executive Officer Mid-level Marketing Managers •Commitment •Understanding •Responsibility Customer Contact Managers Even after divining & aligning strategy still have problem of implementation & performance Marketing Strategy Human Resources Organizational Structure Training & Reward Programs Climate and Culture Implementation Marketing Performance Corporate Culture Shared Beliefs & Values How employees behave w/ each other How employees behave w/ customers/clients How employees view their relationship w/ stakeholders How employees view their relationship w/ community How the organisation treats its employees – Benefits of “Strategic Planning” 1. 2. 3. 4. Makes managers more alert to “winds of change, new opportunities, as well as threatening developments” Guides entire firm regarding “what it is we are trying to do and to achieve Unifies numerous strategy-related decisions and organizational efforts Provides basis for evaluating competing budget requests objectives Strategy Operations Forces you to make choices on what you will do ¬ do Strategy Involves: Strategic thinking planning & management within & across all levels of the organization Specifically-thinking about the way things have been & are now… AND- the way things could/should be NEW CULTURE OLD Circus Traditional animal acts, painted clowns, and high-wire stunts make for a very tired form of entertainment. NEW Cirque du Soleil dramatic rethinking of what a circus can be, with amazing costumes, music & gymnastics OLD Grocery stores are big, messy places where you go to buy plastic-wrapped and hot-house grown fruits and vegetables. NEW Whole Foods where food shopping is a full on aesthetic experience-this is their wall of cheese! OLD Cotton Mop P&G studied the art of cleaning in search of something better than a wet mop, which spreads as much dirt as it picks up NEW Swiffer P&G came up with a whole new way to clean--using electrostatic attraction. A revolutionary dry mop is born NEW Sirius-Subscriber model brings a rich variety of content via satellite to your car and your handheld. OLD Radio Same old, same old adchoked, preprogrammed music and talk, from big national chains. “At Sony we assume that all products of our competitors have basically the same technology, price, performance and features. Design is the only thing that differentiates one product from another in the marketplace.” Norio Ohga OLD Best Buy has crowded shelves, overwhelming choice, and standard sales pitches. NEW The Apple Store is spare, elegant, and appealingly interactive—a hip place to be on a Sat. night. OLD Golden Nugget Casino: Las Vegas' early emphasis on gambling overshadowed amenities, entertainment, and atmosphere. NEW Luxor Hotel and Casino: Exotically themed hotels with elaborate décor and highend restaurants have given Vegas added allure.